THE CHINATOWN EFFECT
Read more
THE CHINATOWN EFFECT
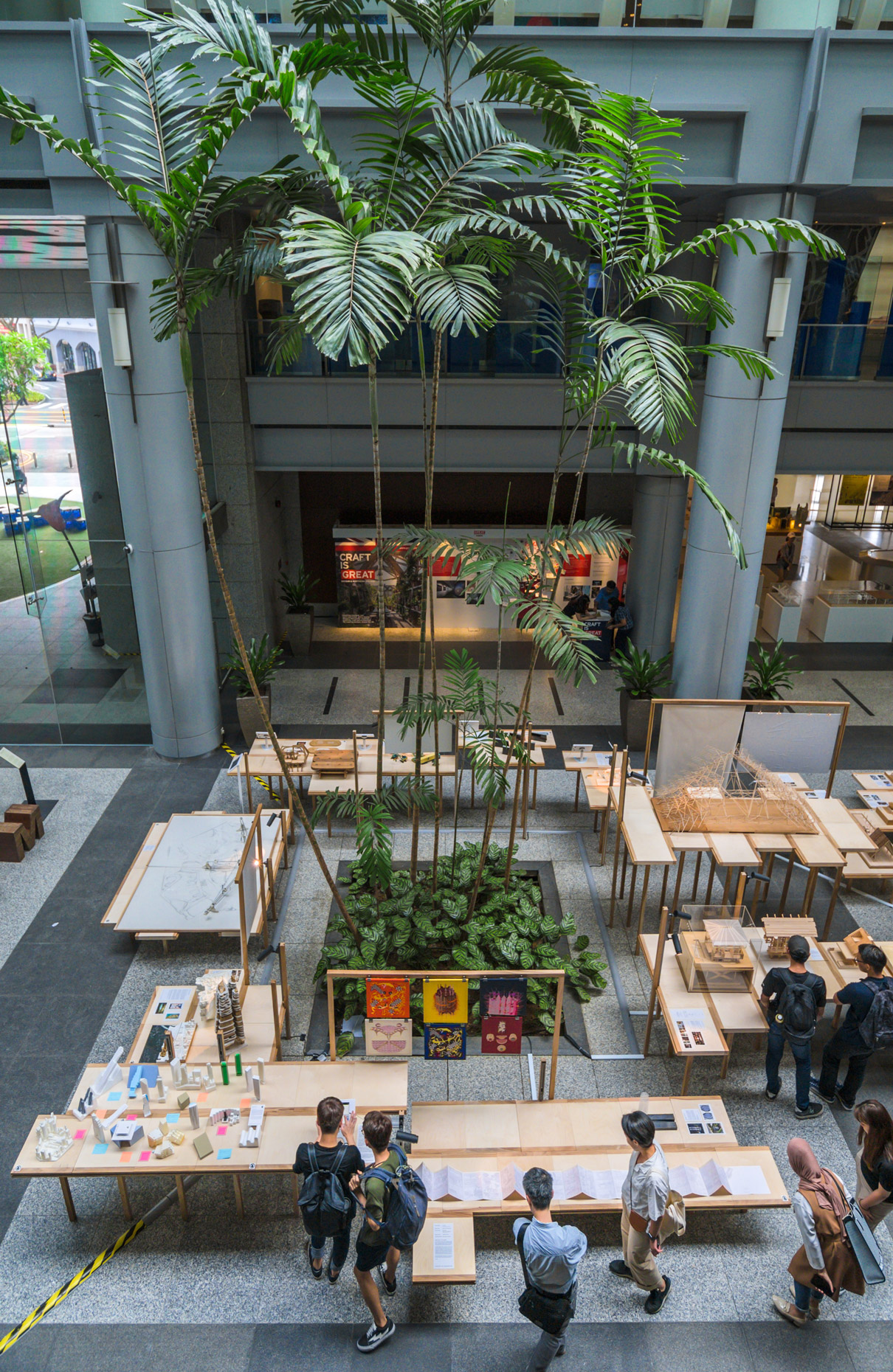
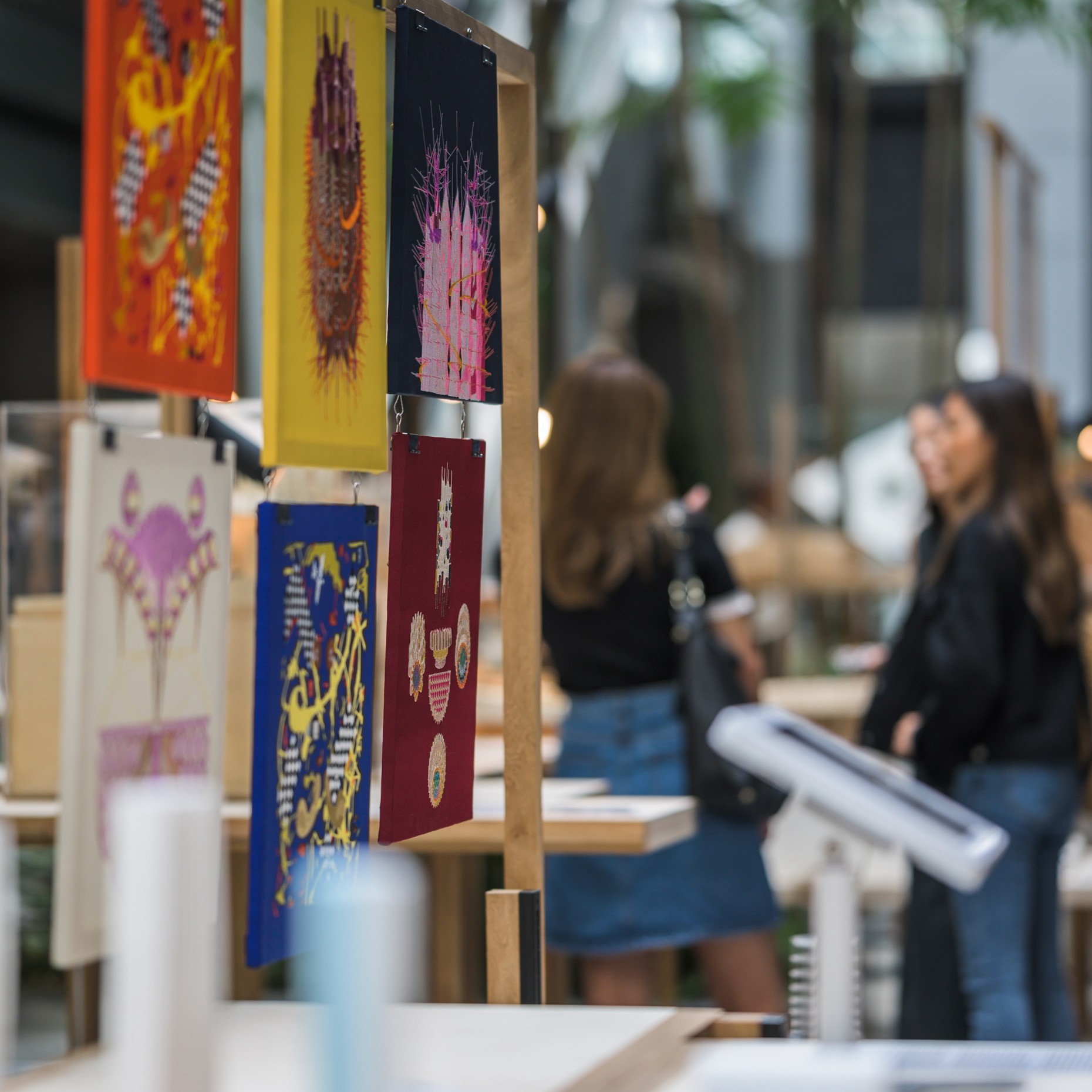
INDA workshop and exhibition
@ATT19 Gallery
Bangkok,
2019
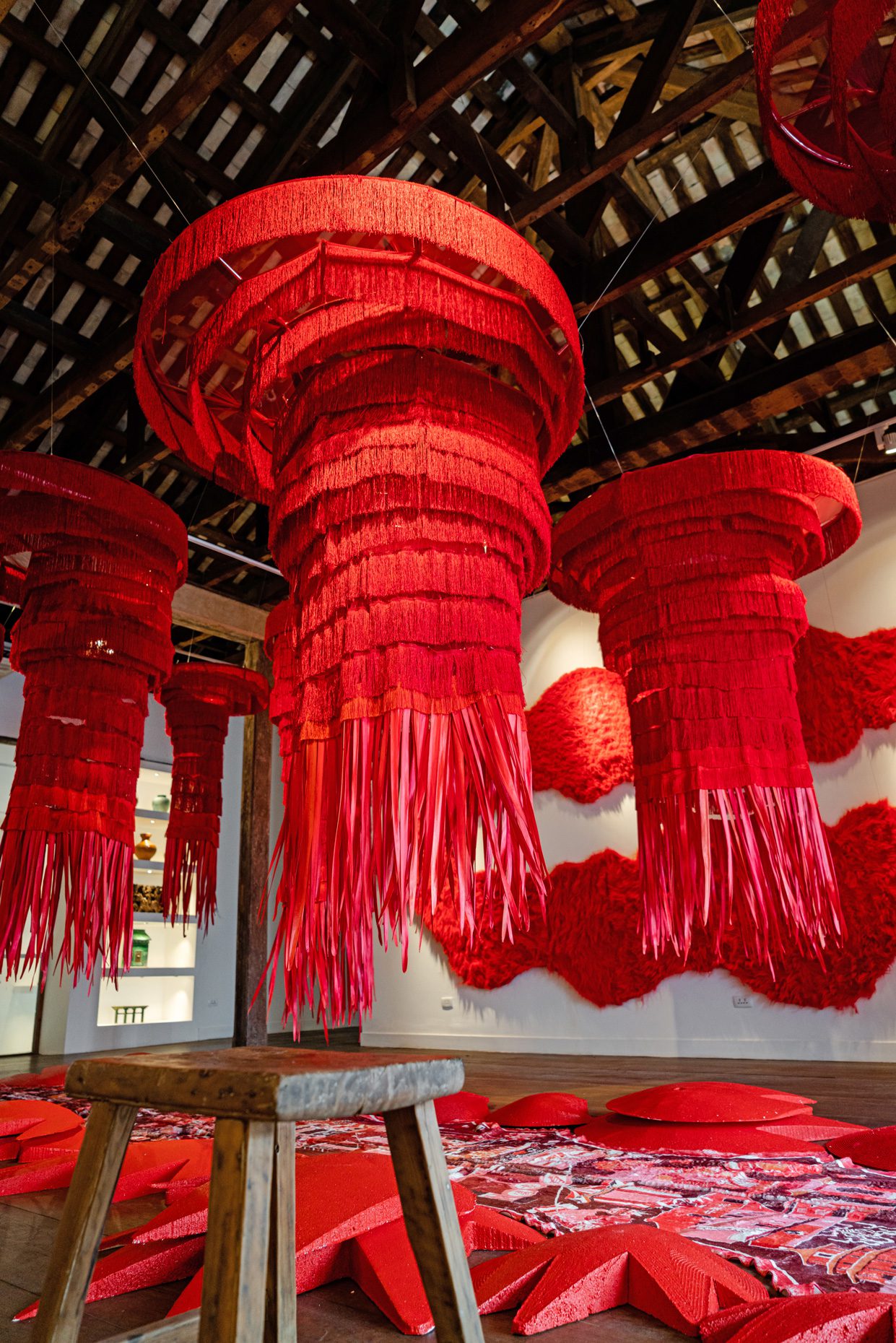
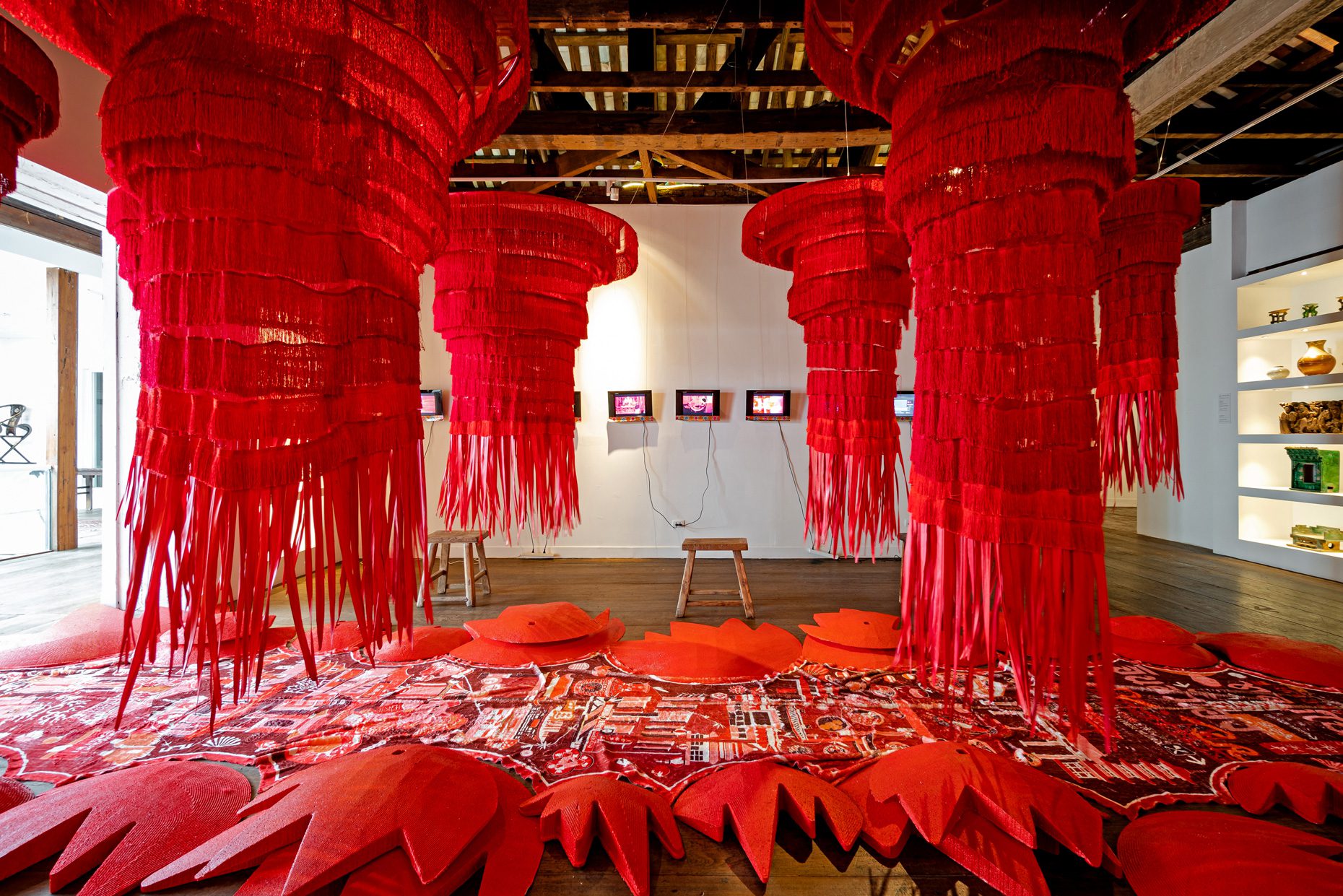
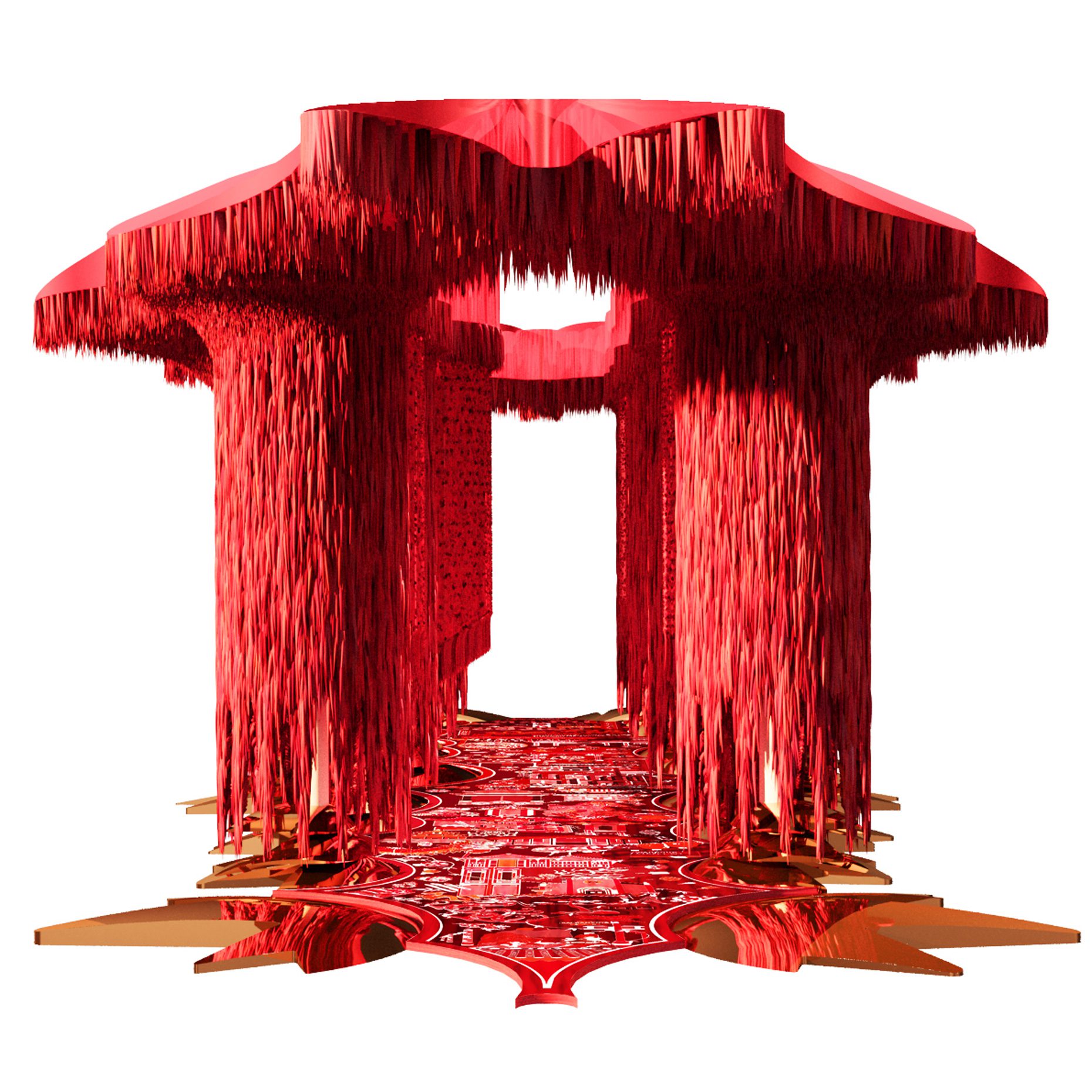
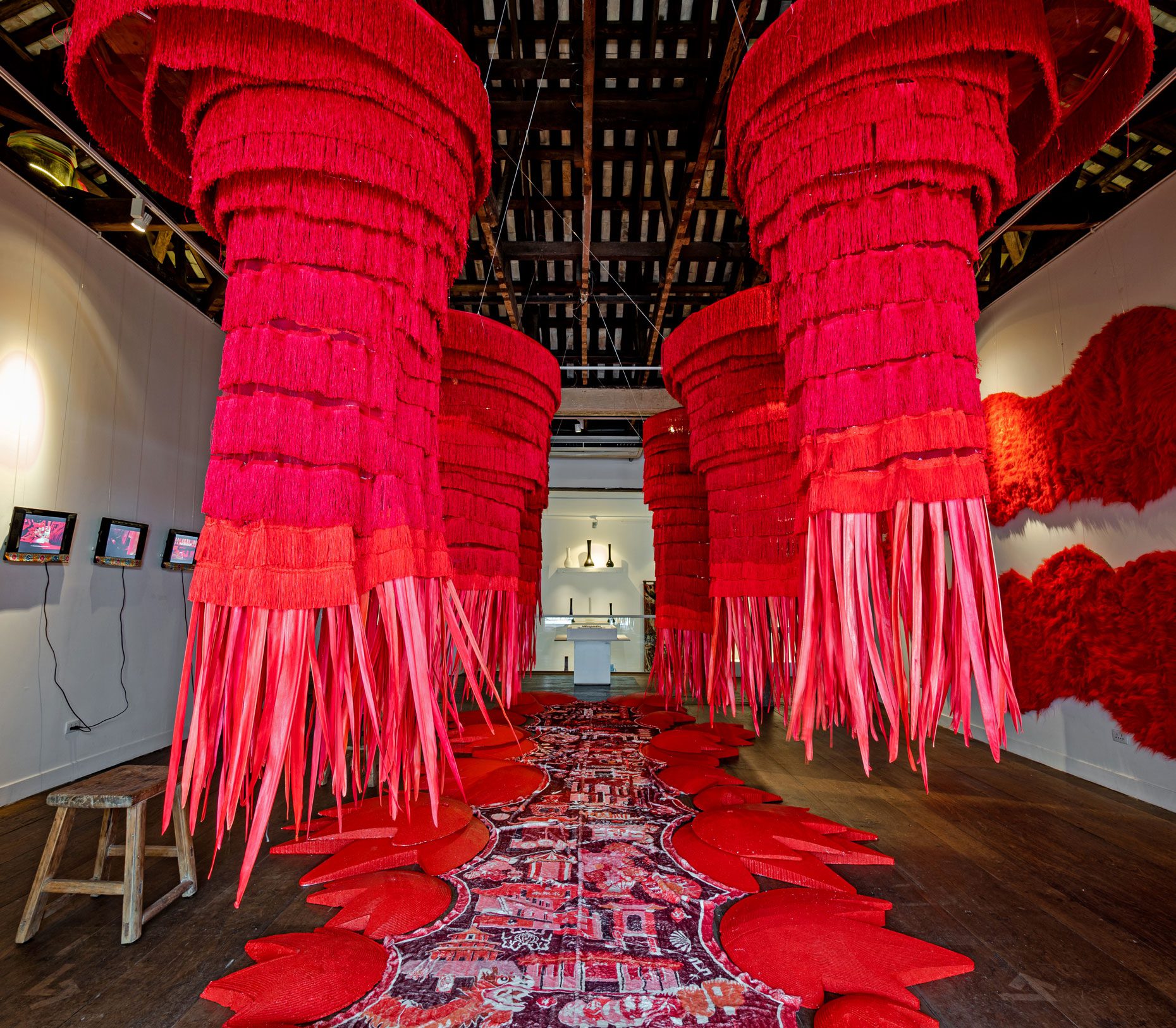
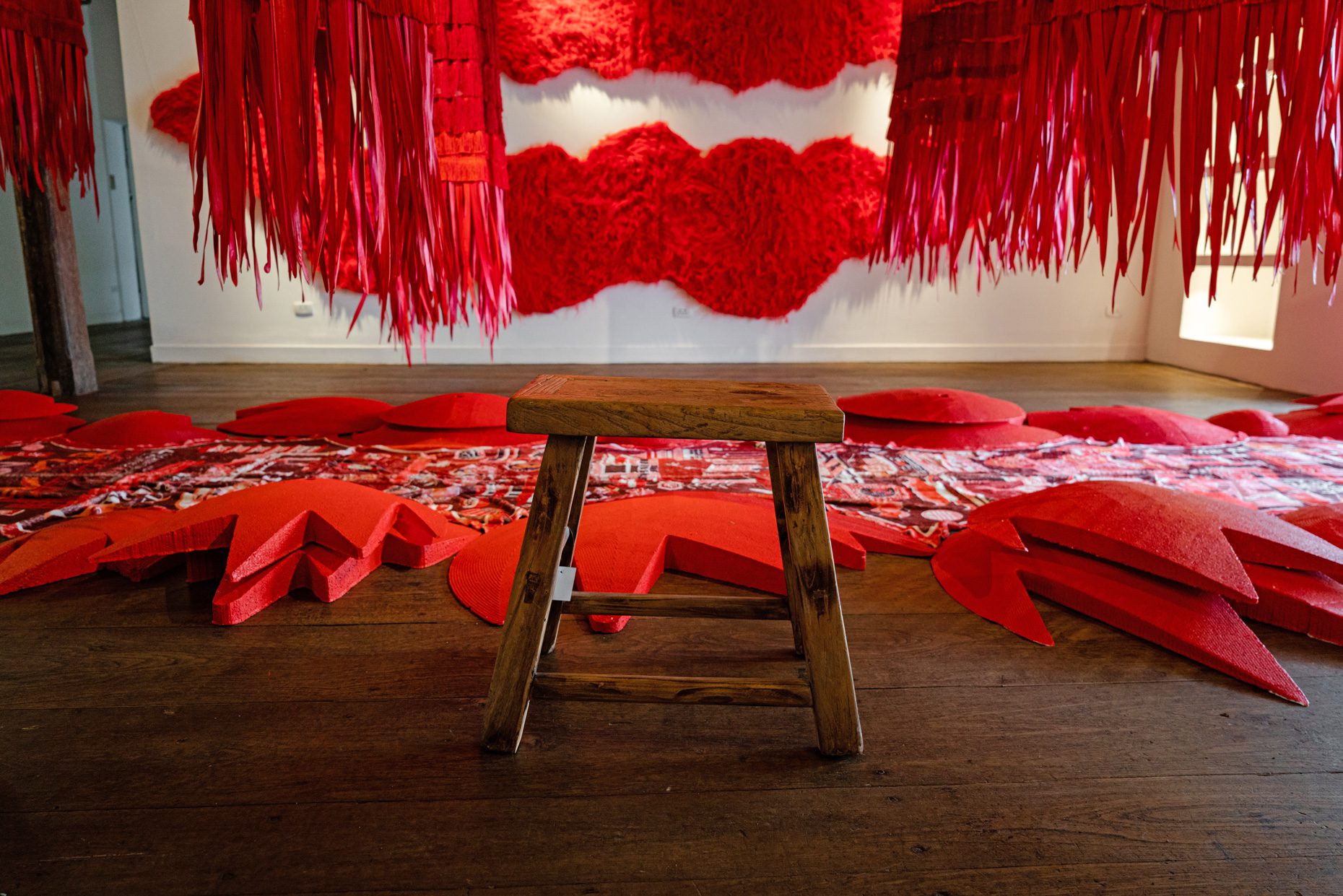
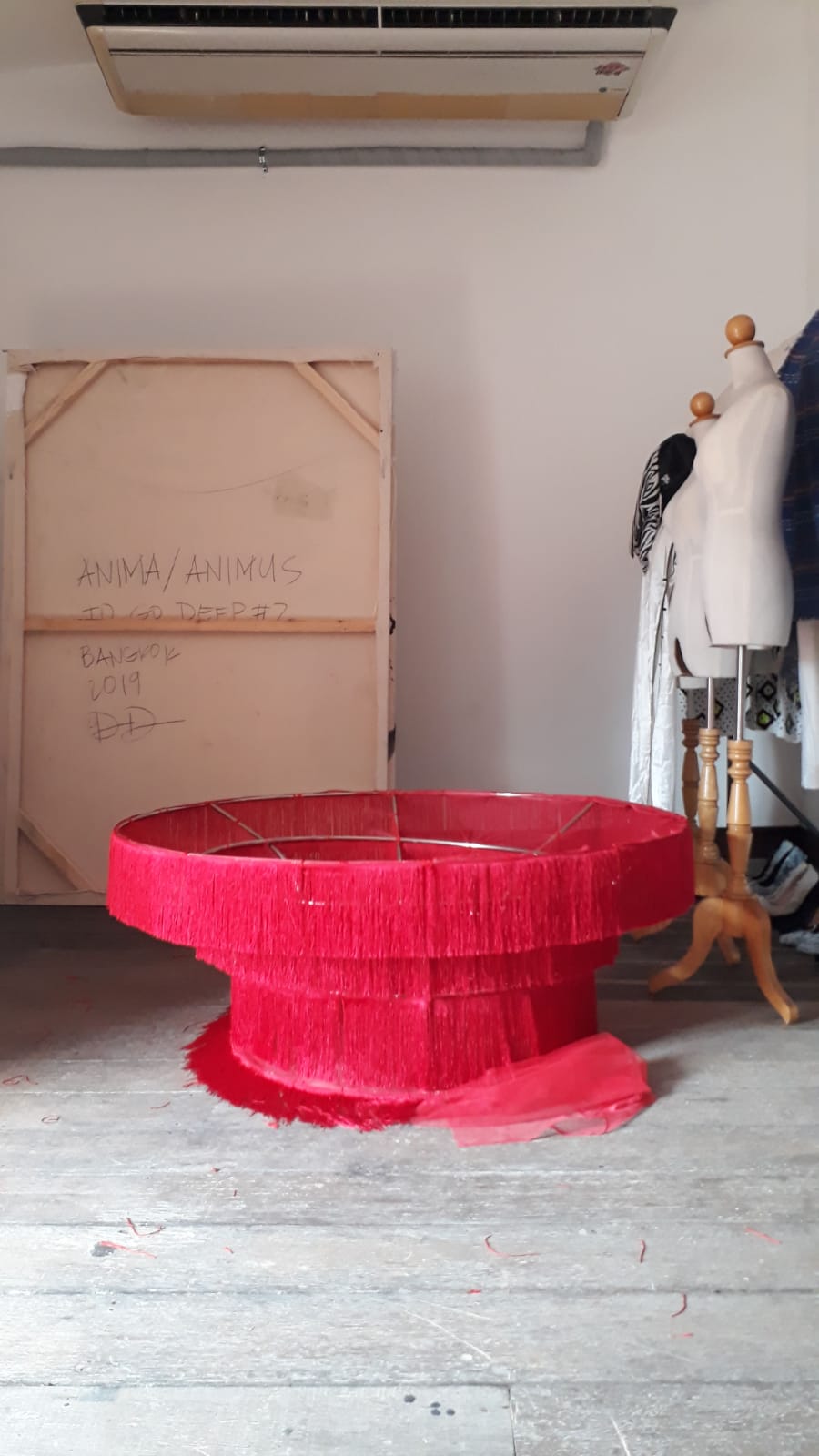
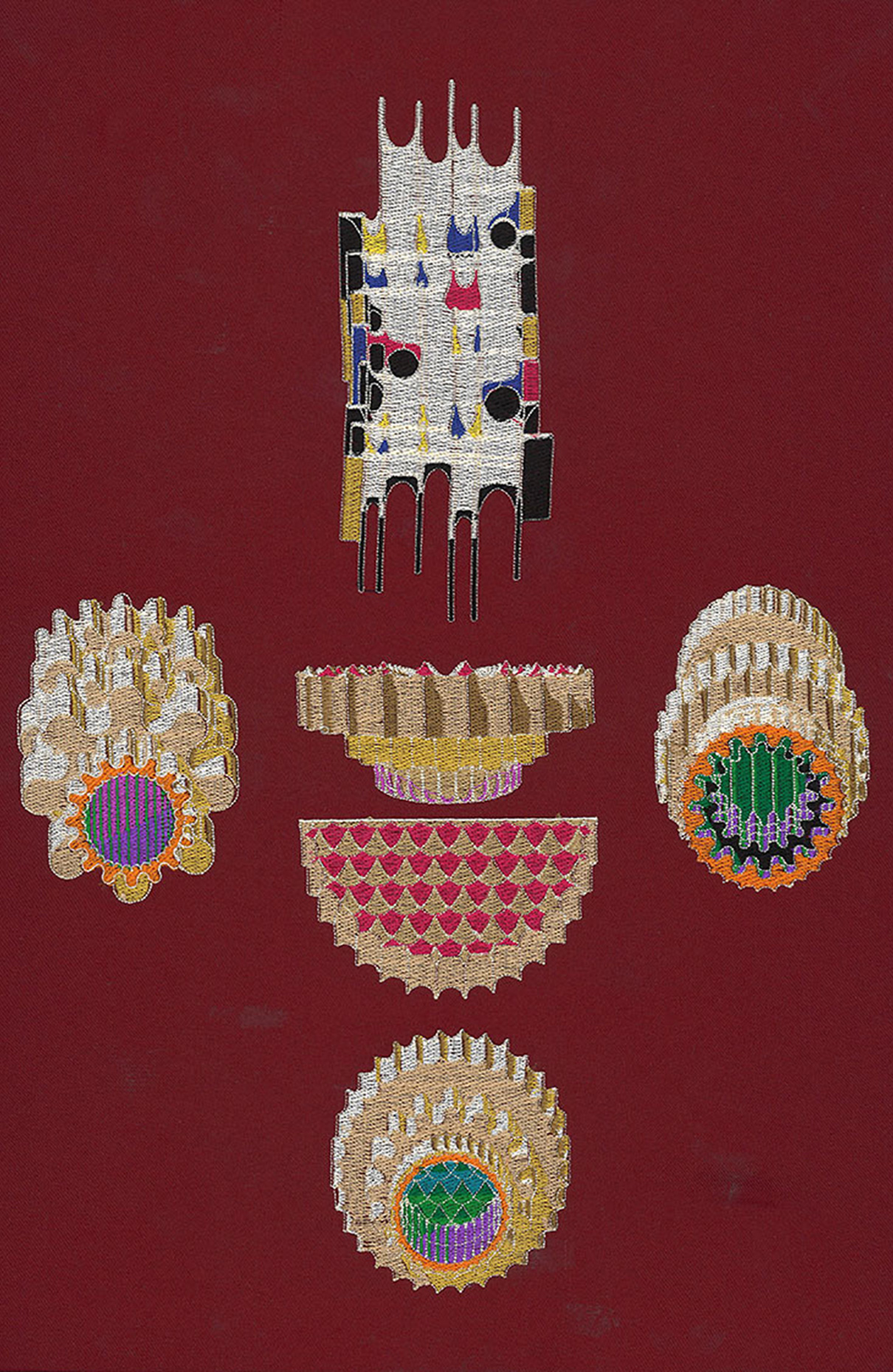
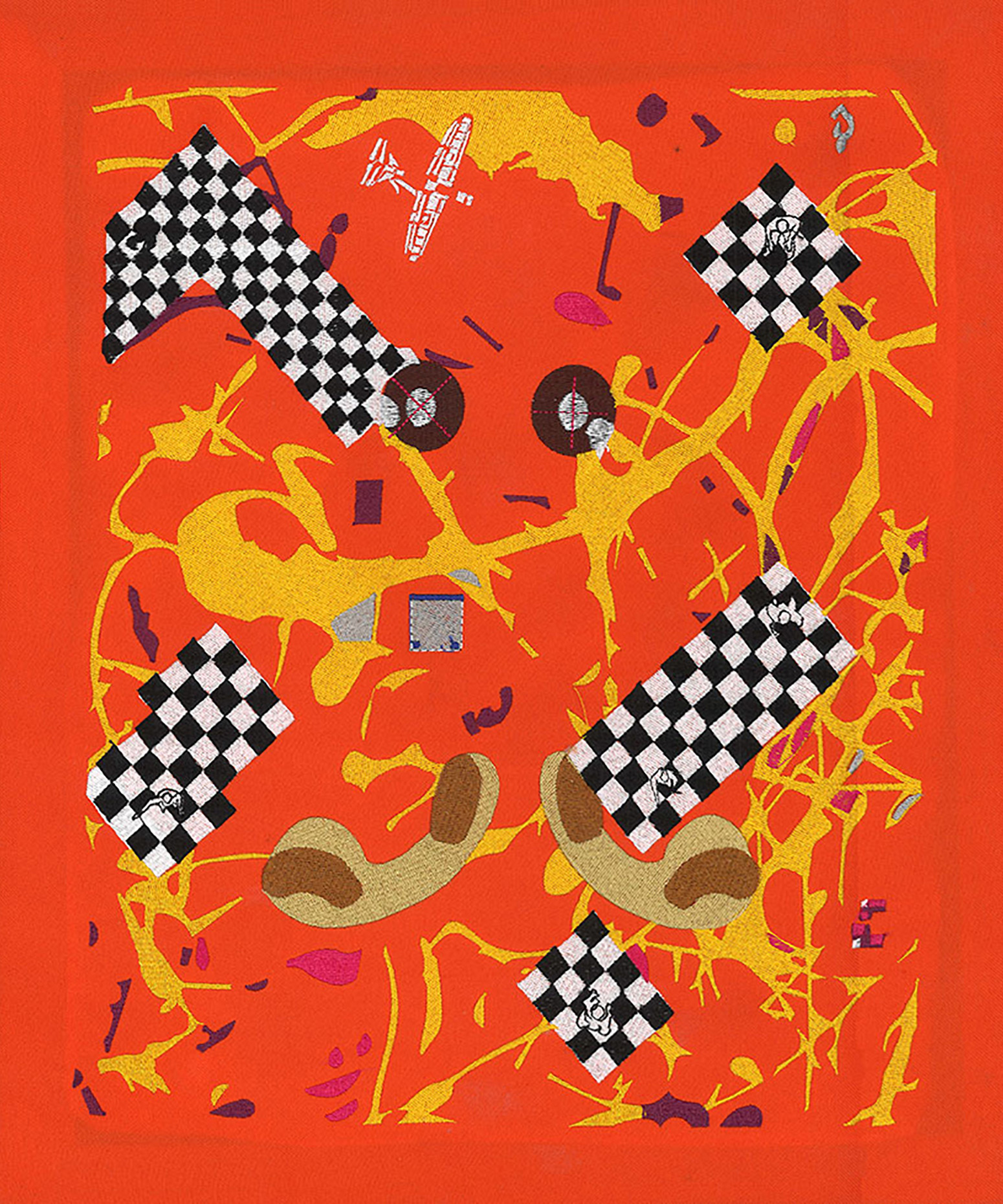
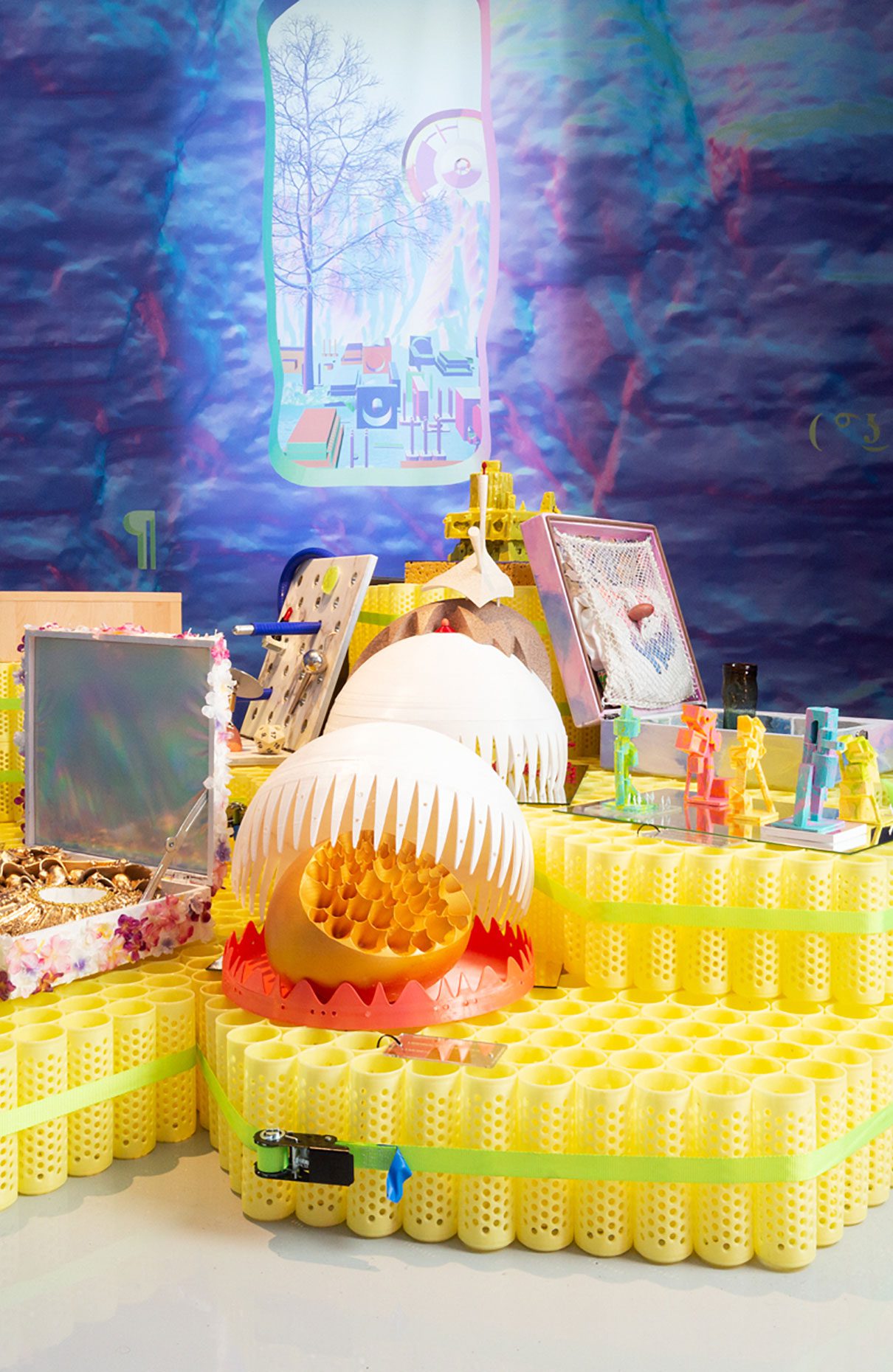
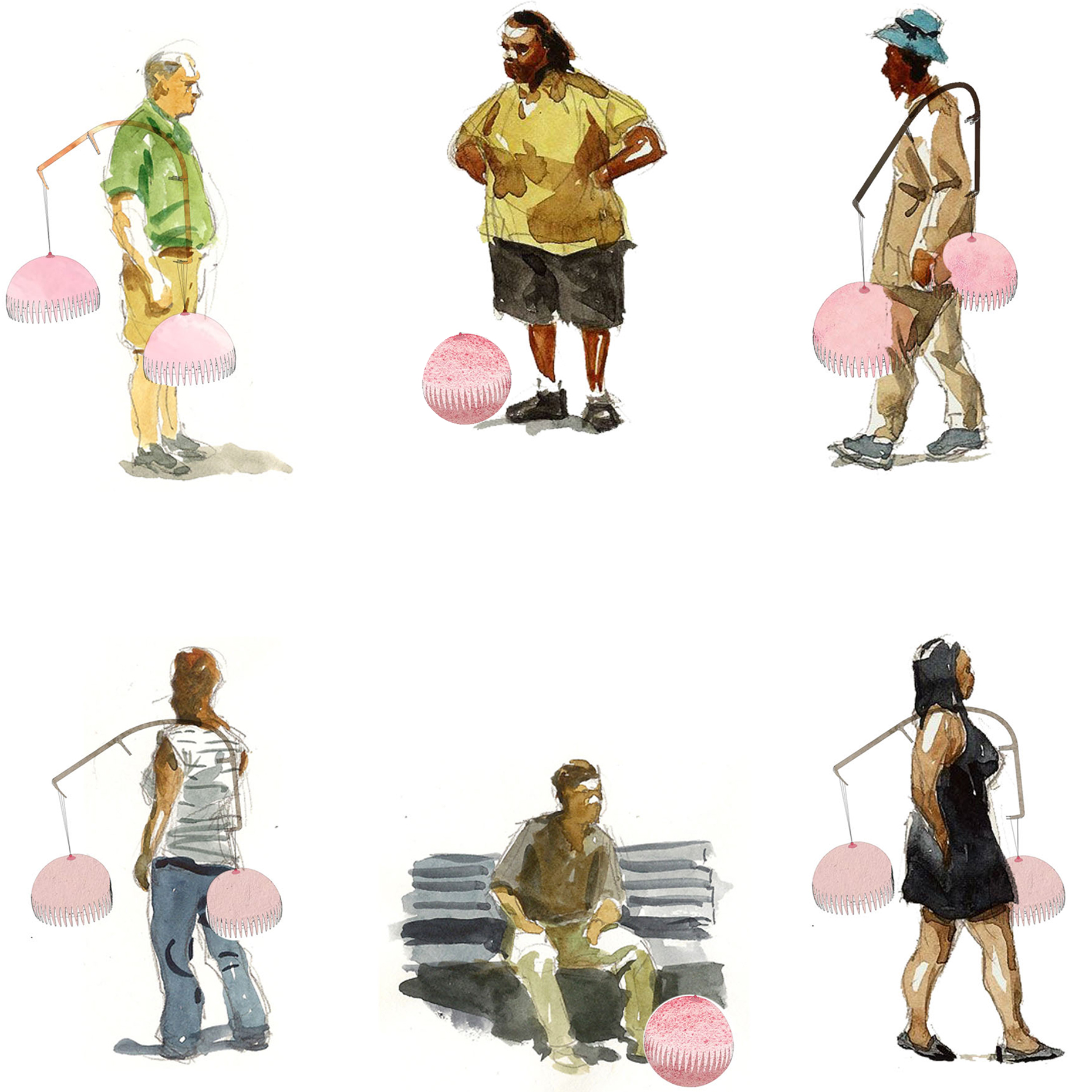
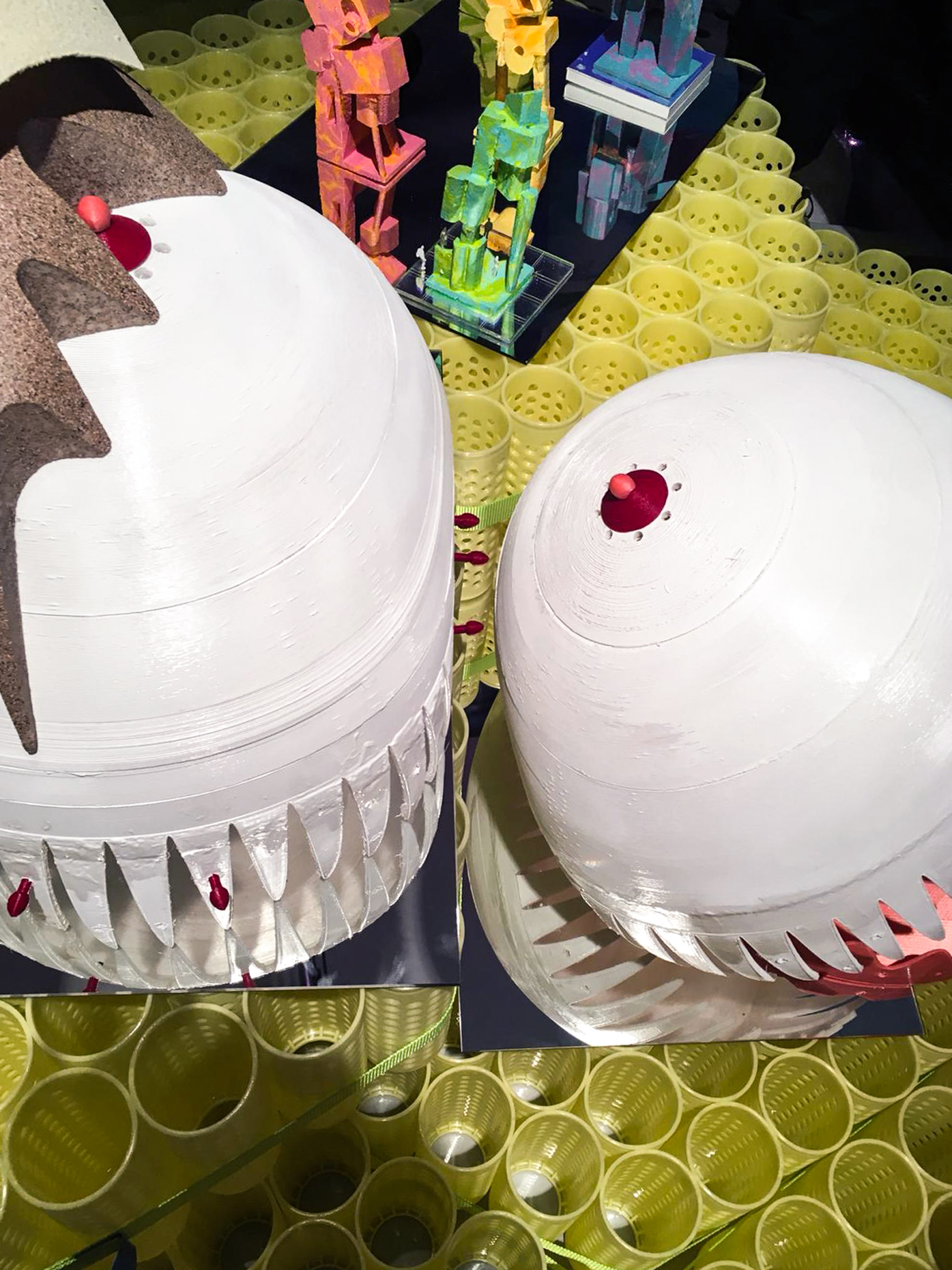
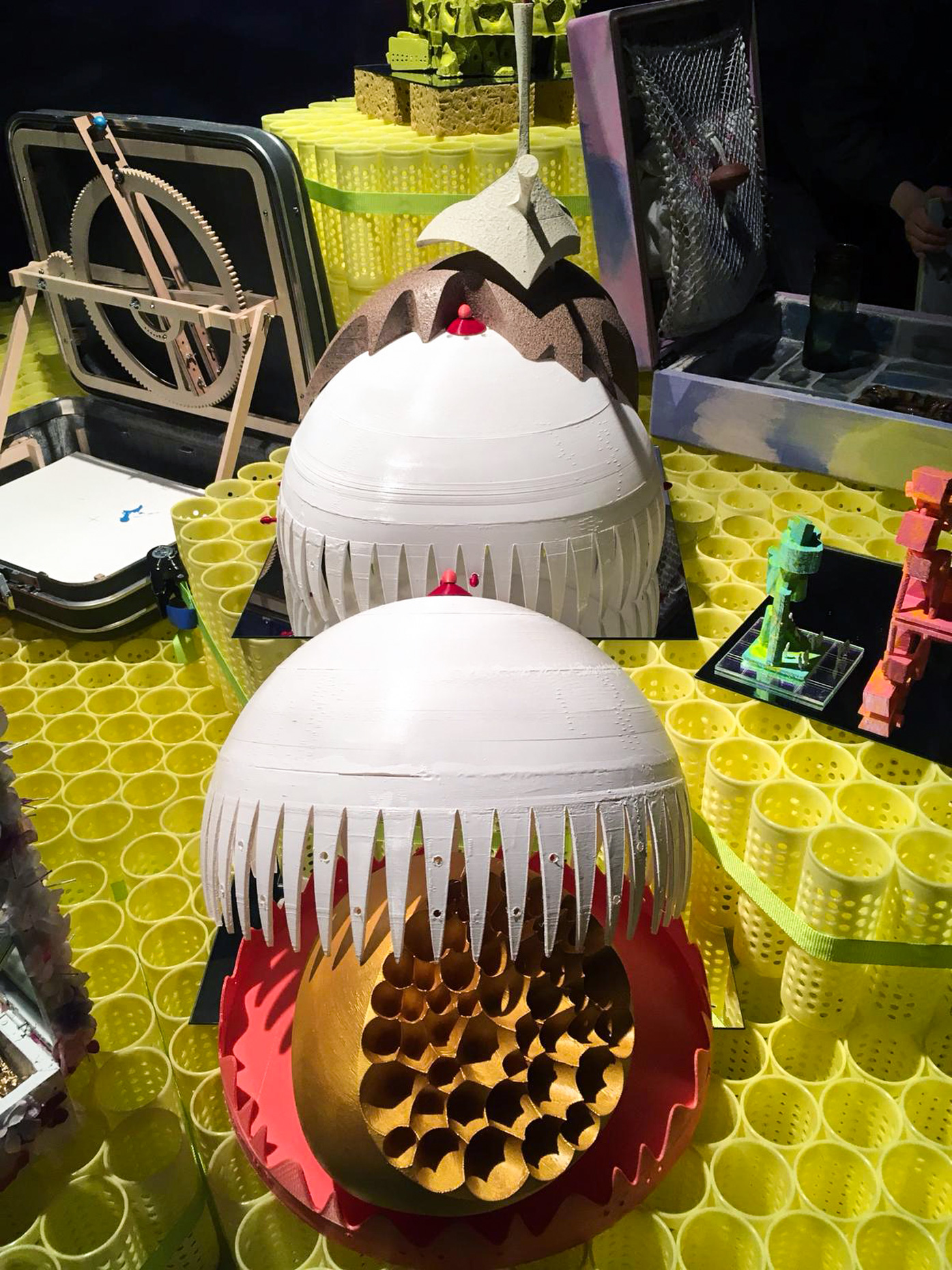
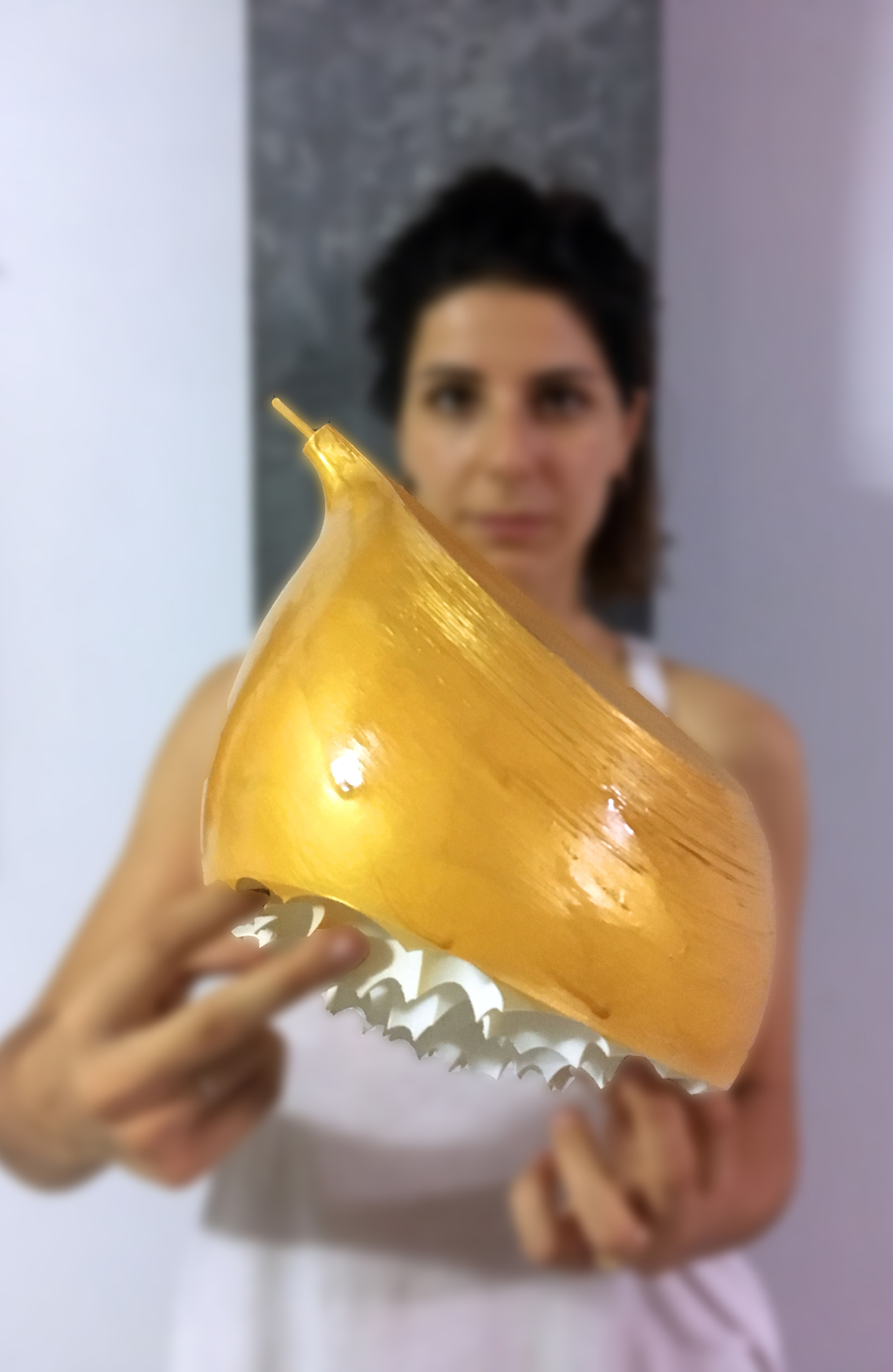
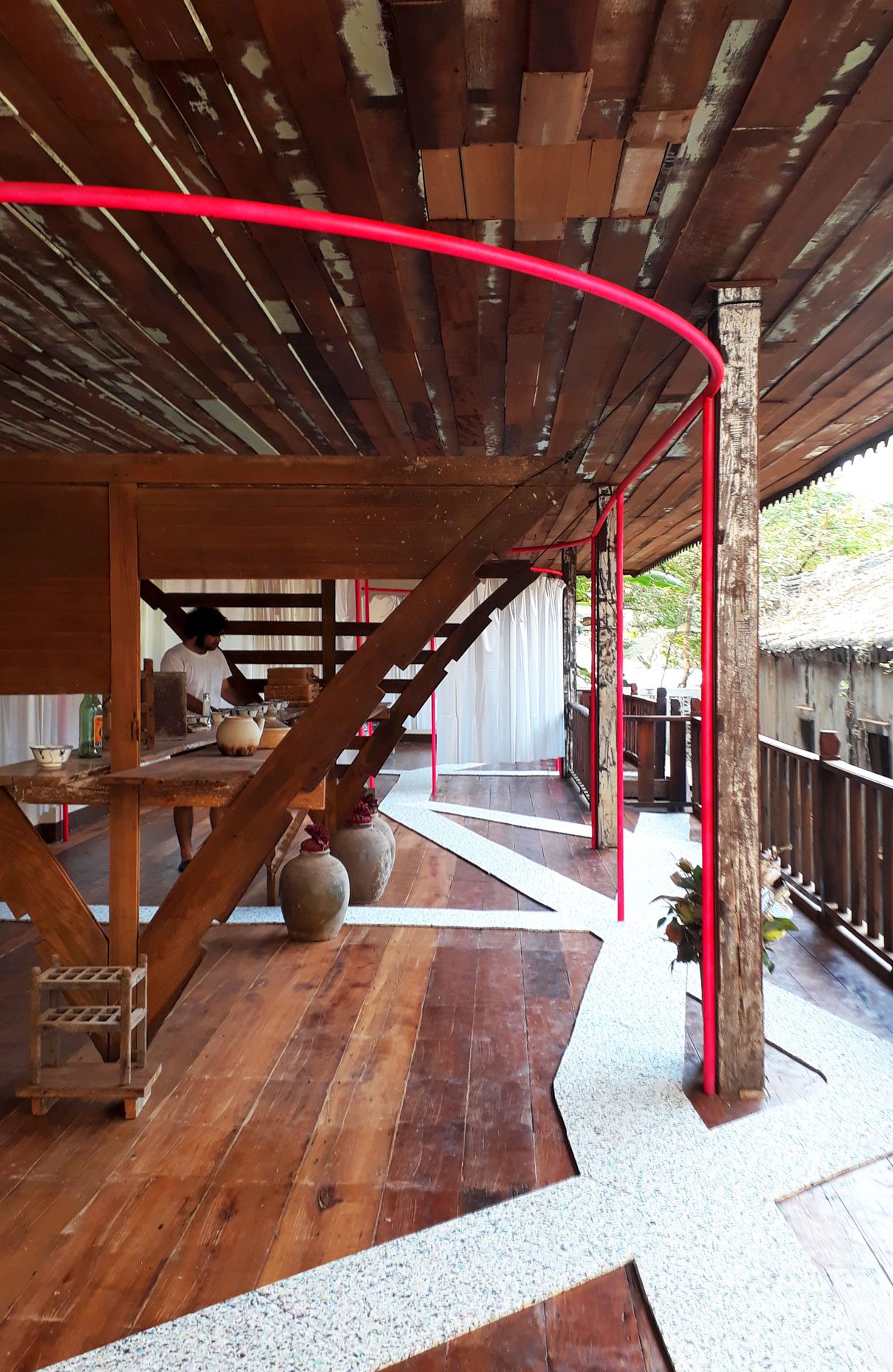
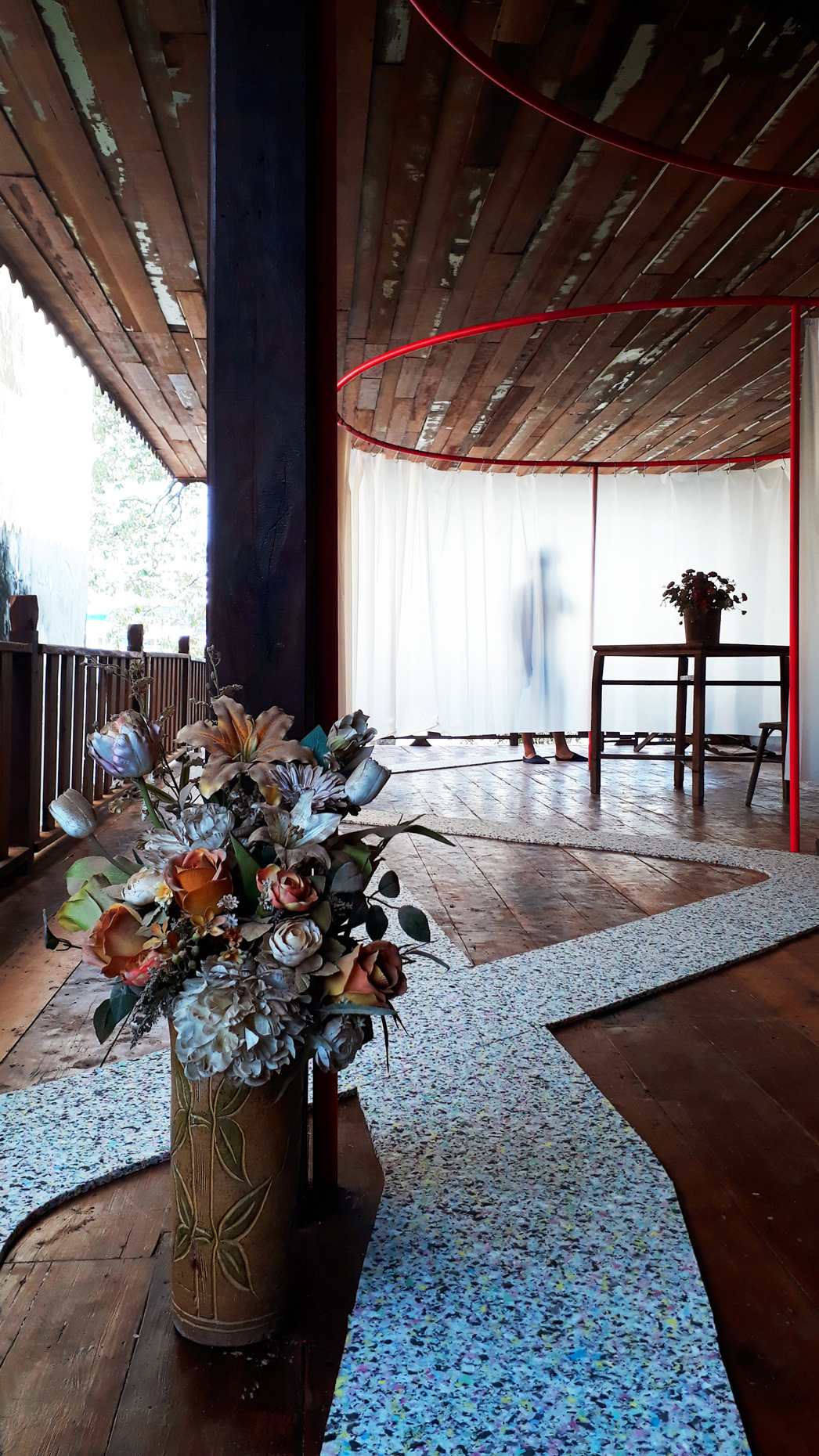
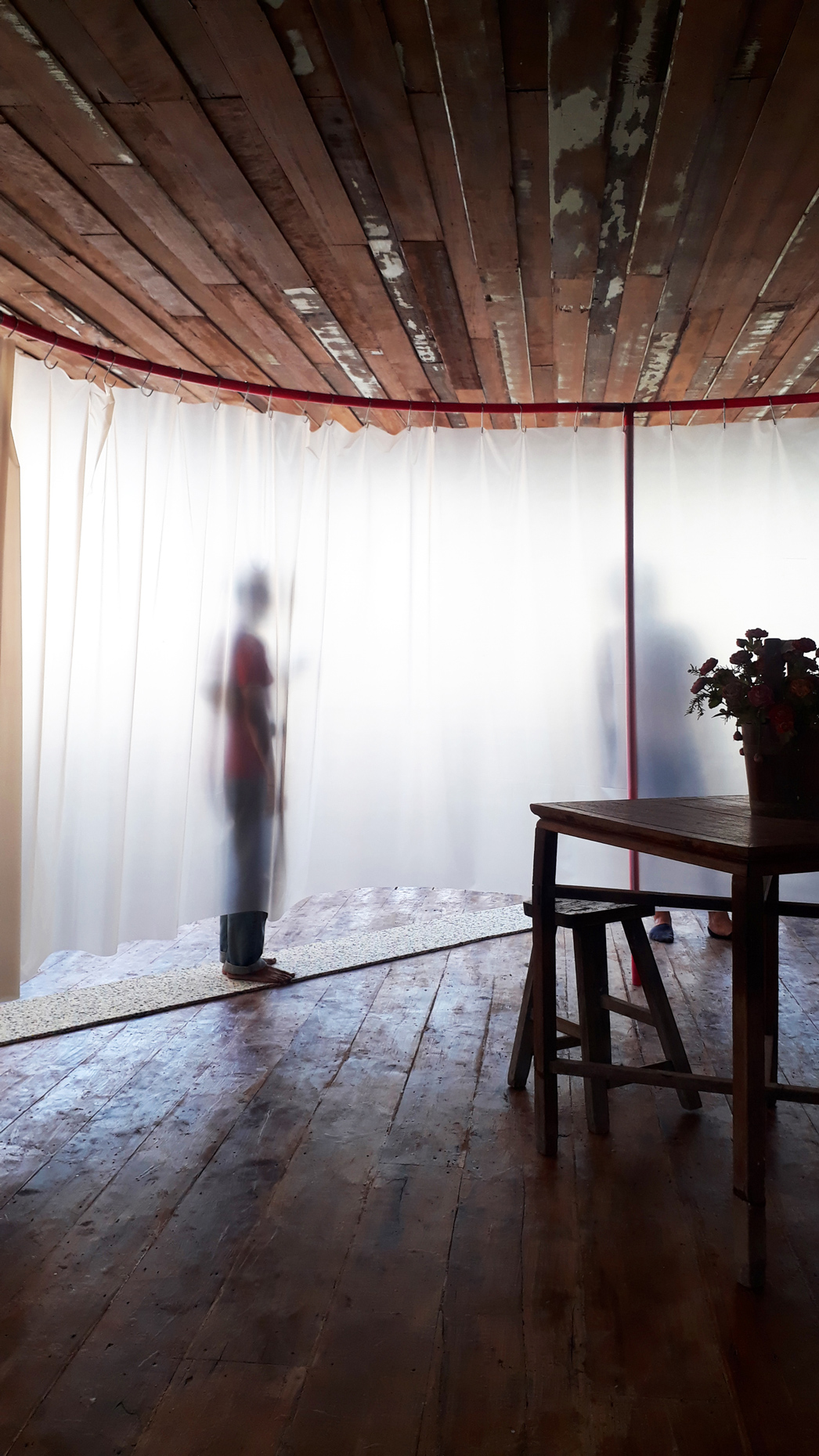
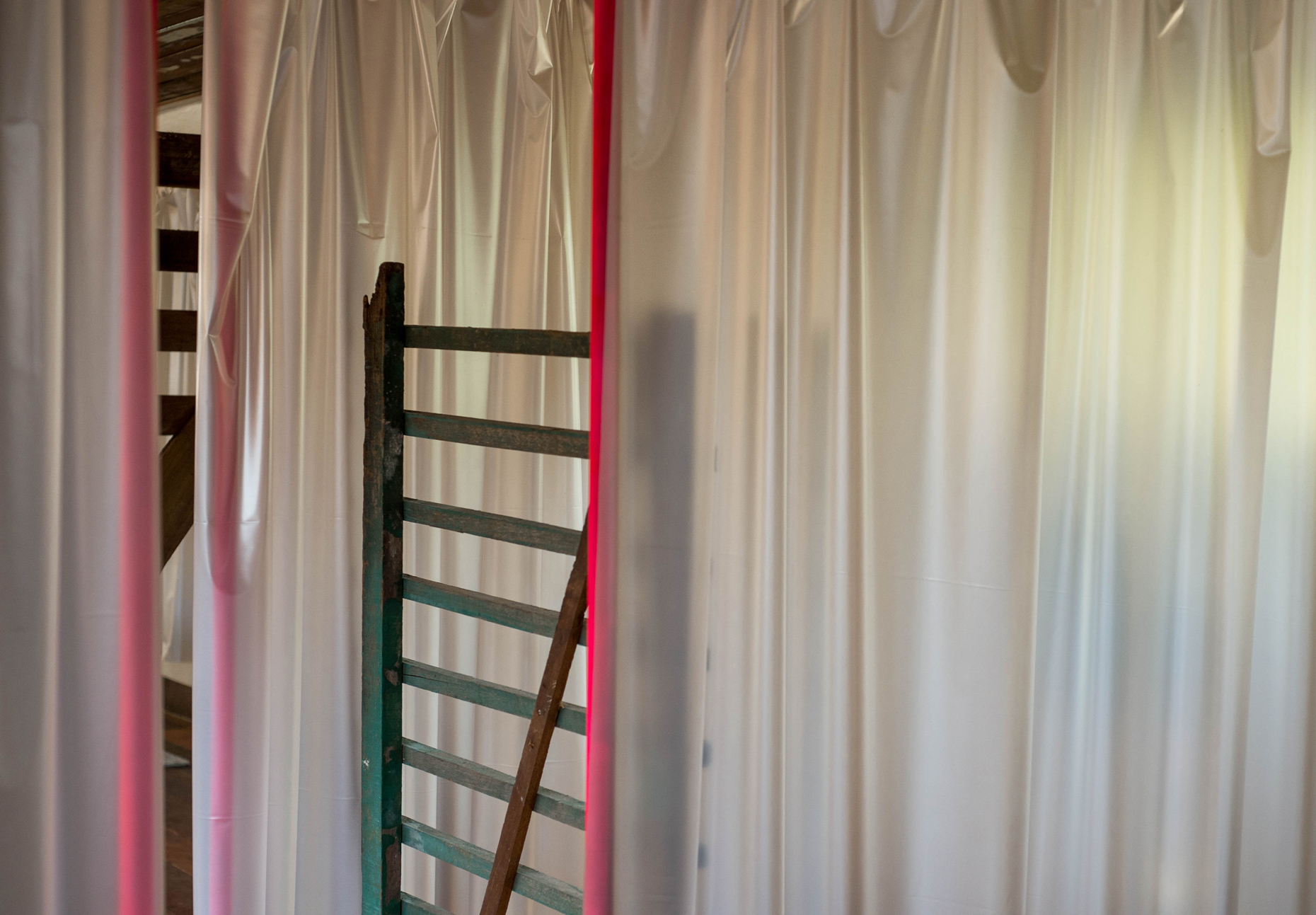
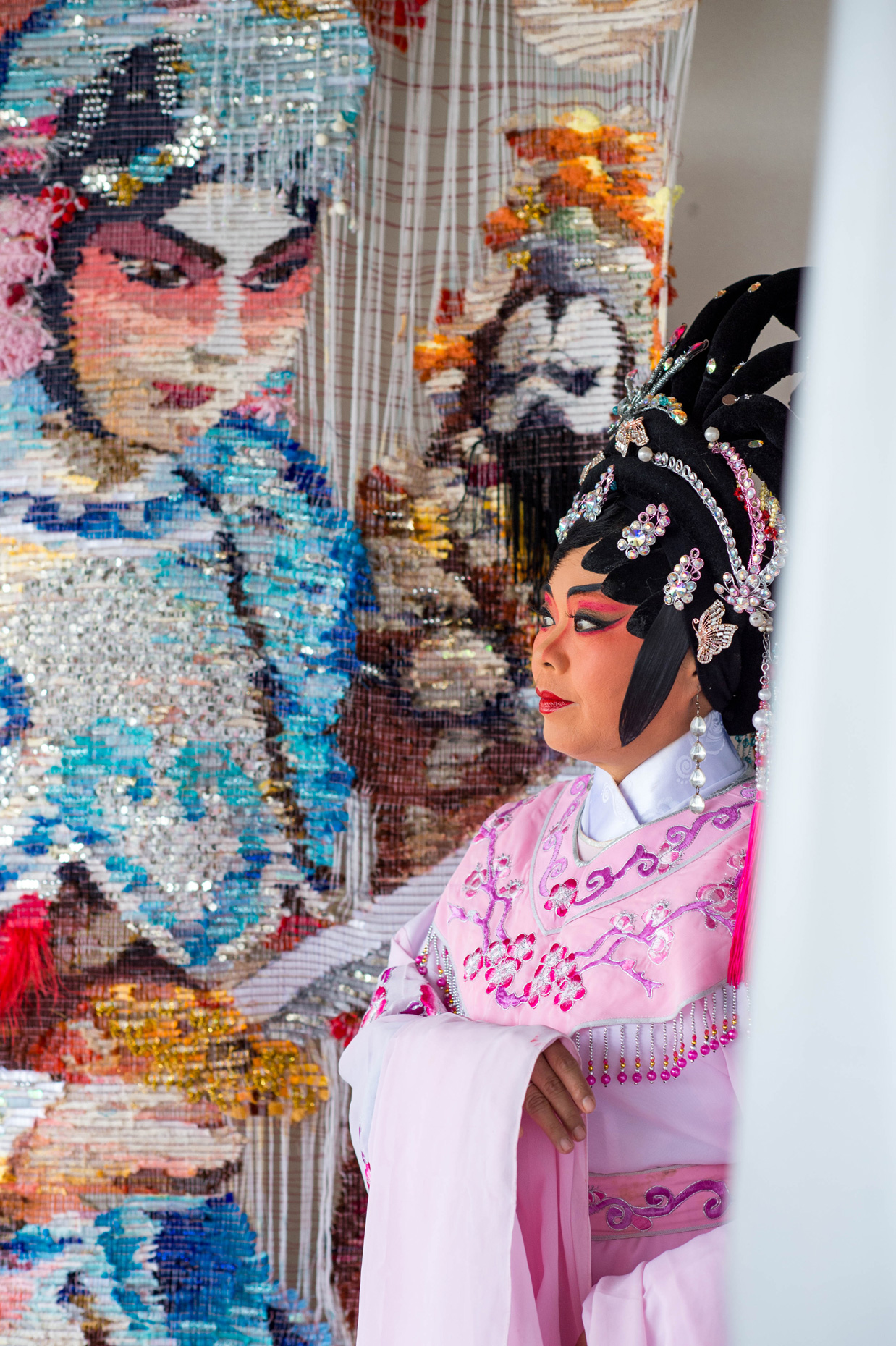
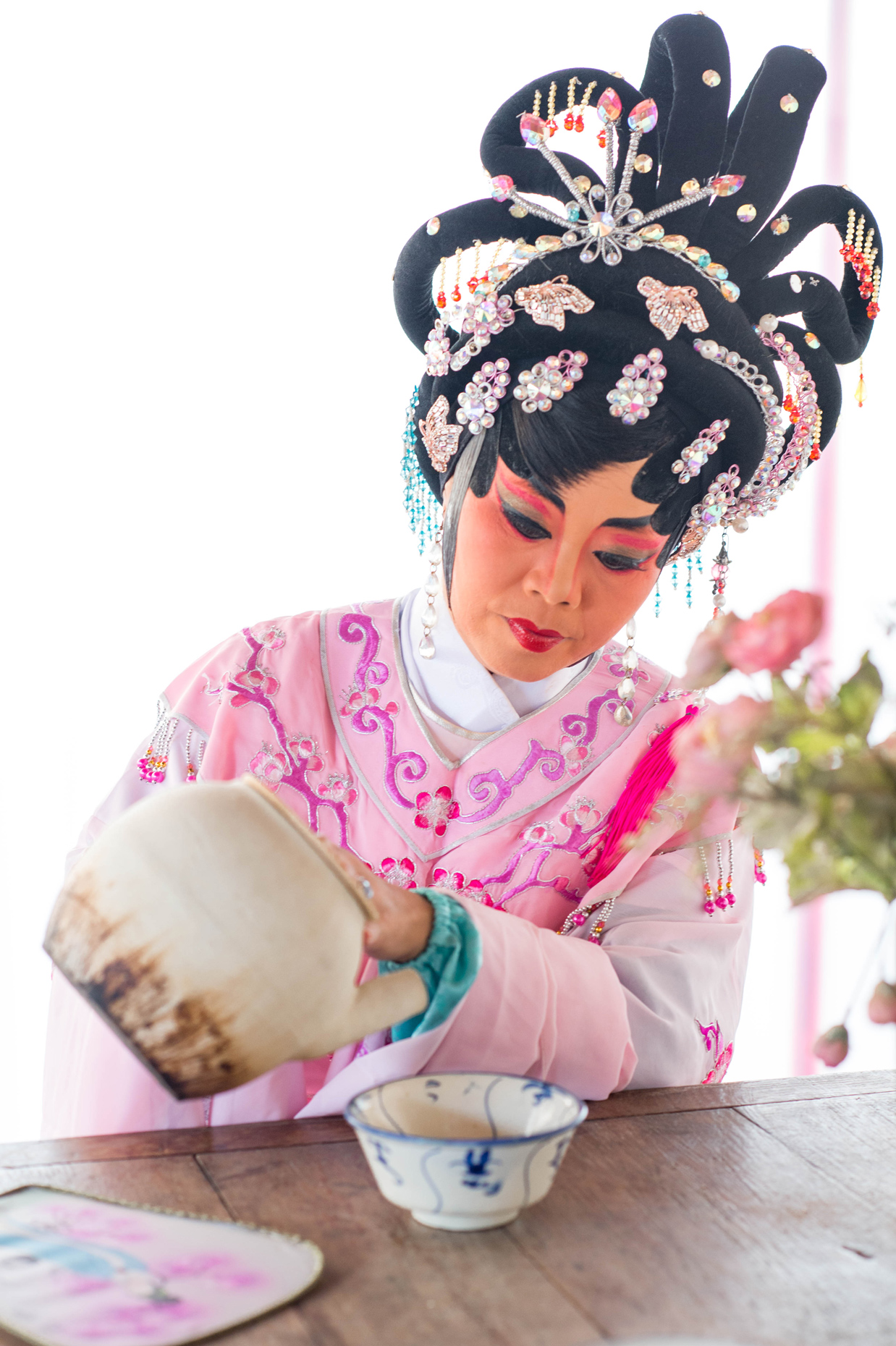
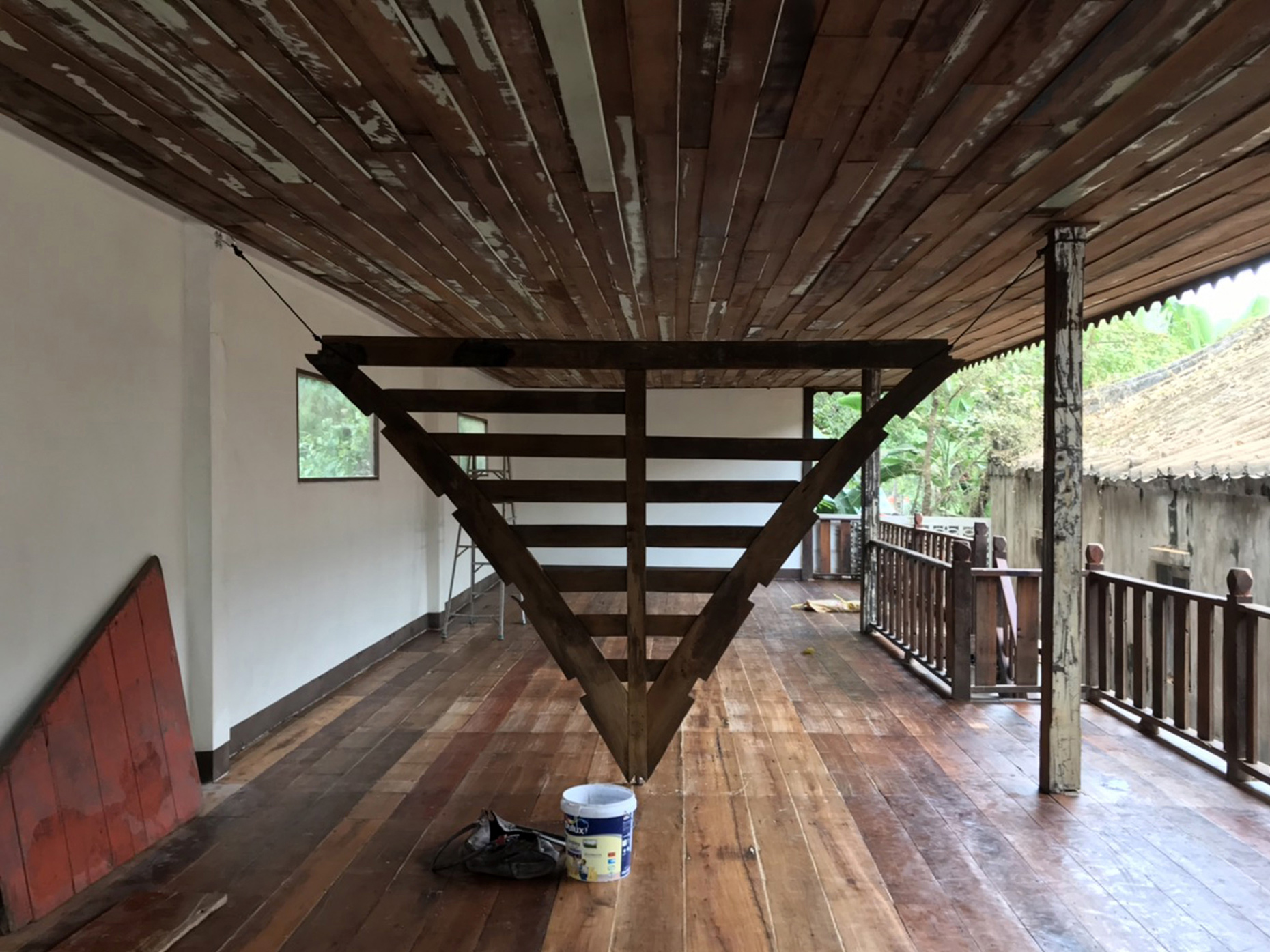
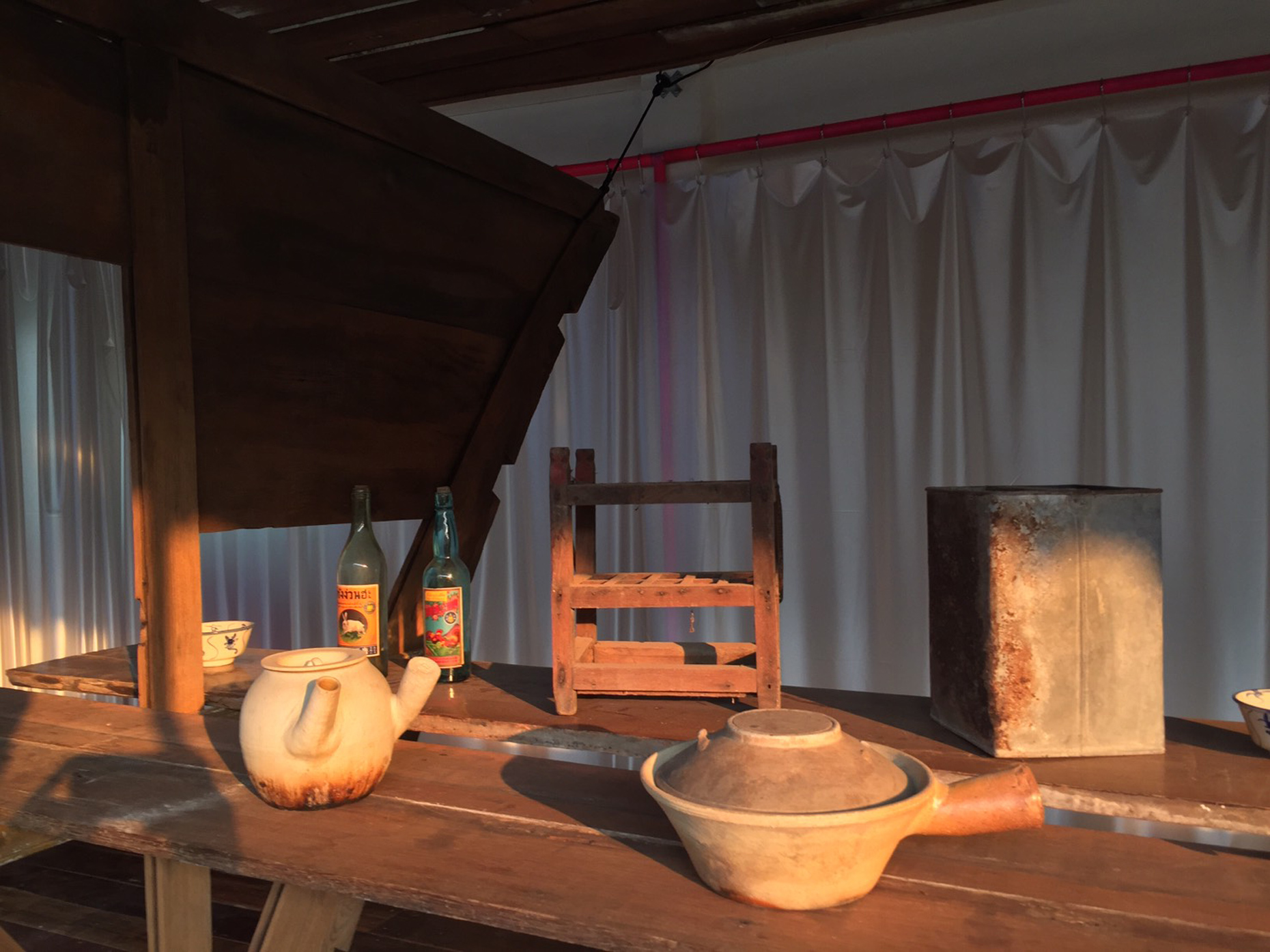
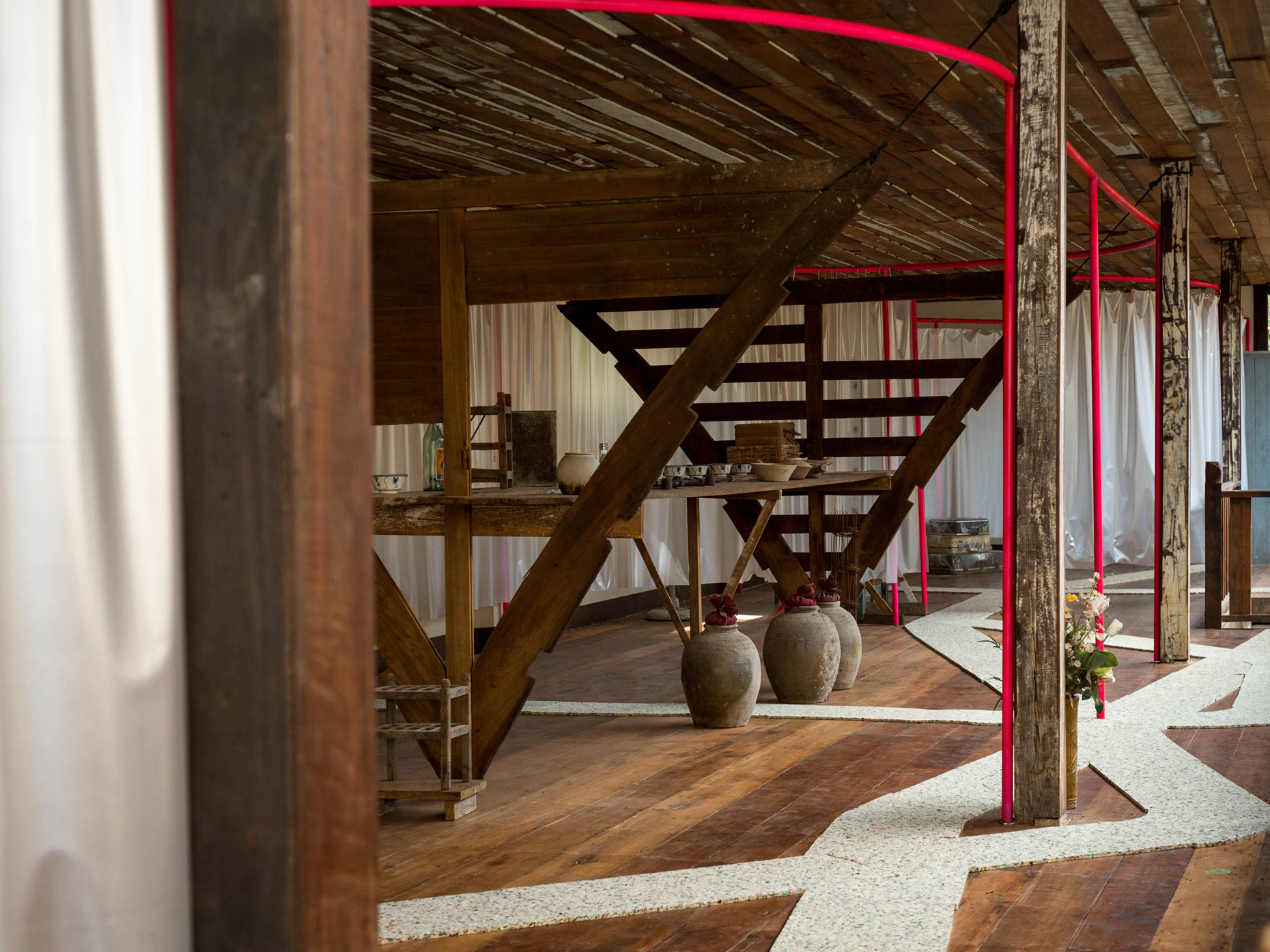
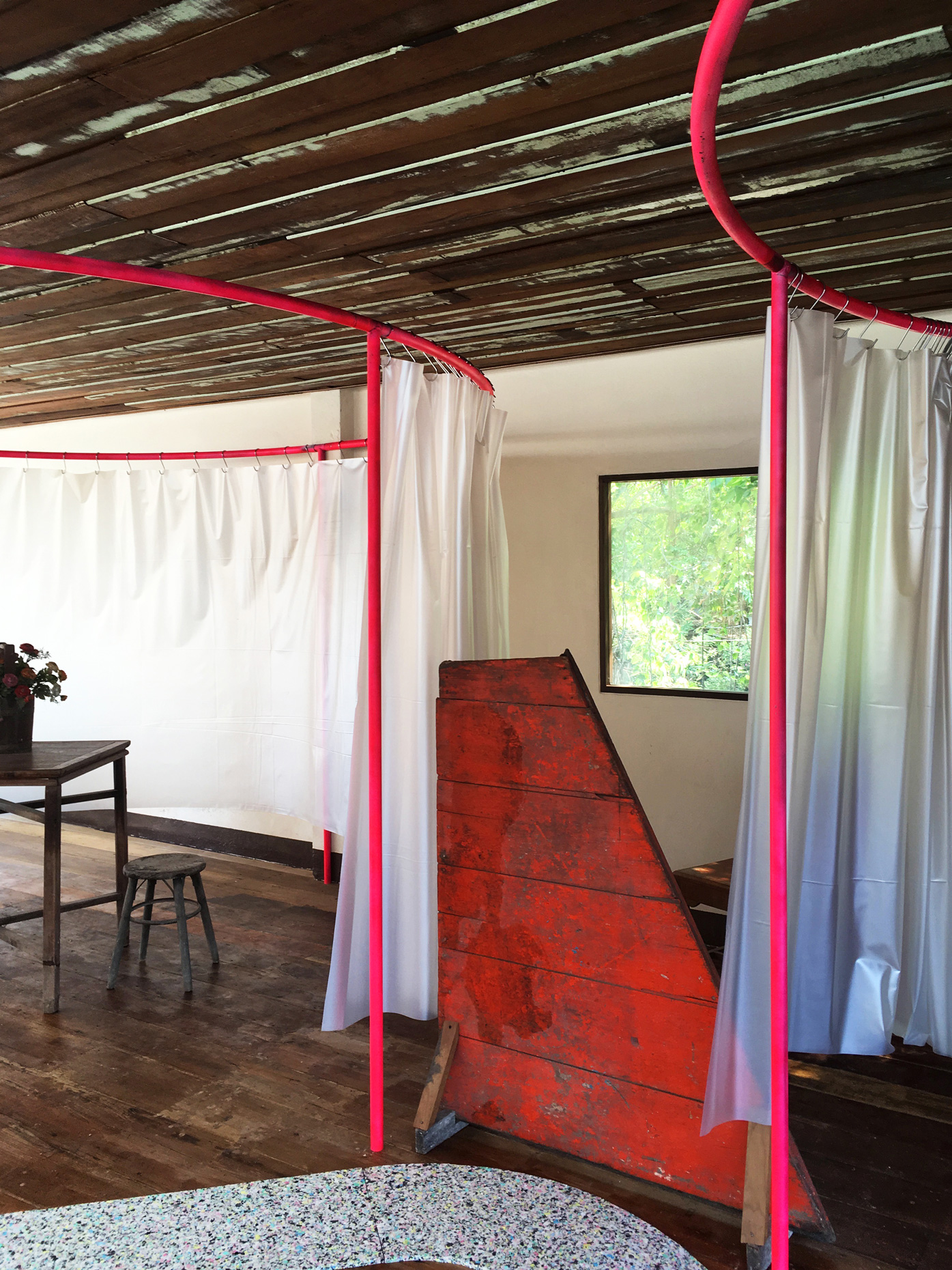
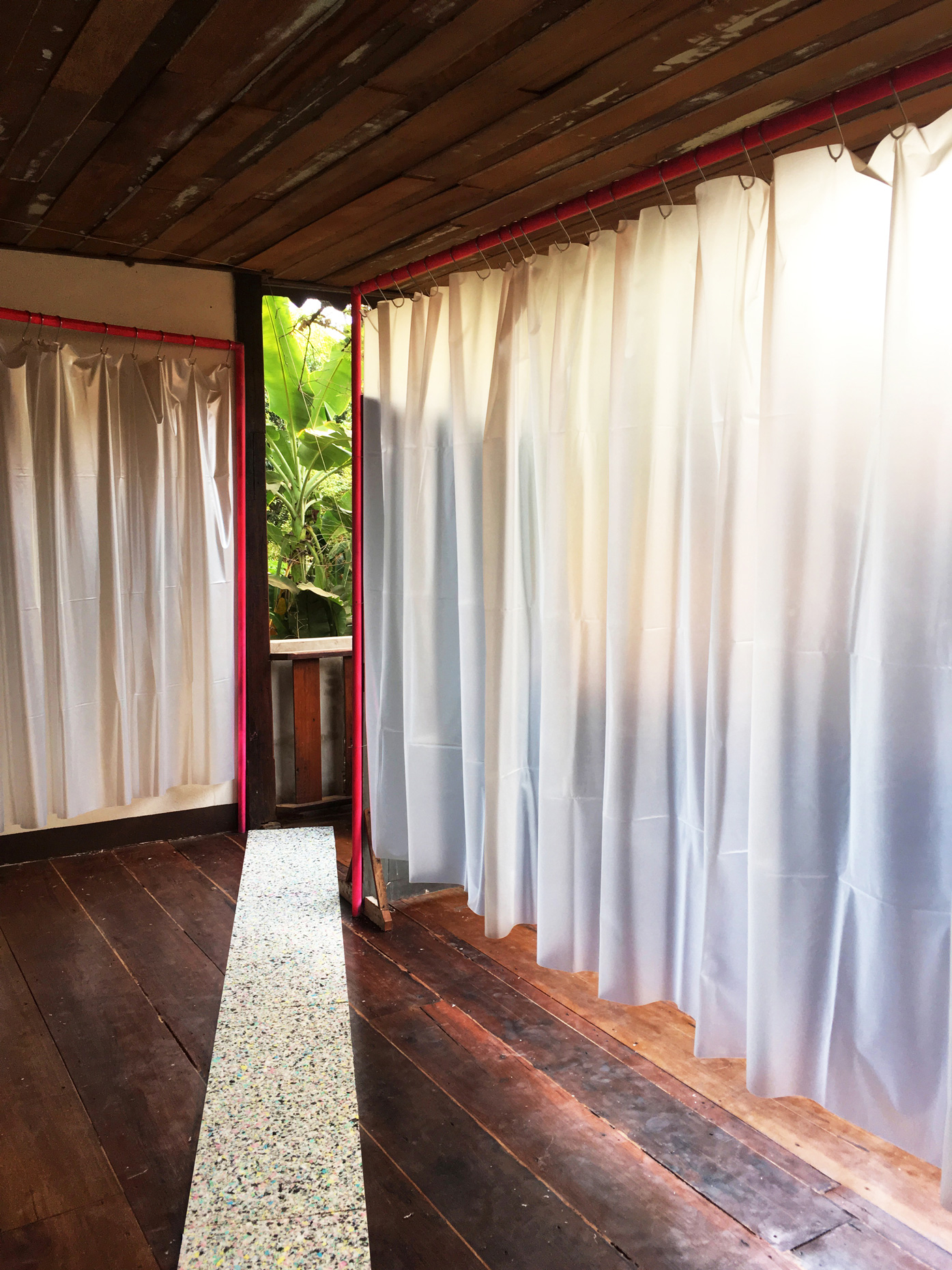
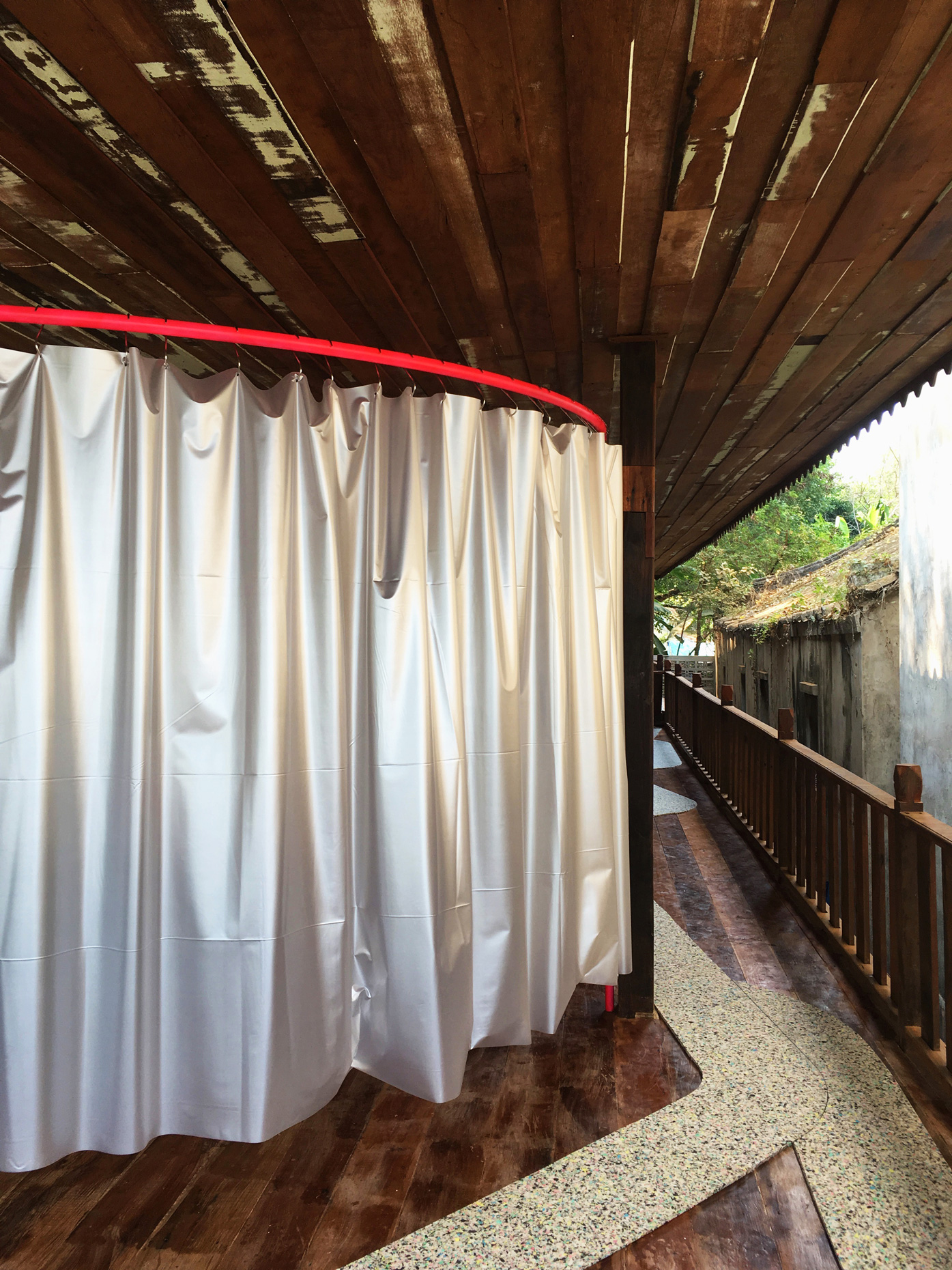
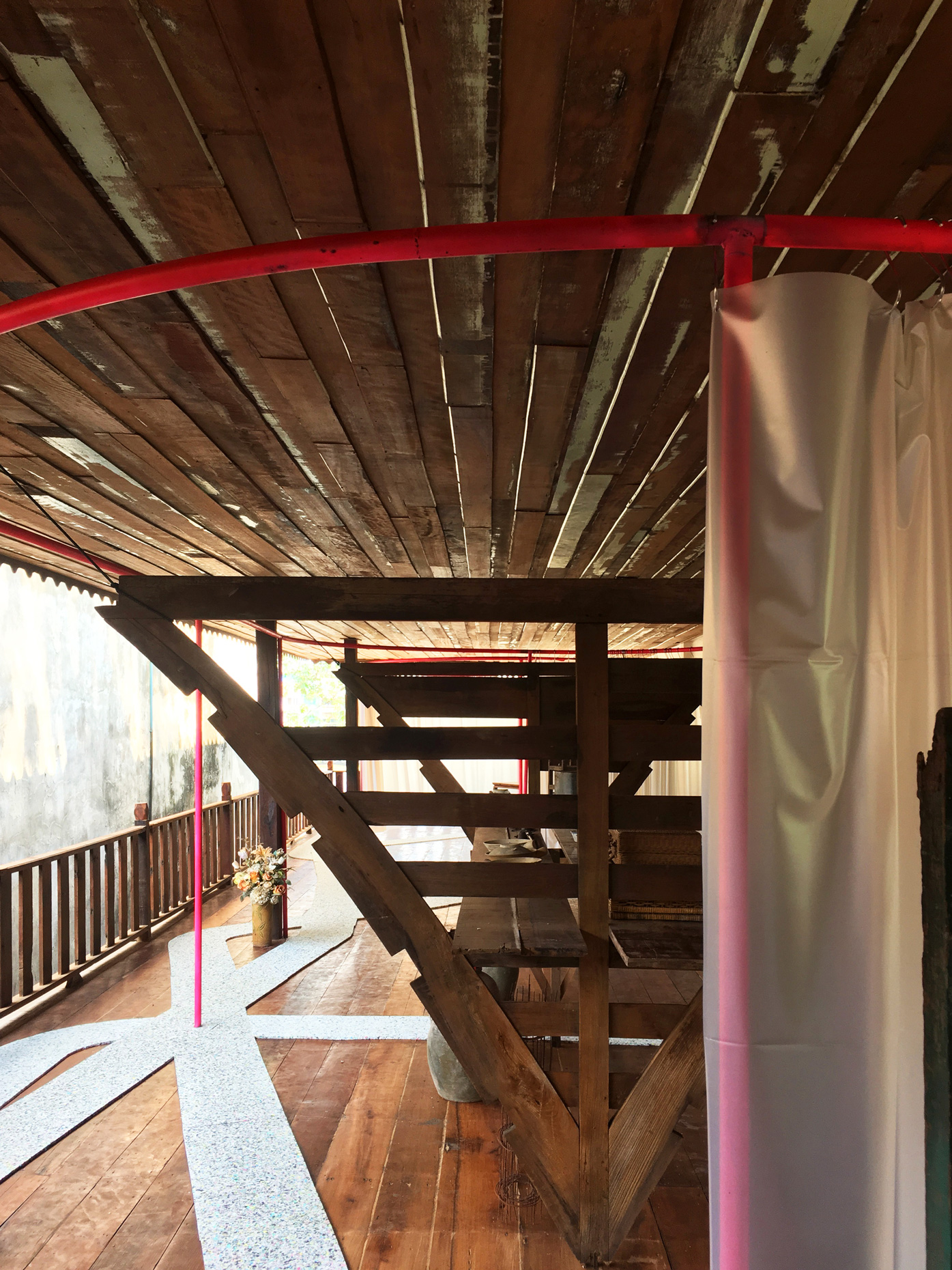
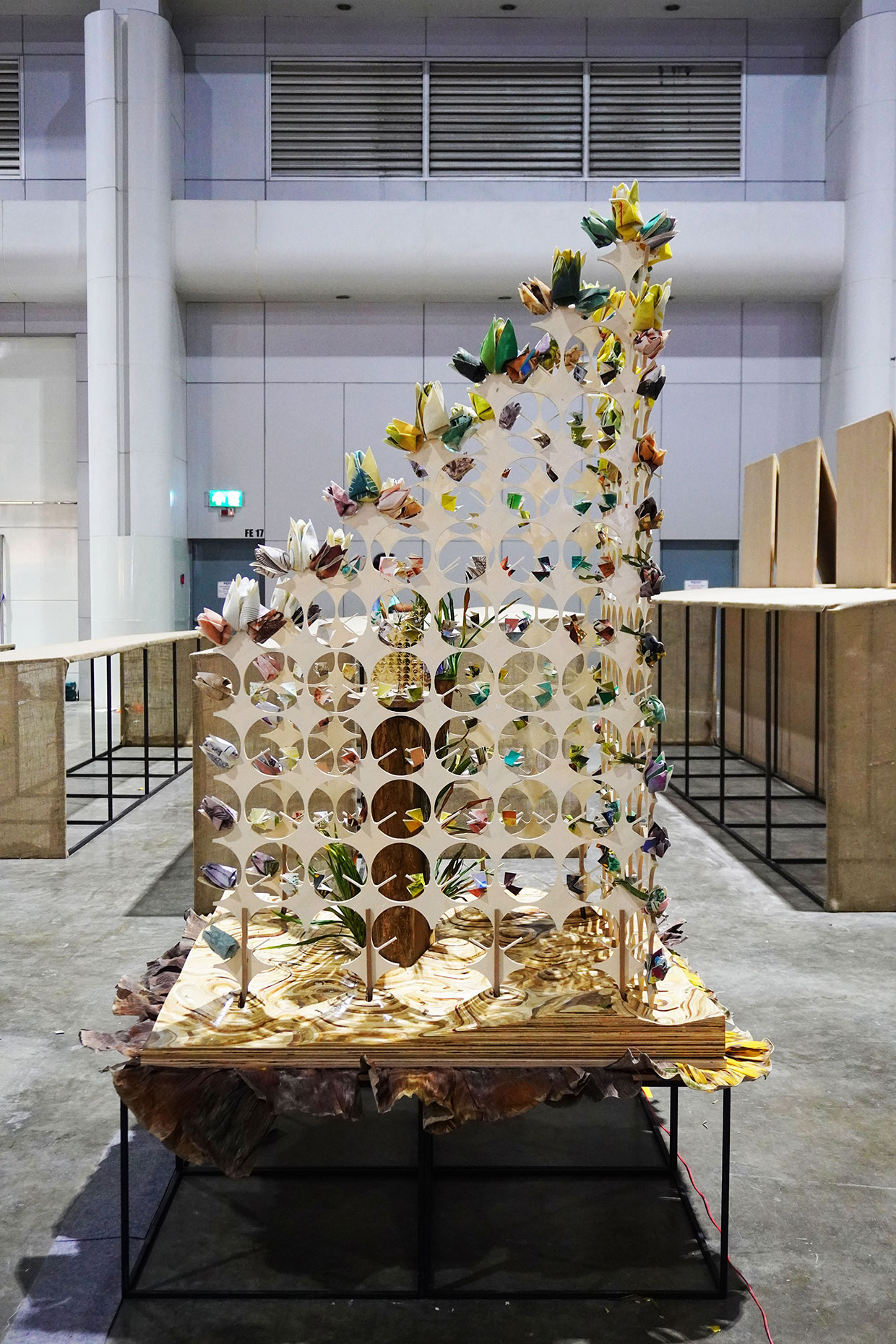
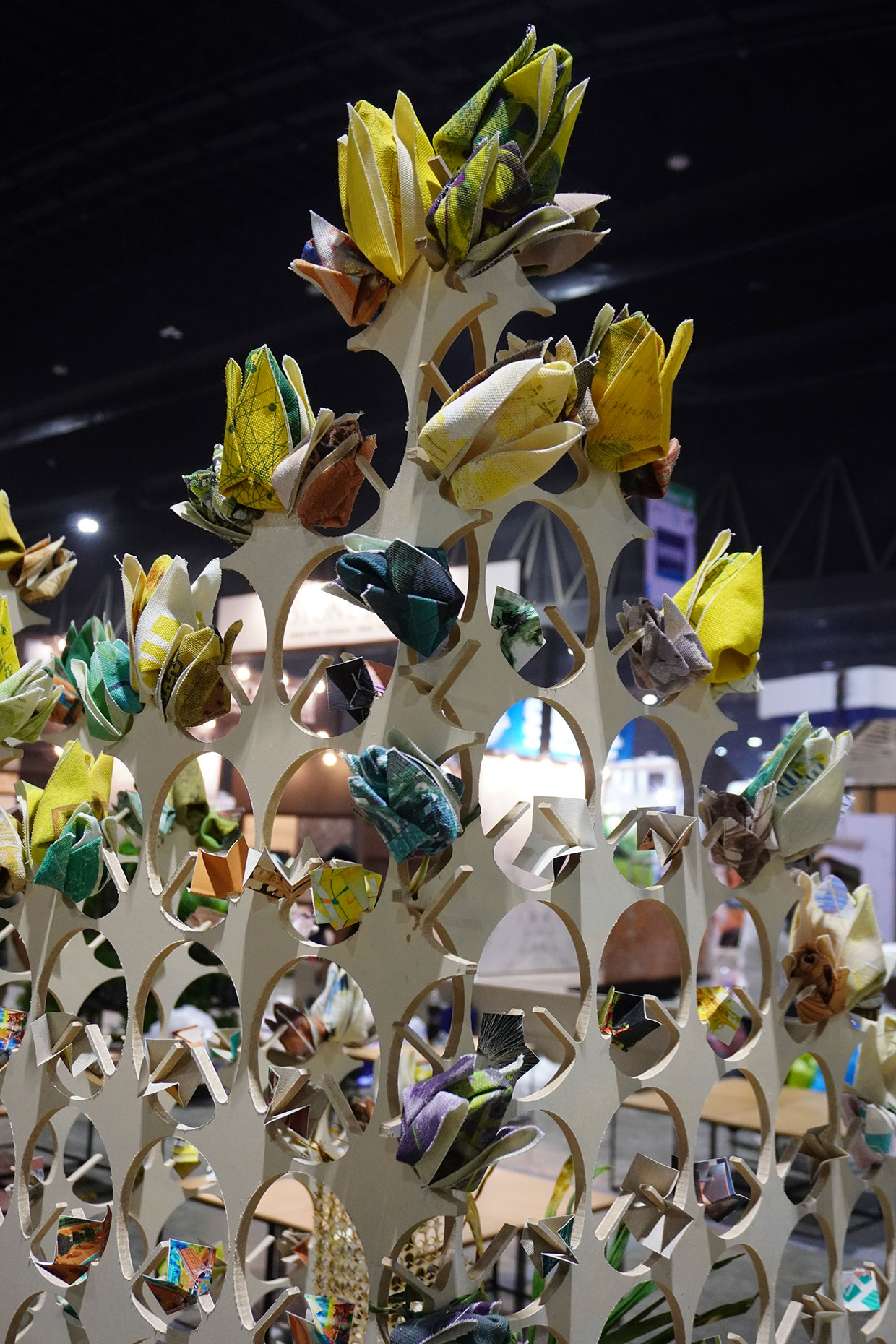
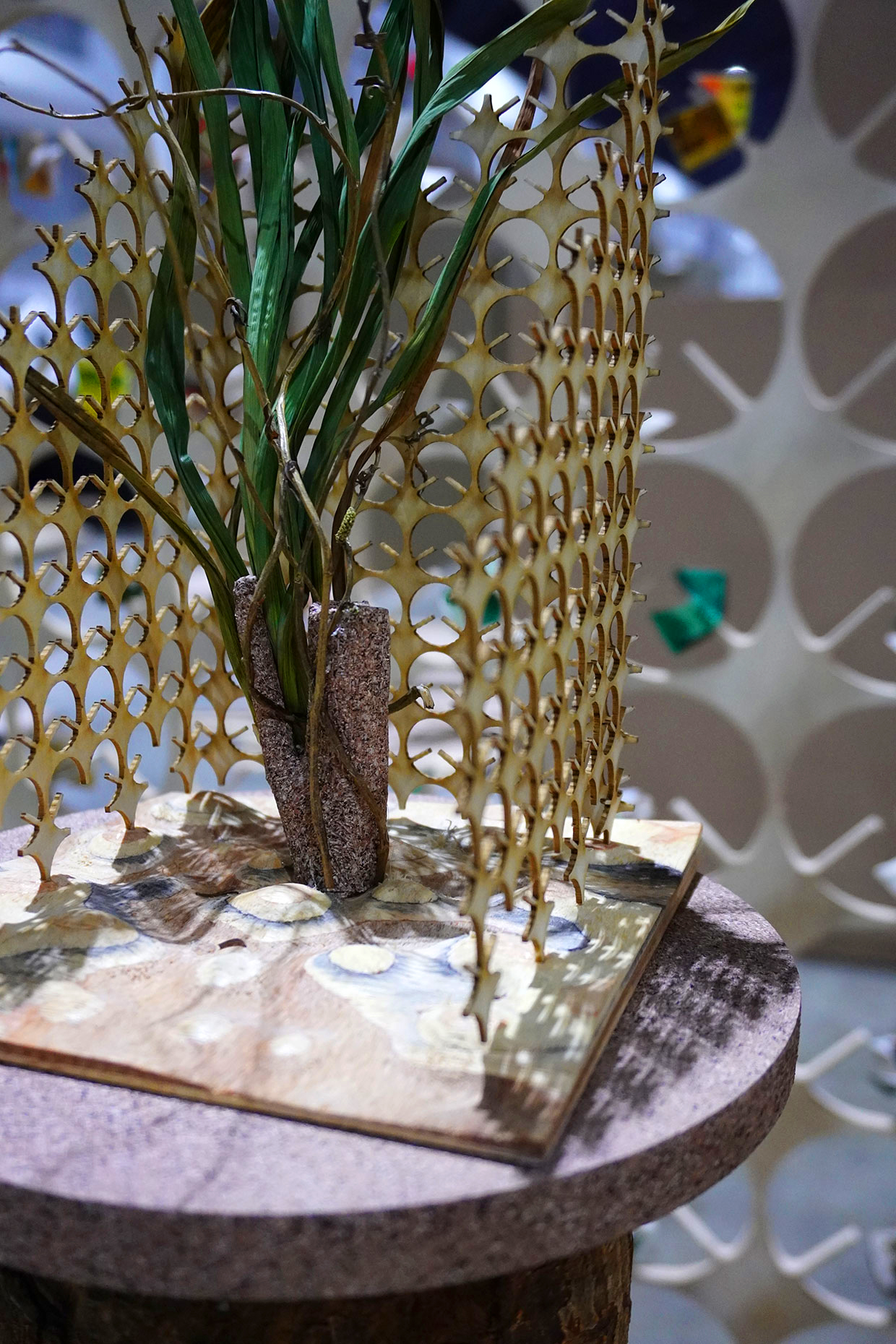
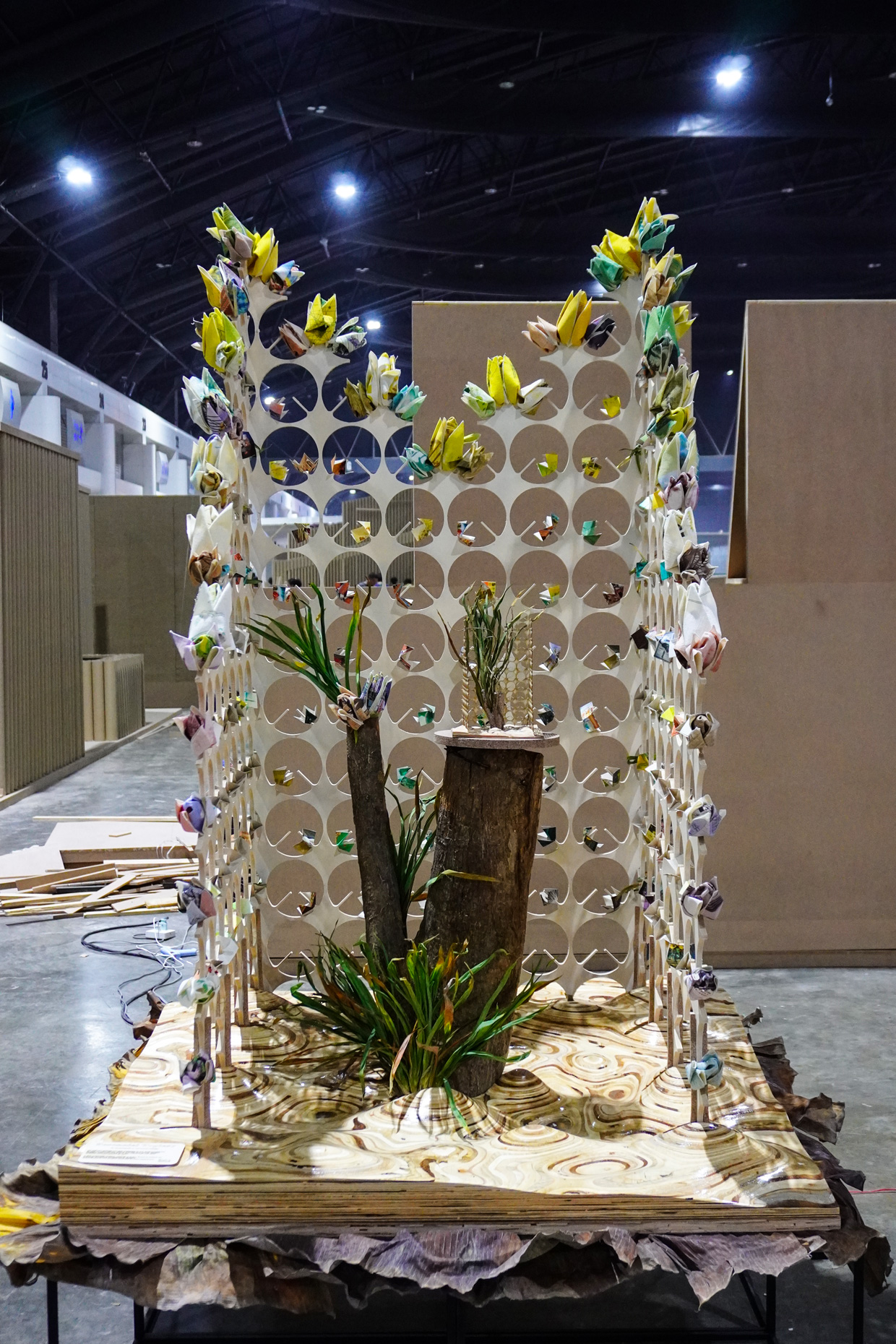
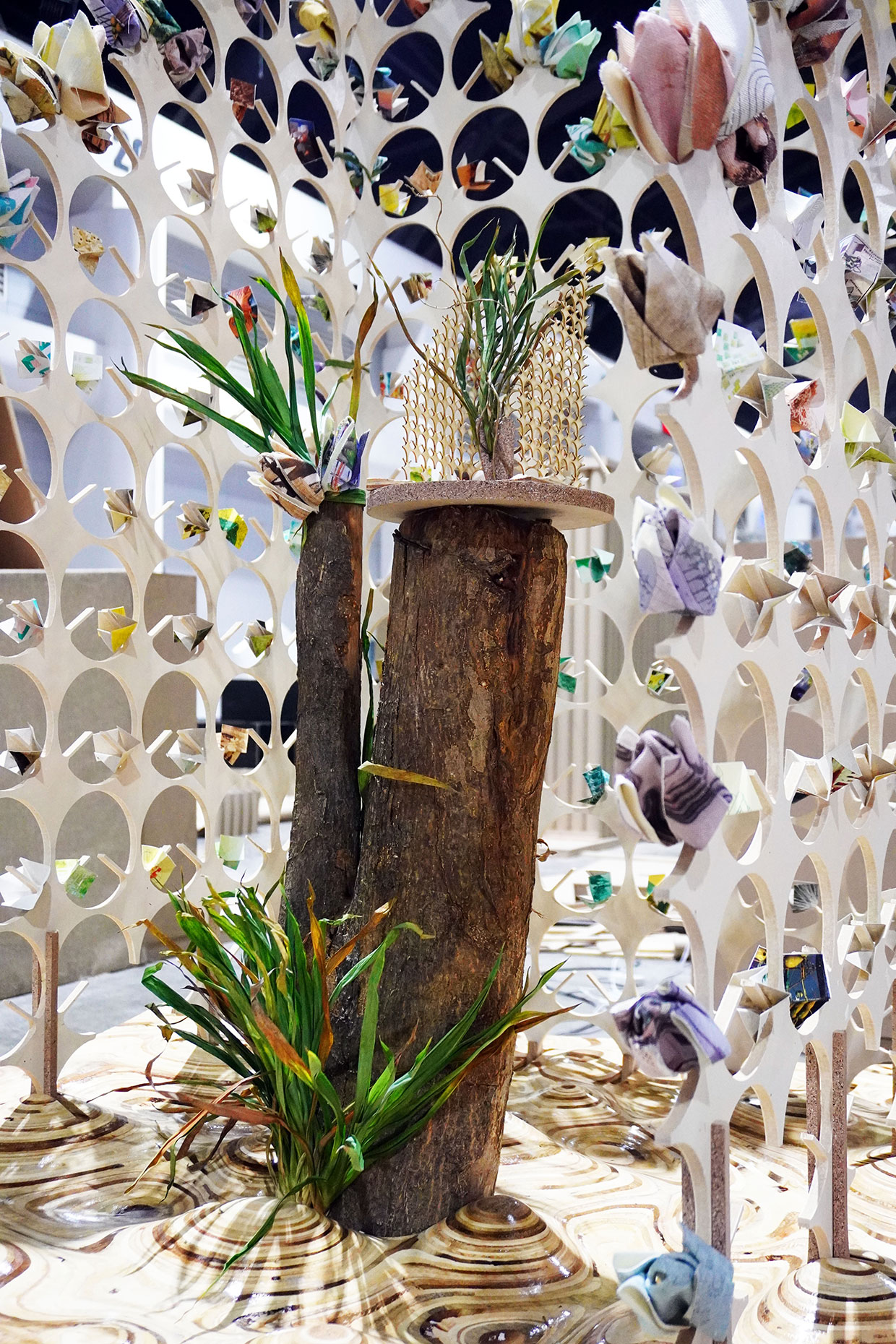
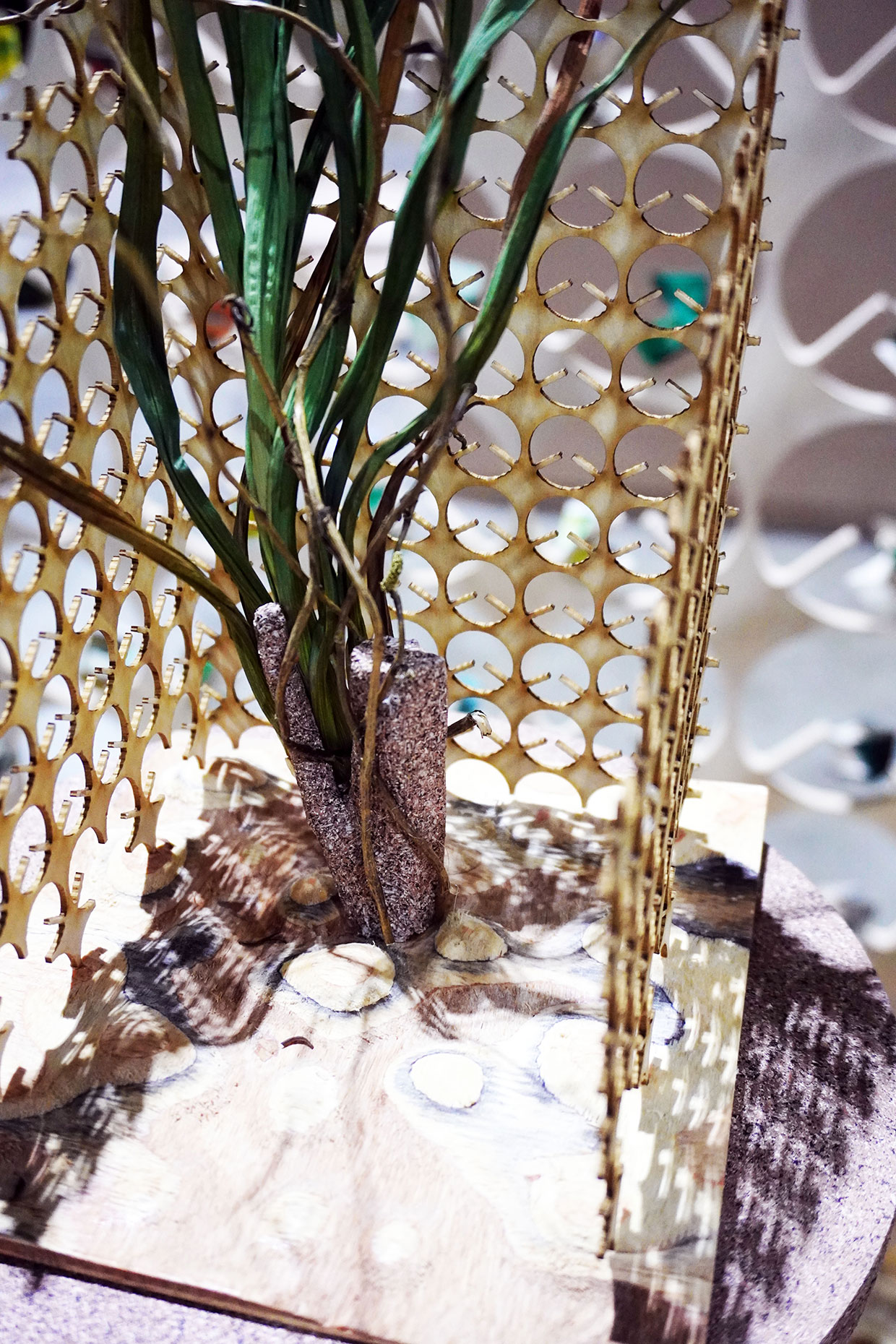
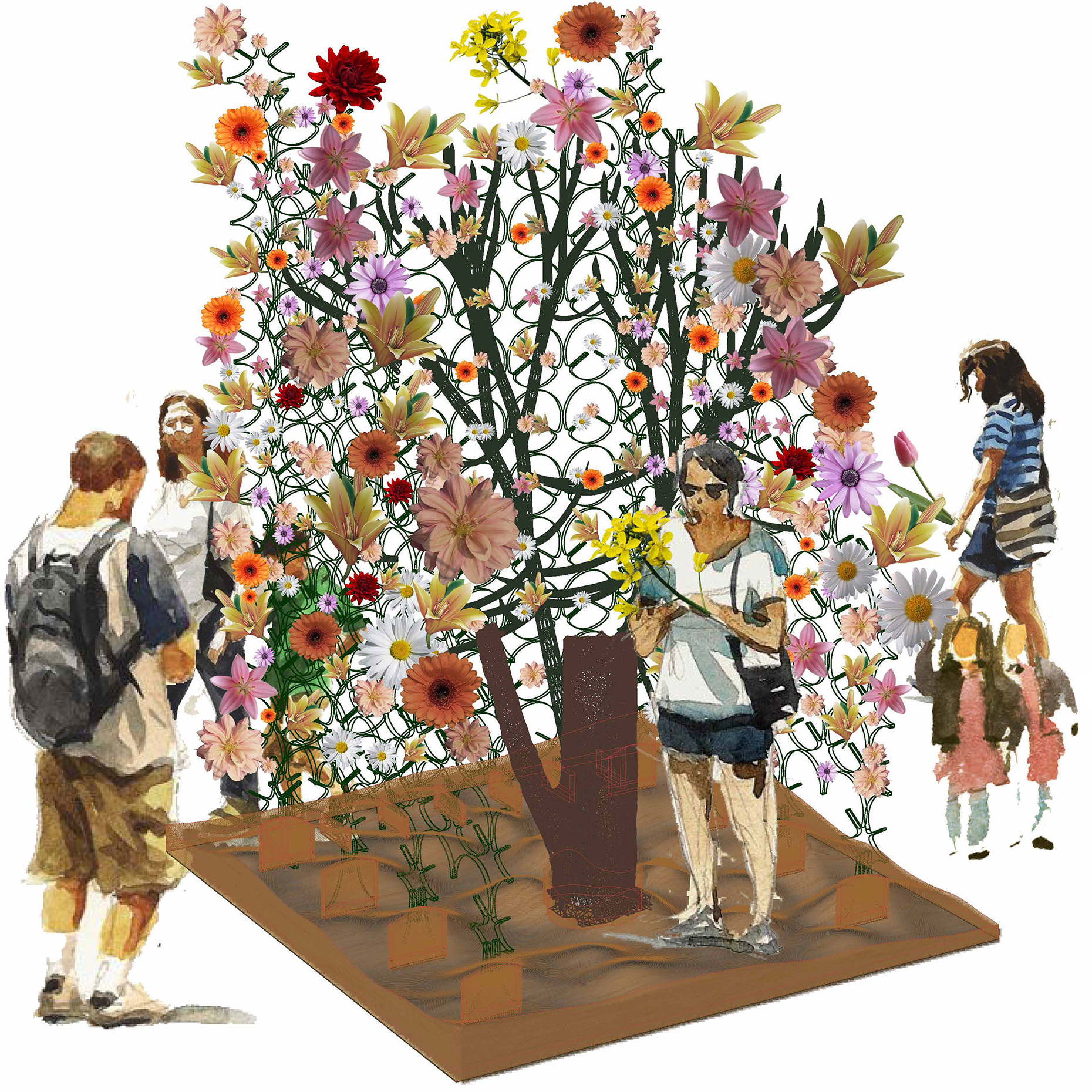
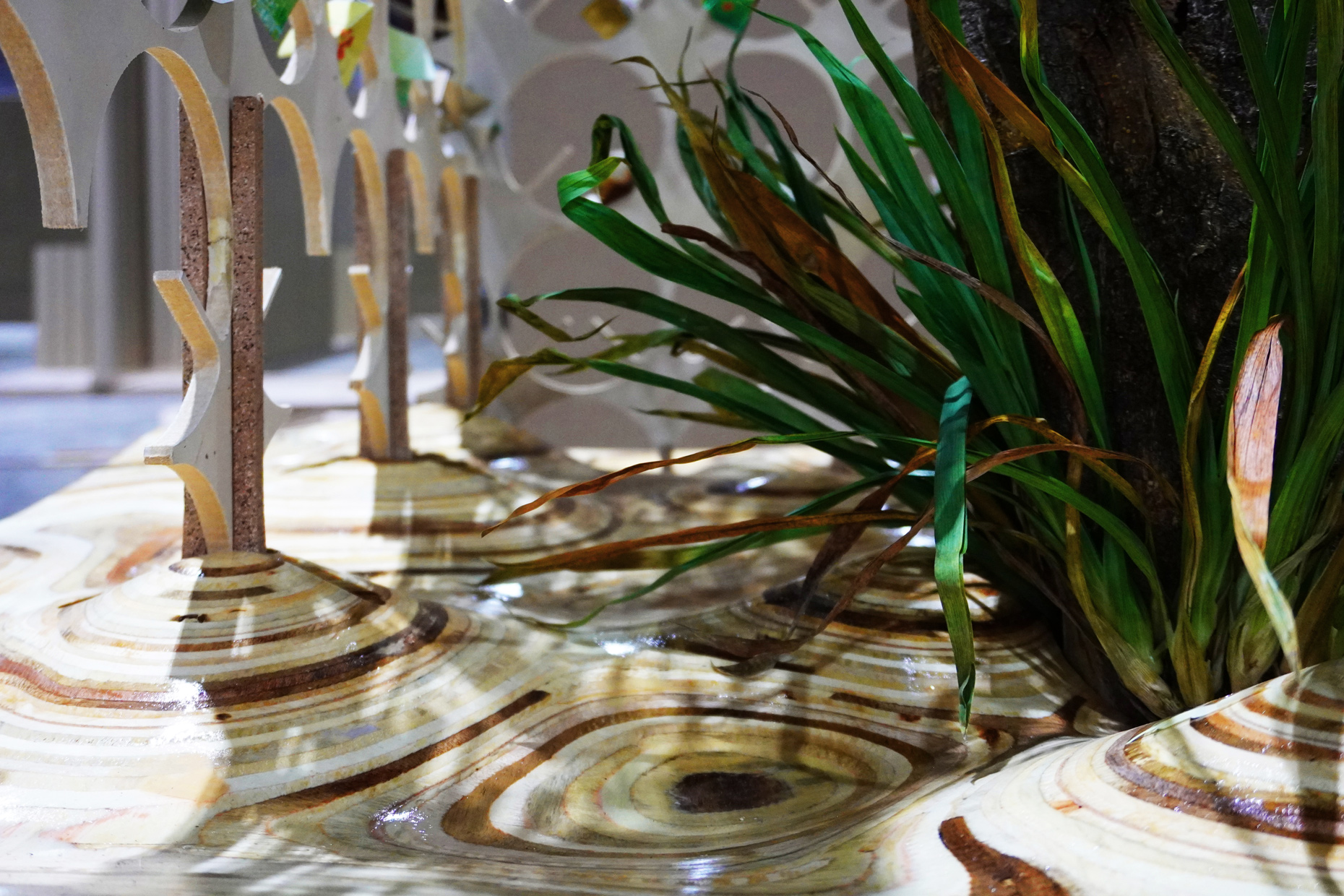
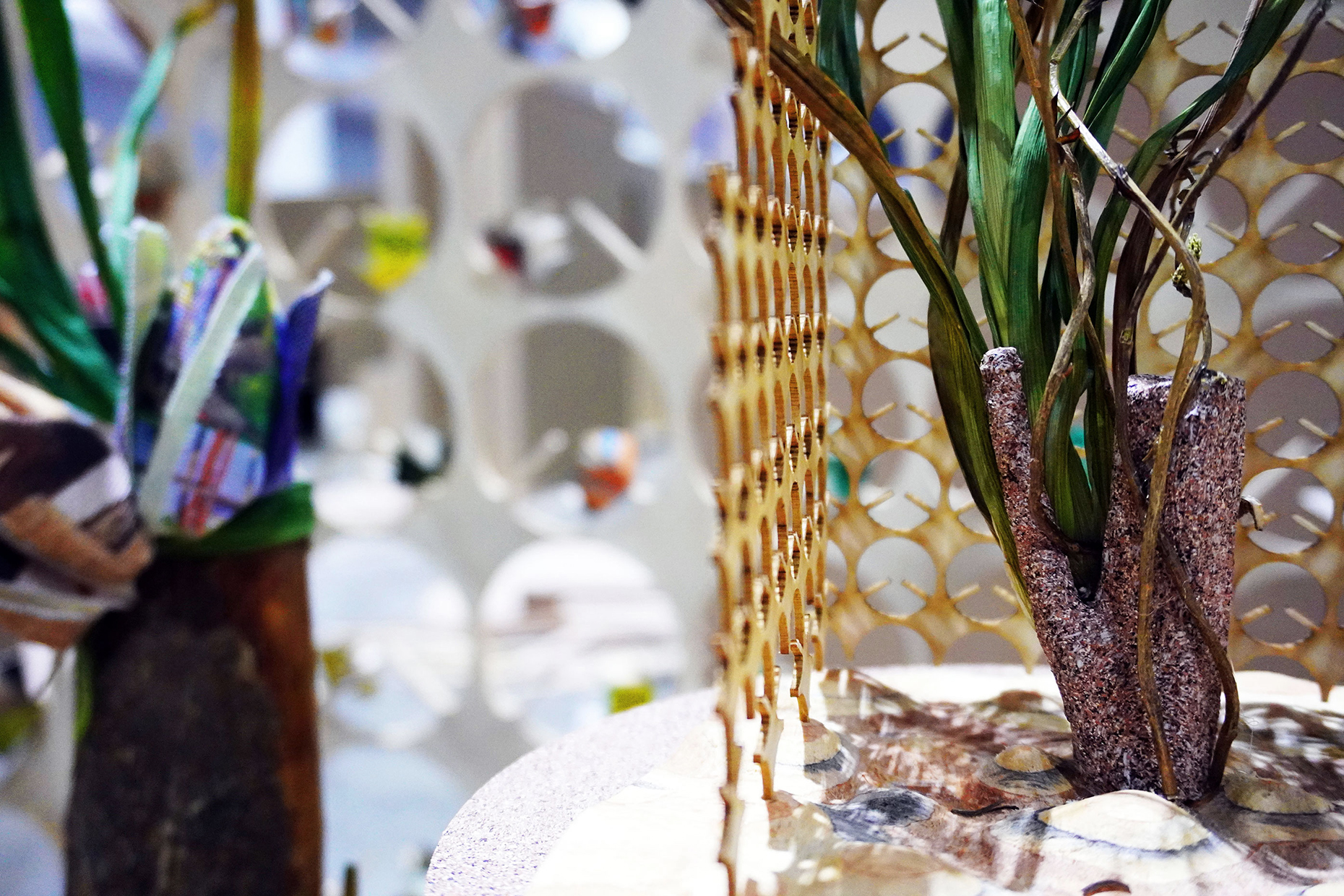
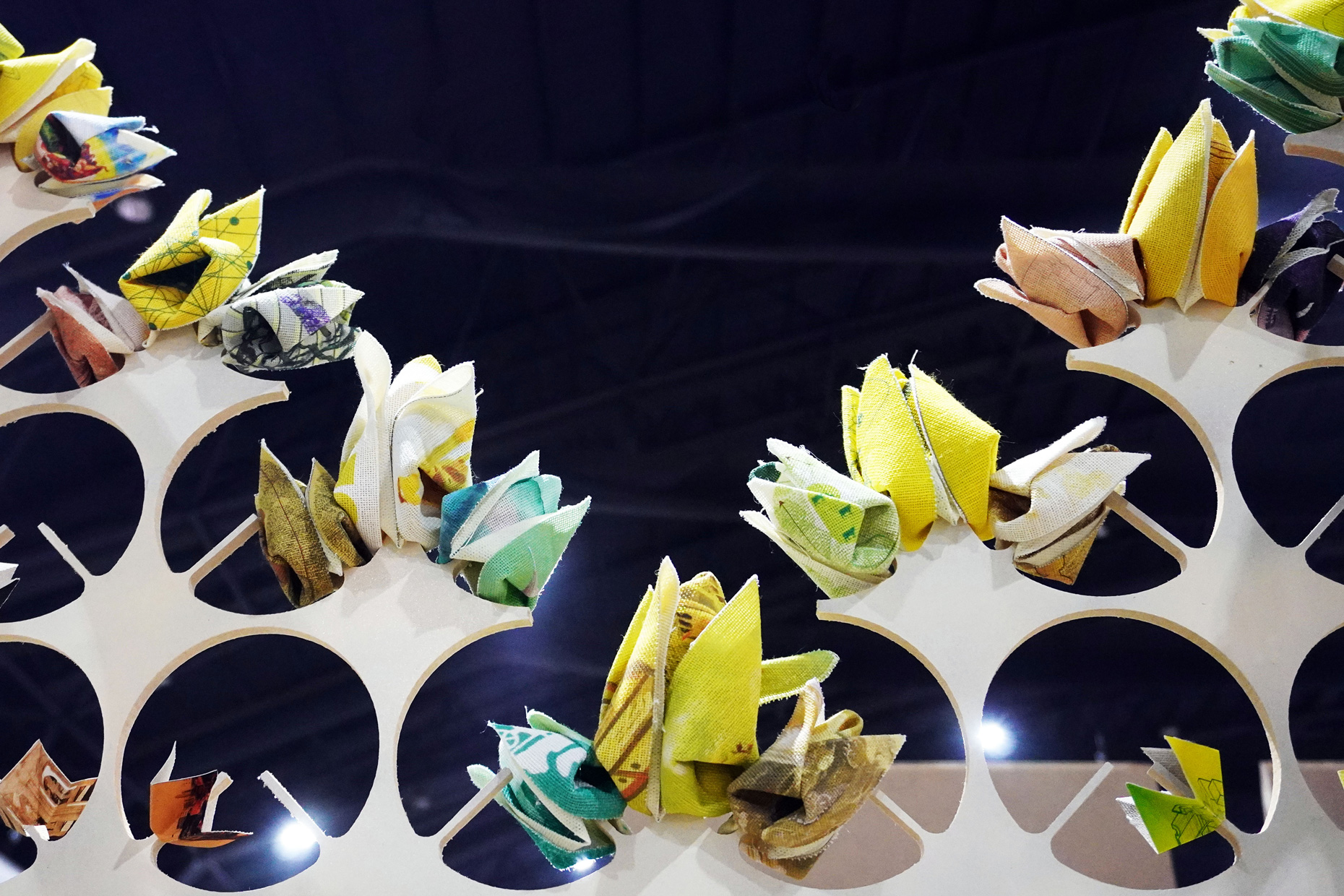
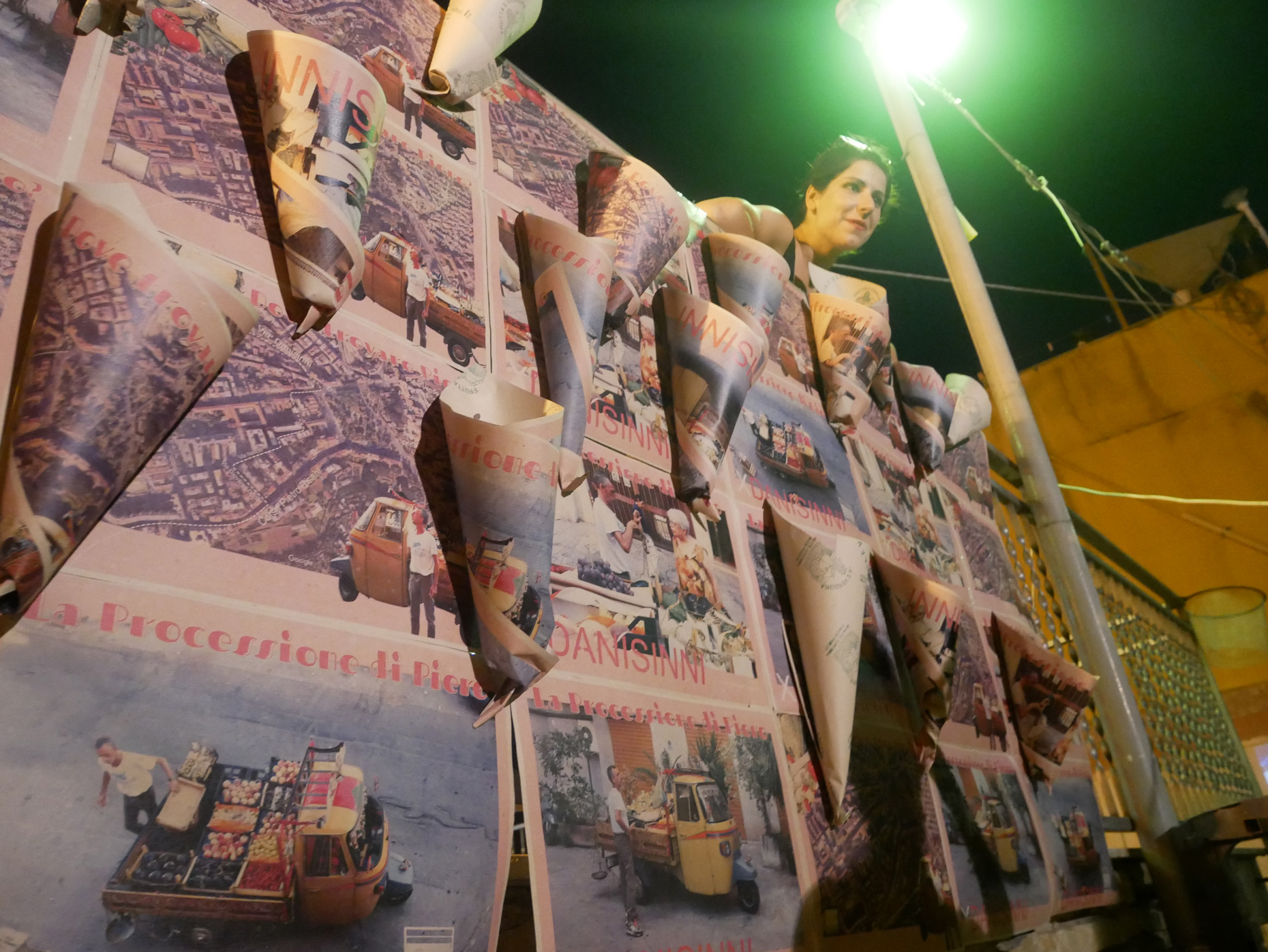
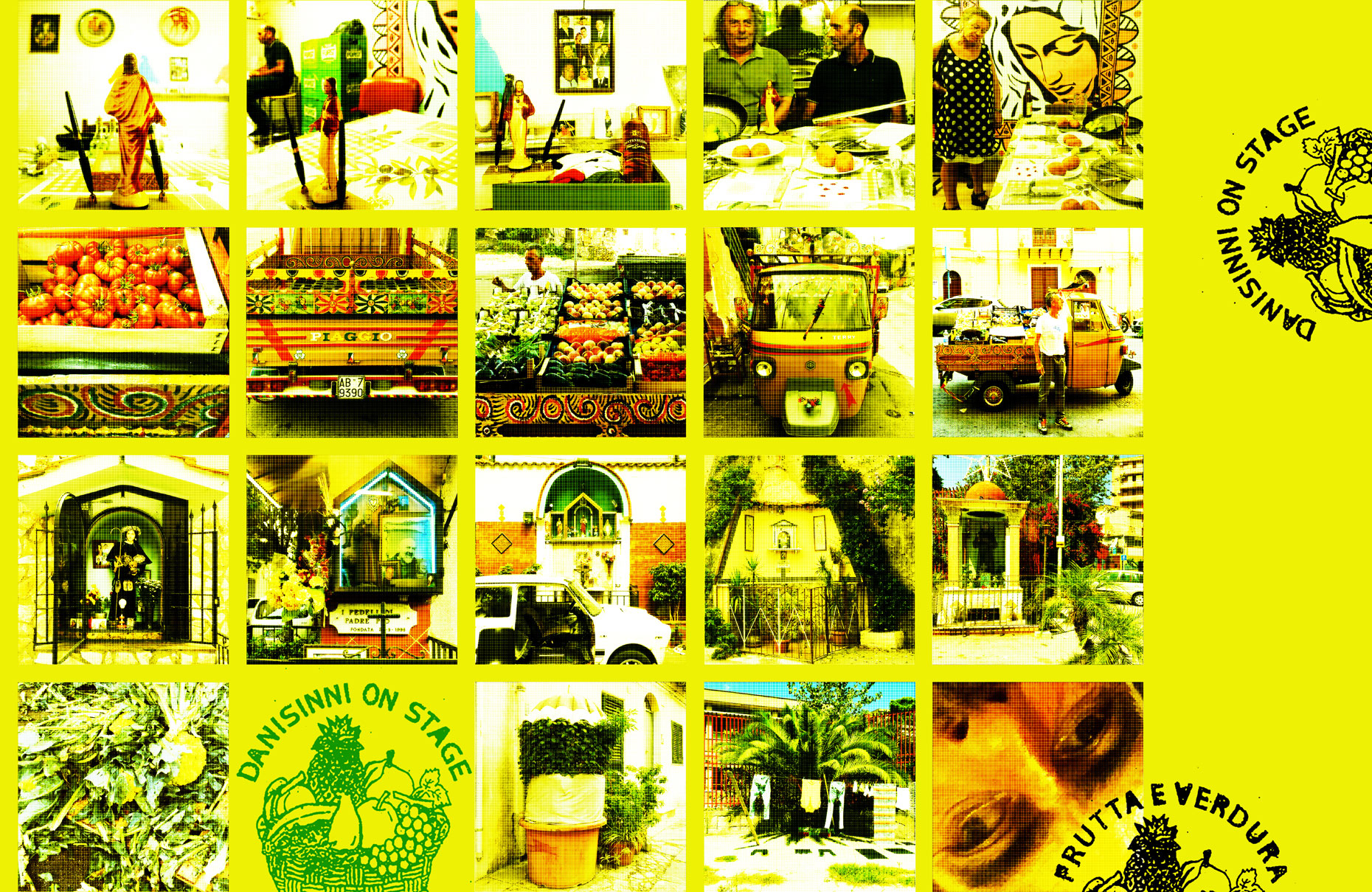
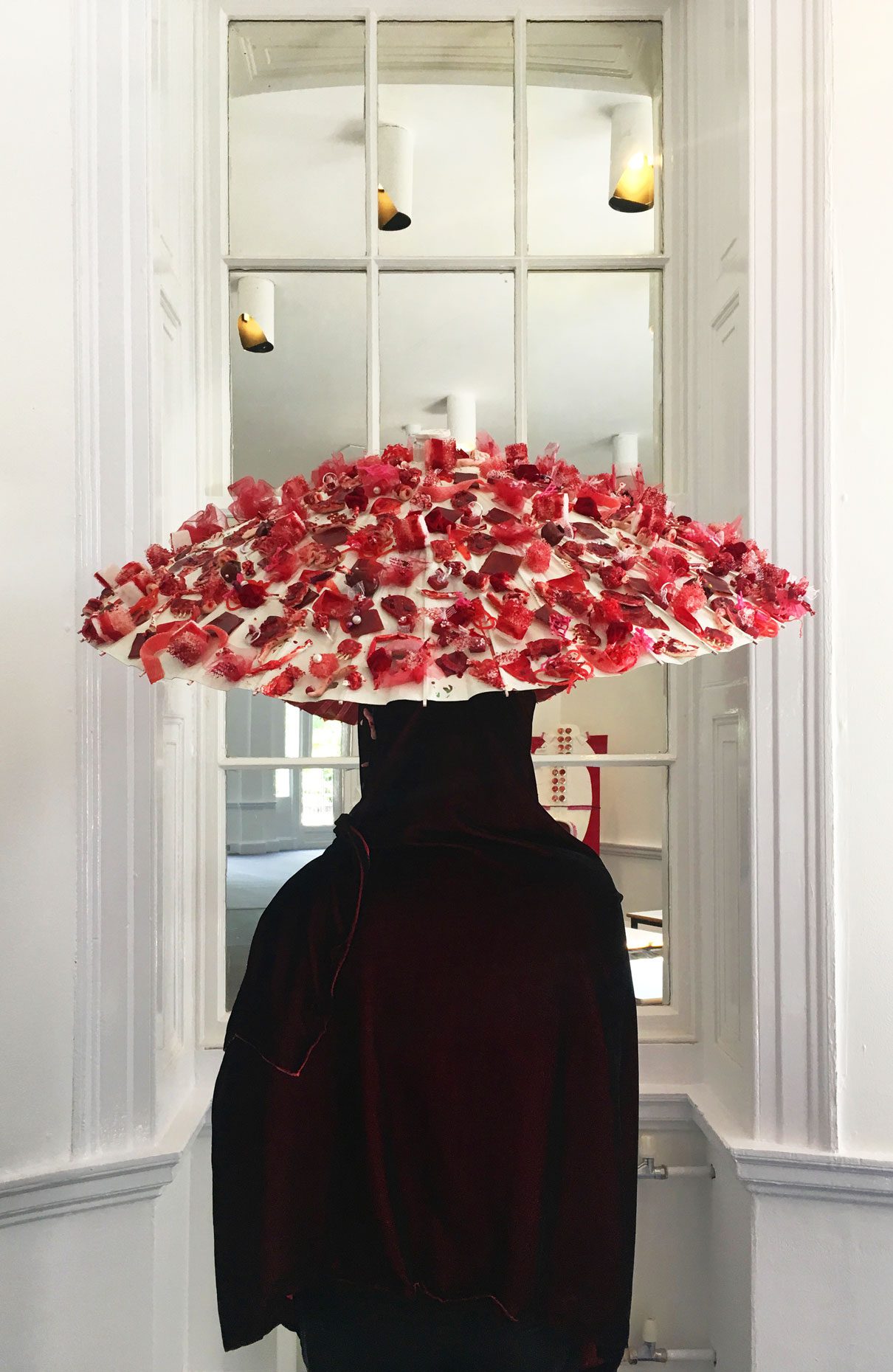
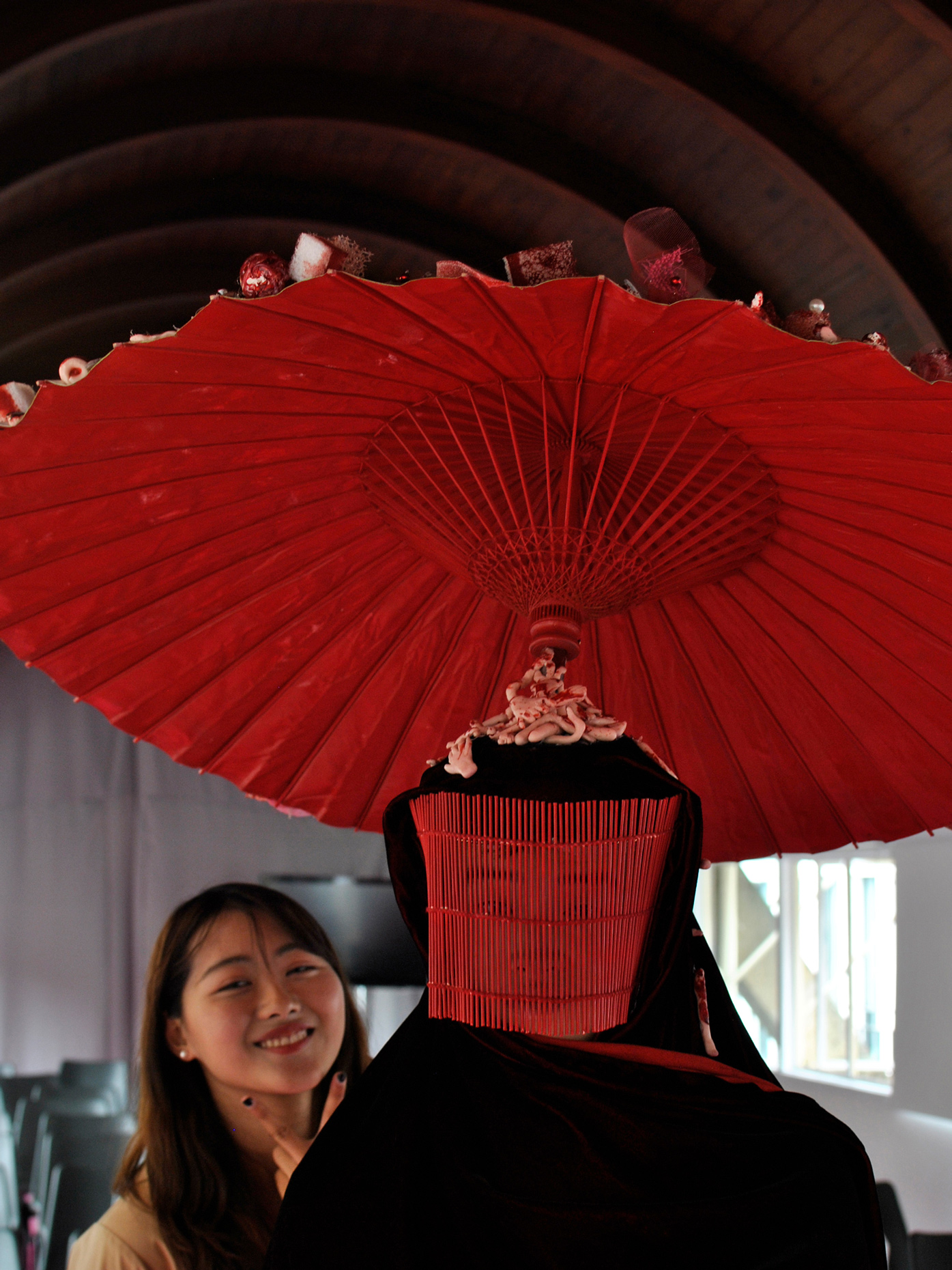
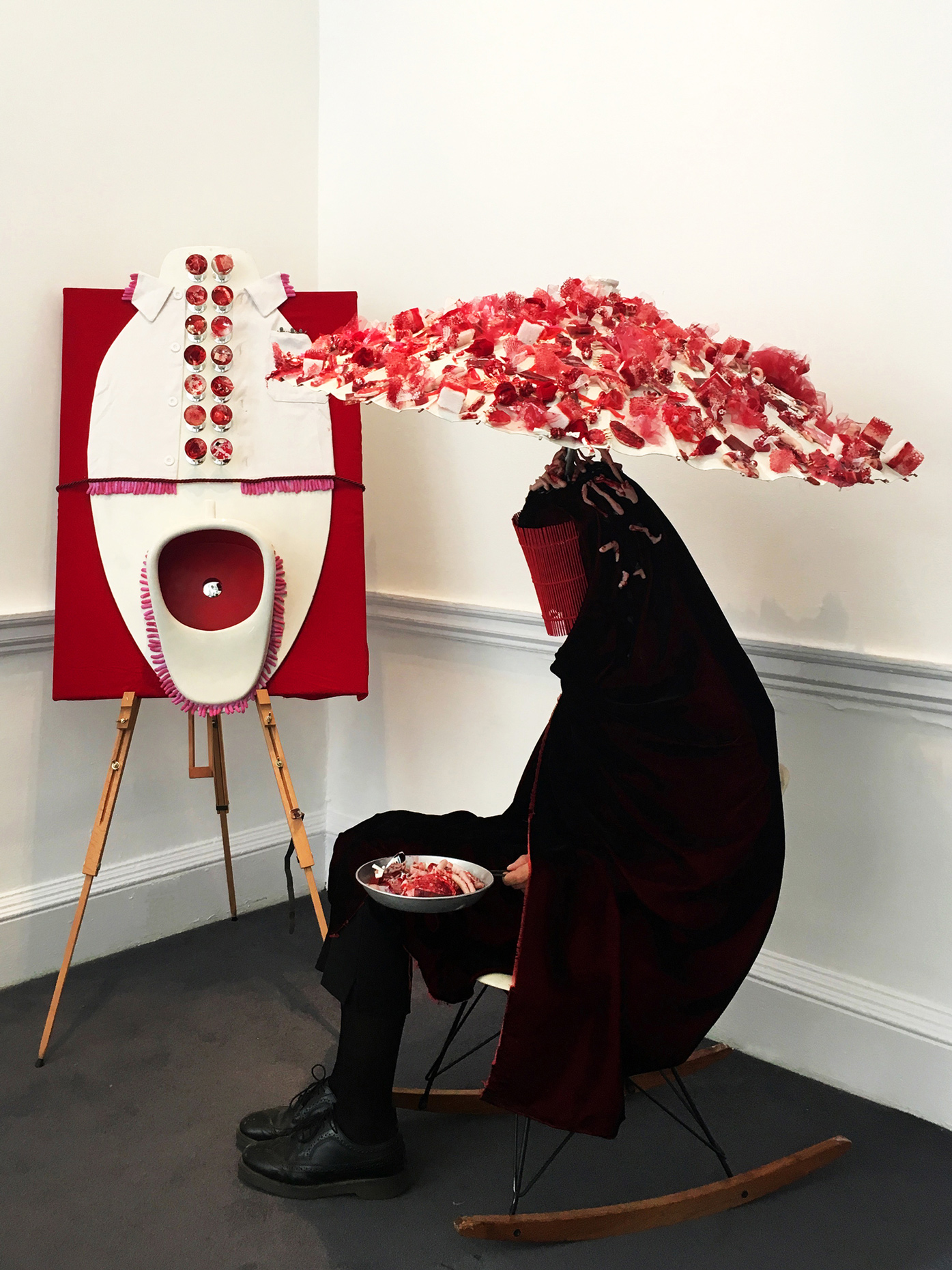
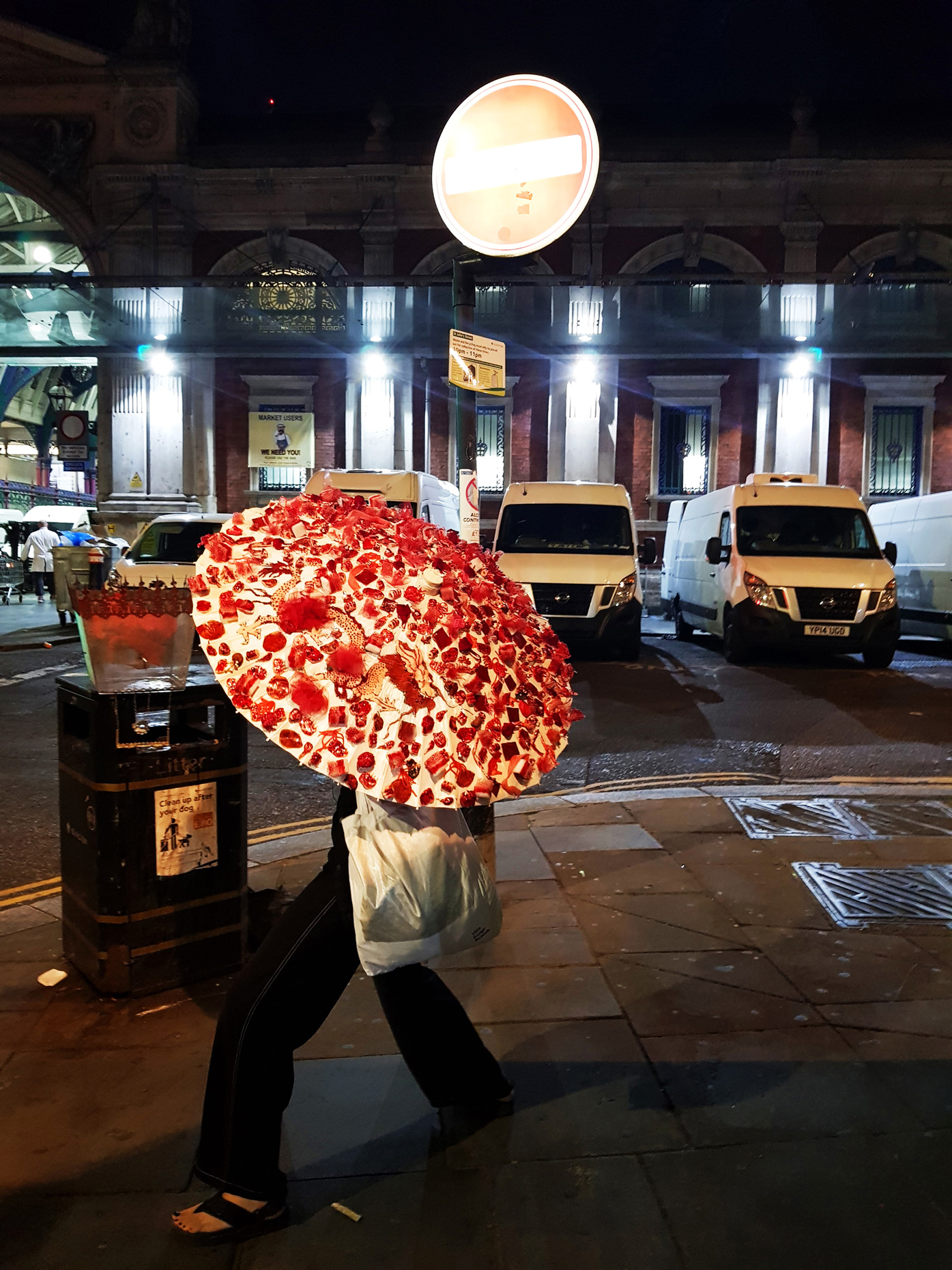
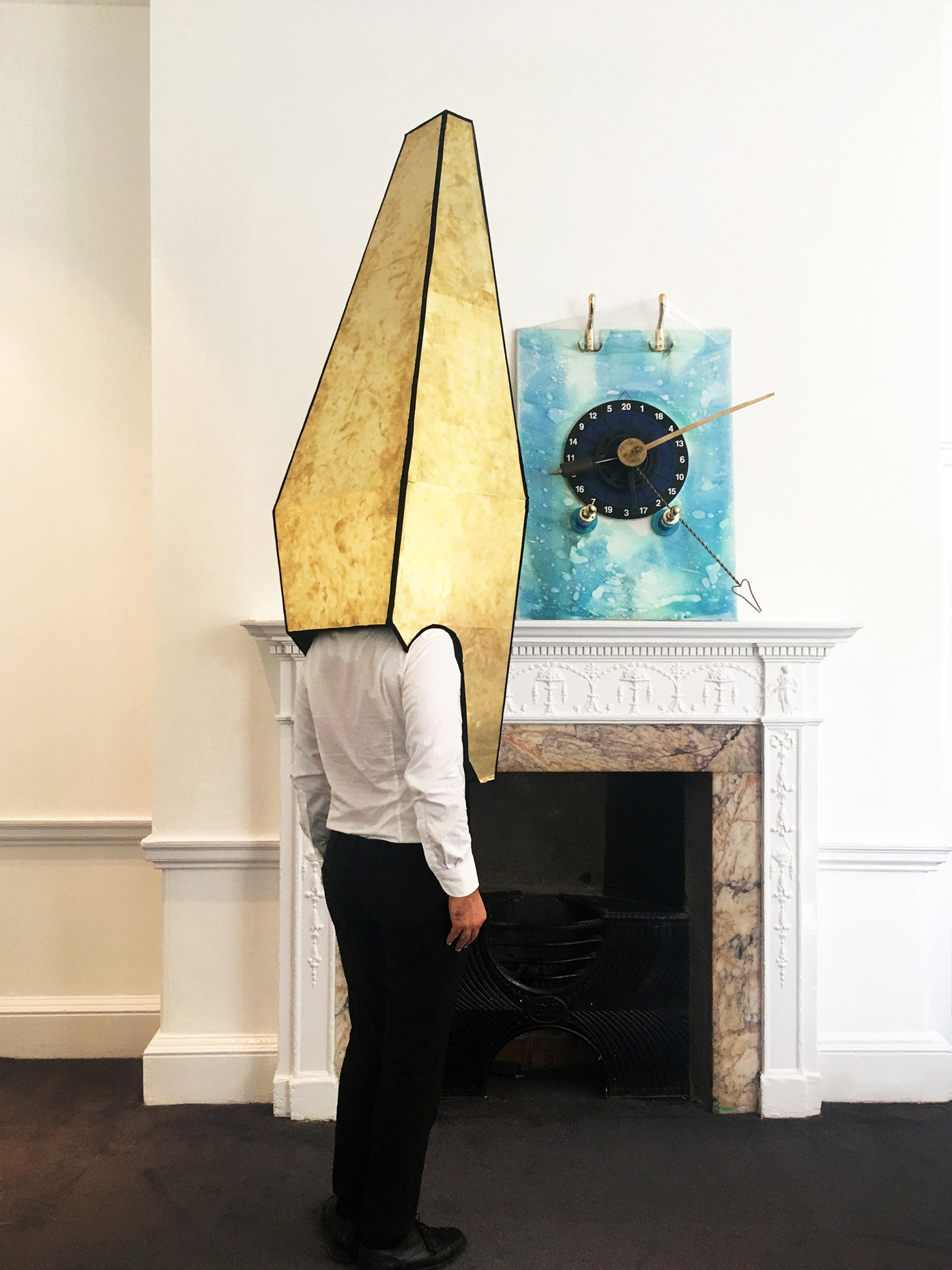
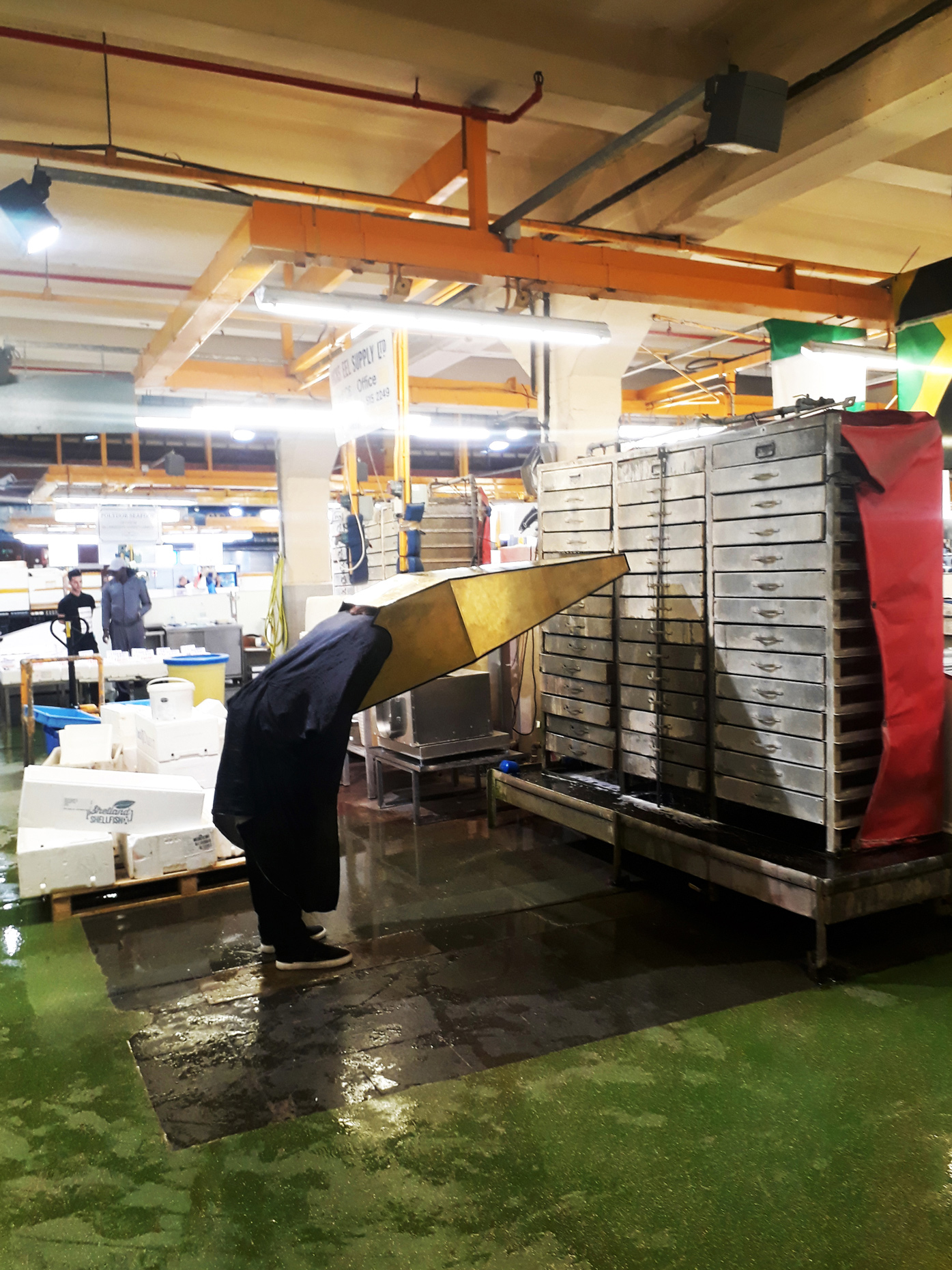
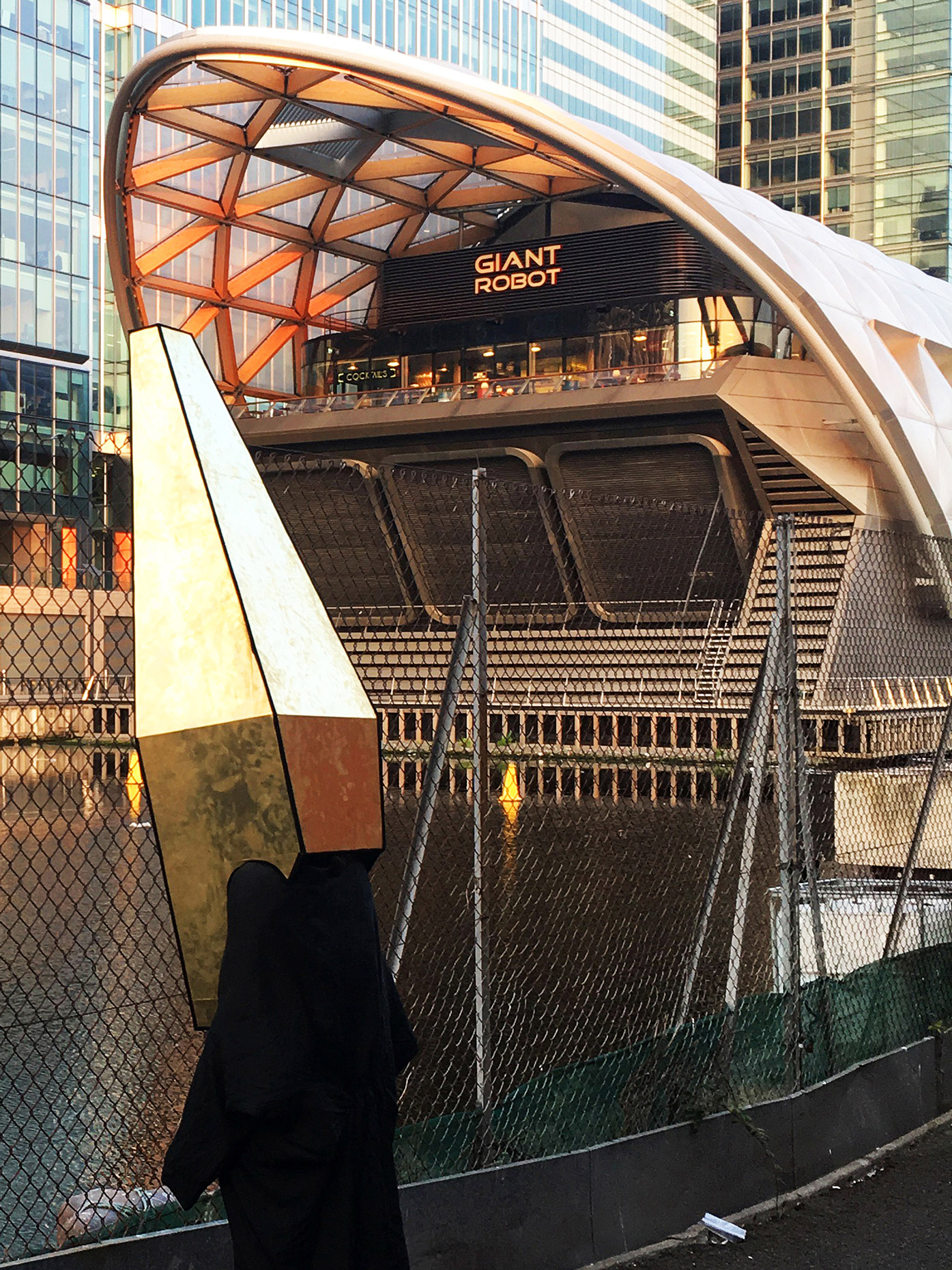
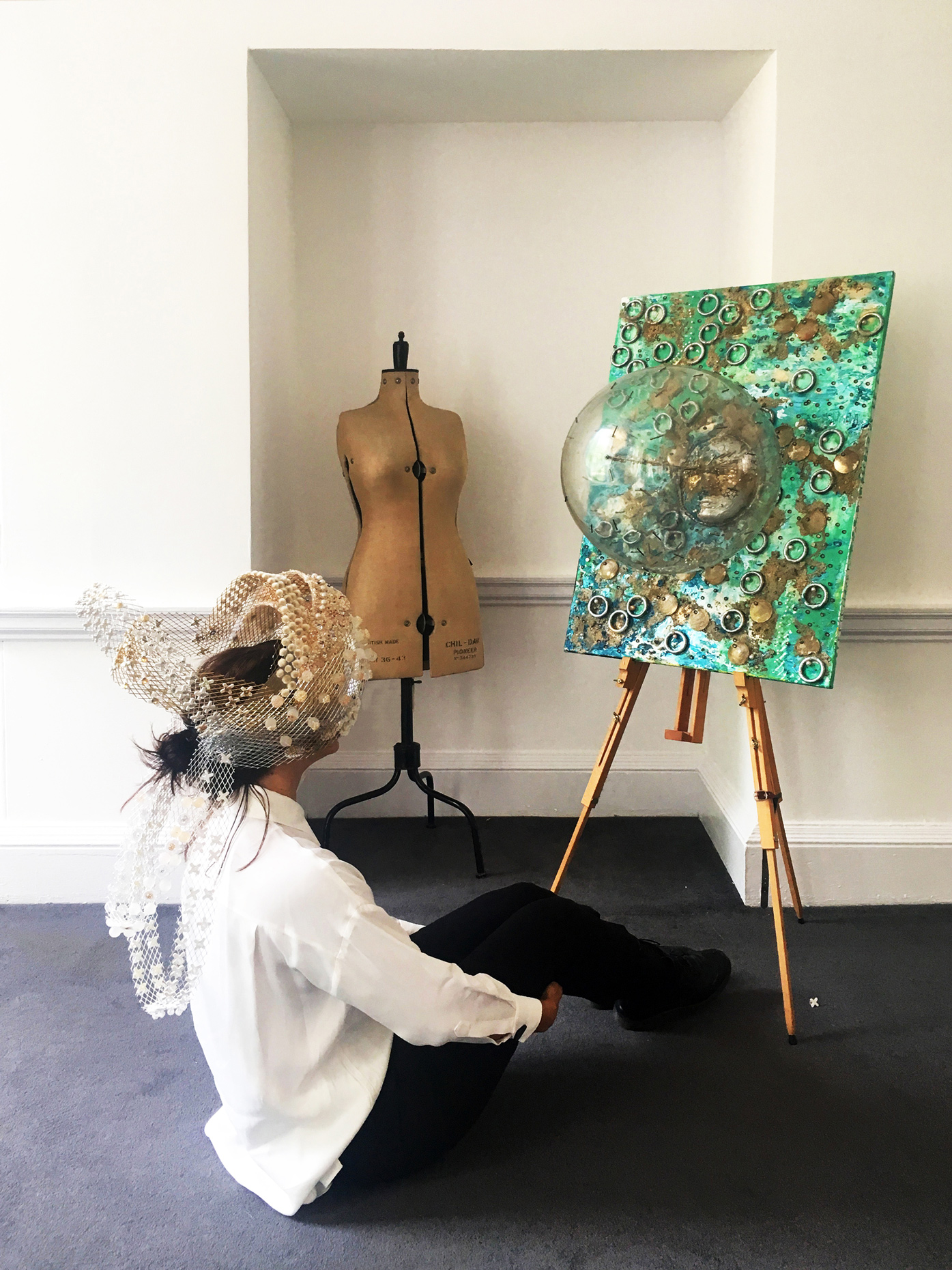
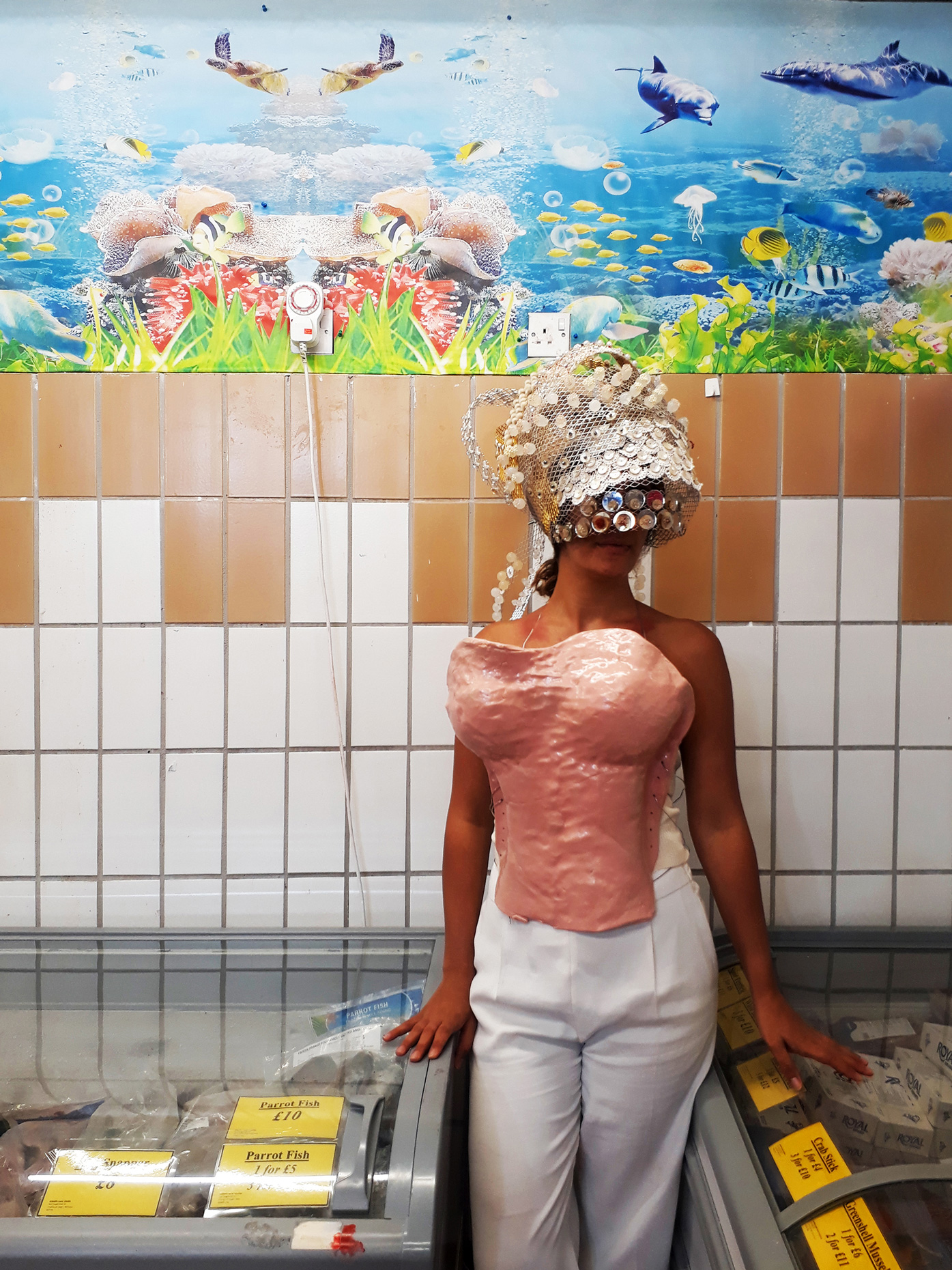
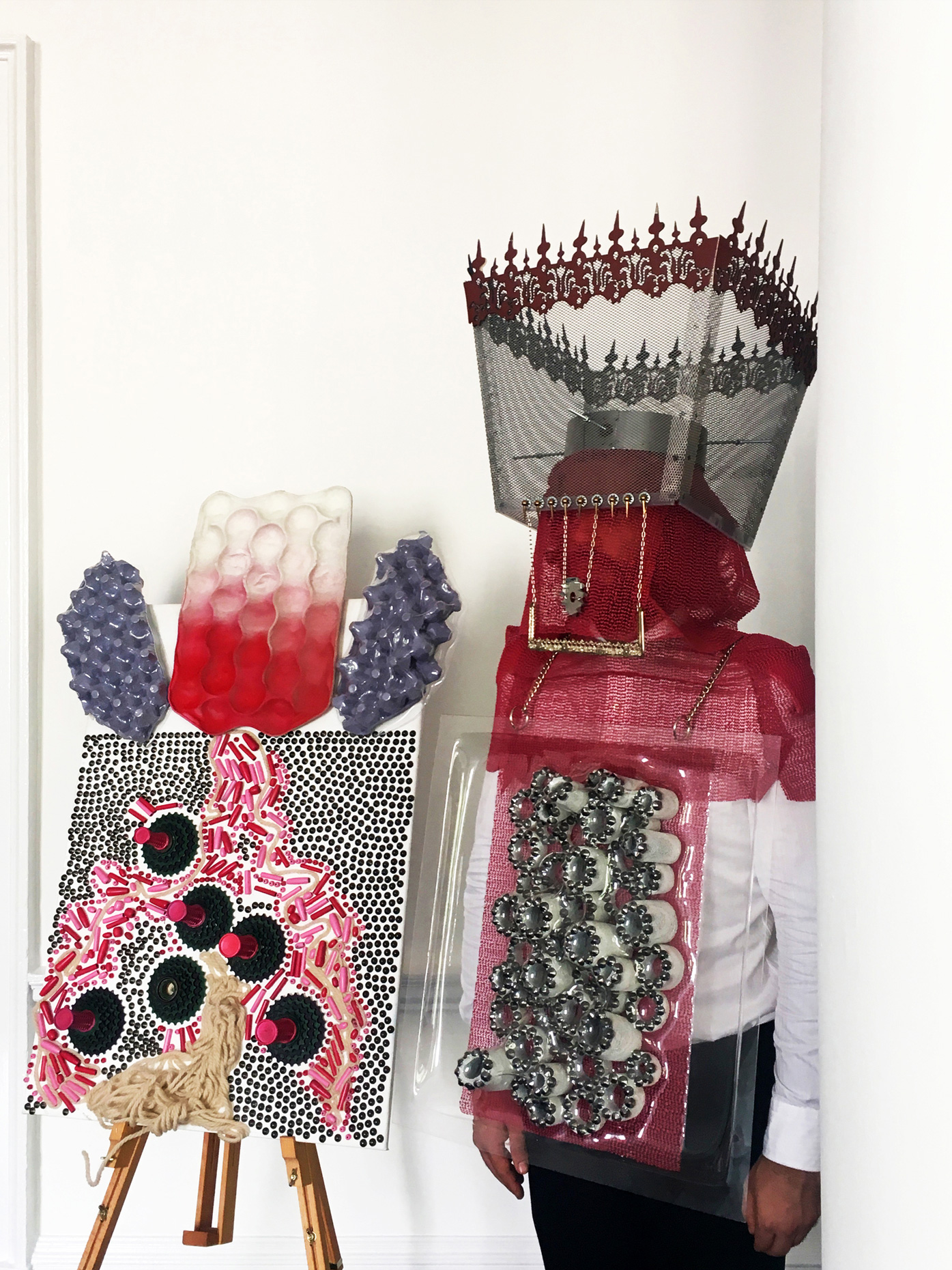
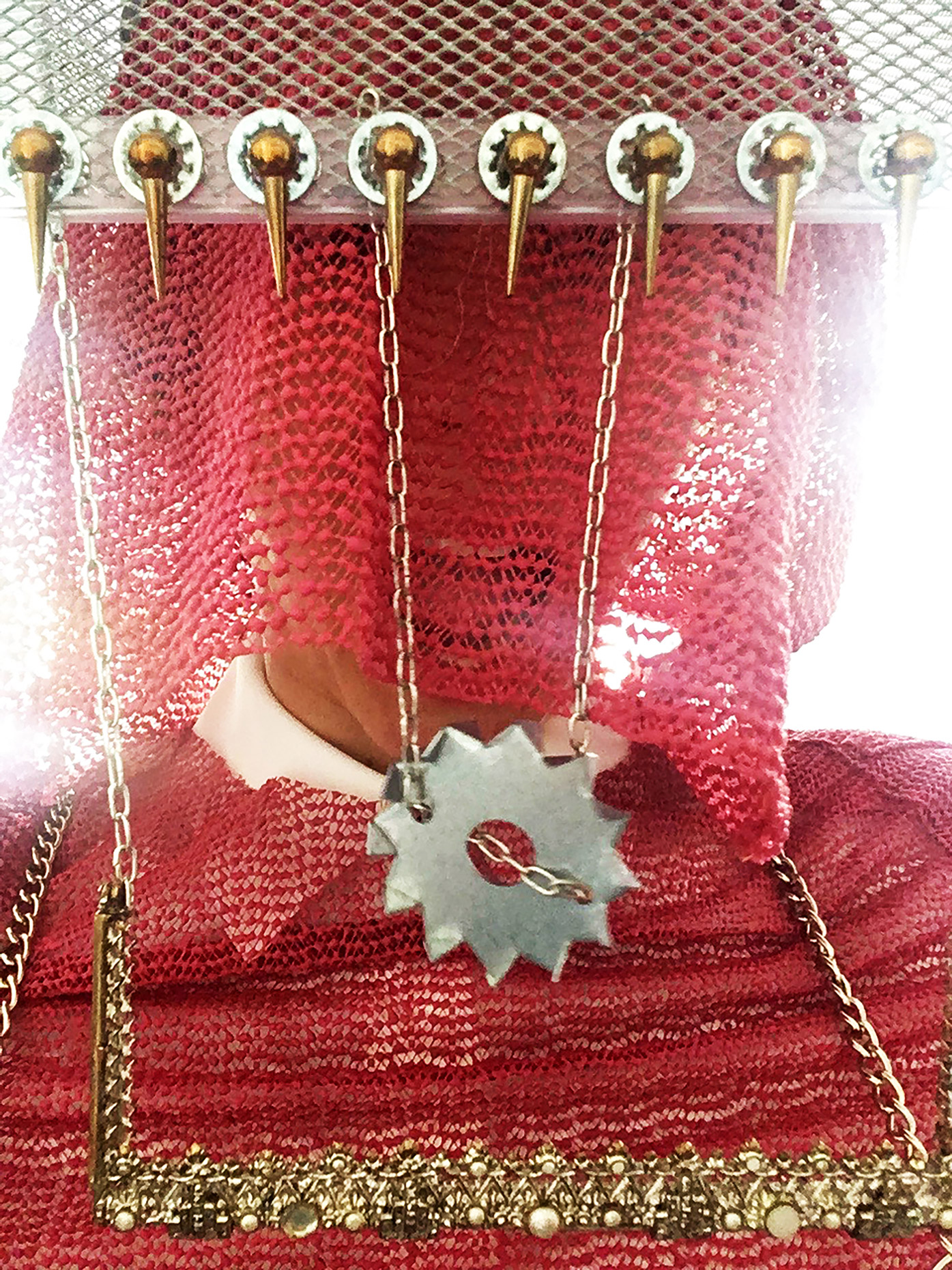
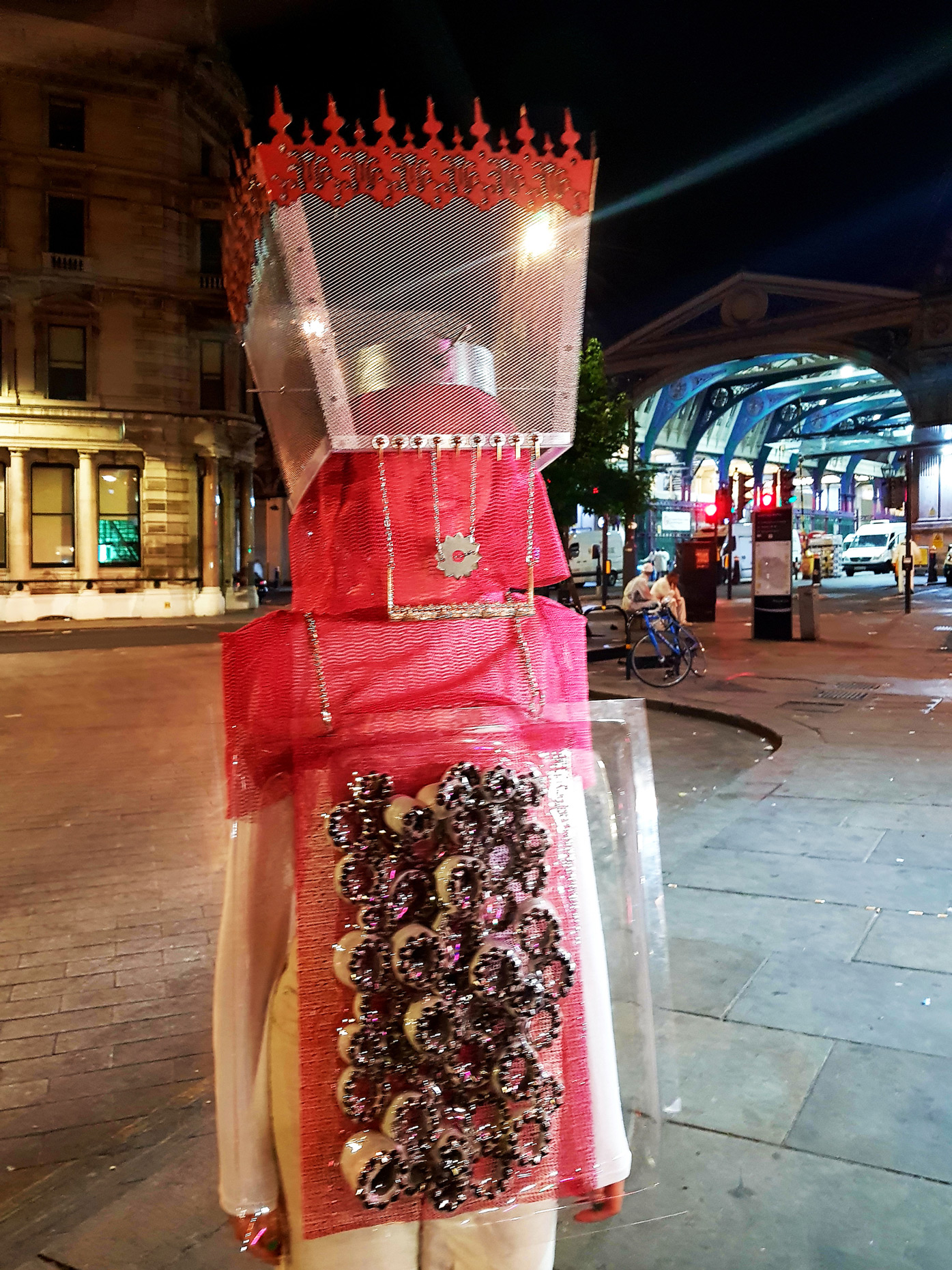
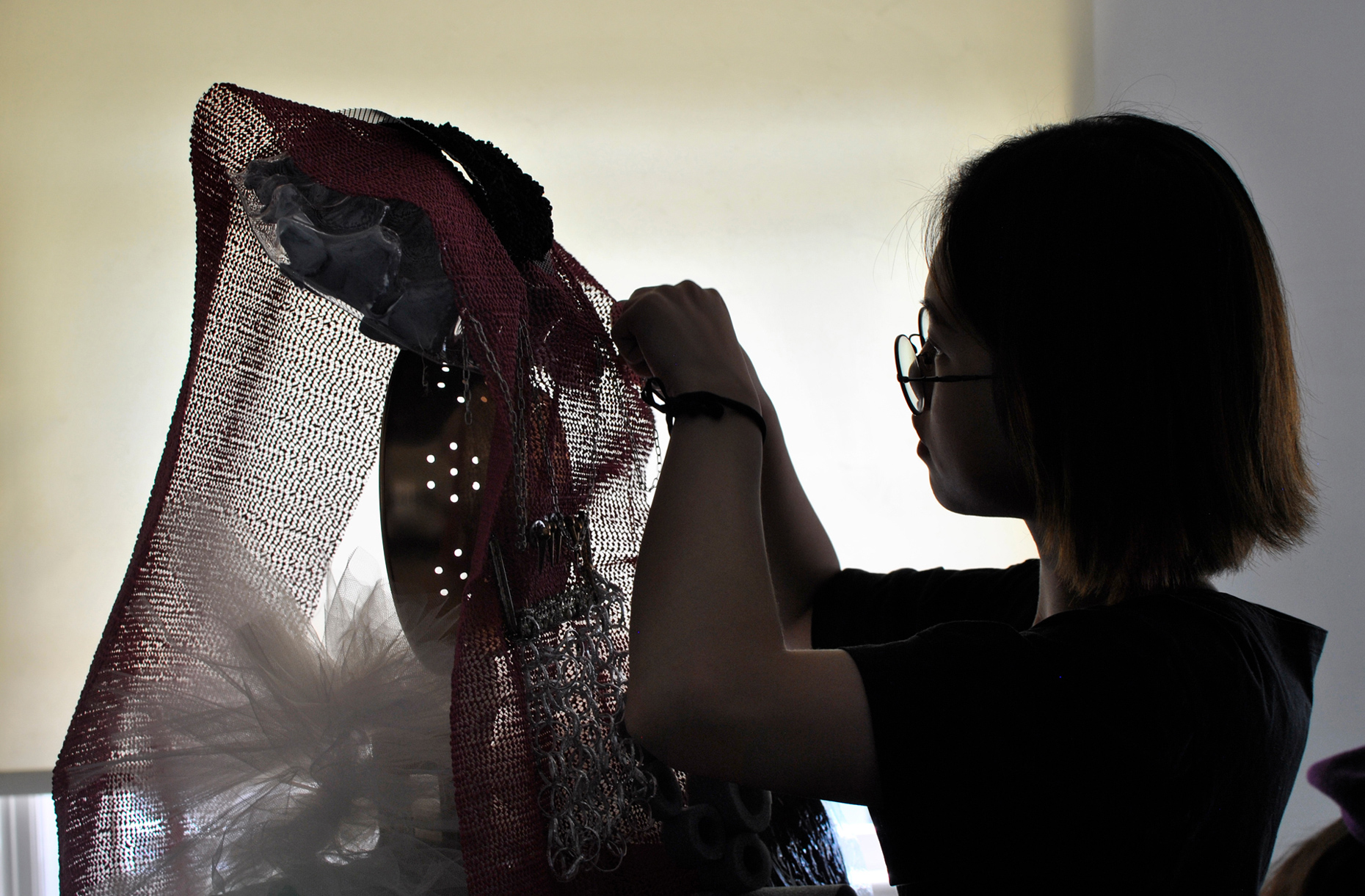
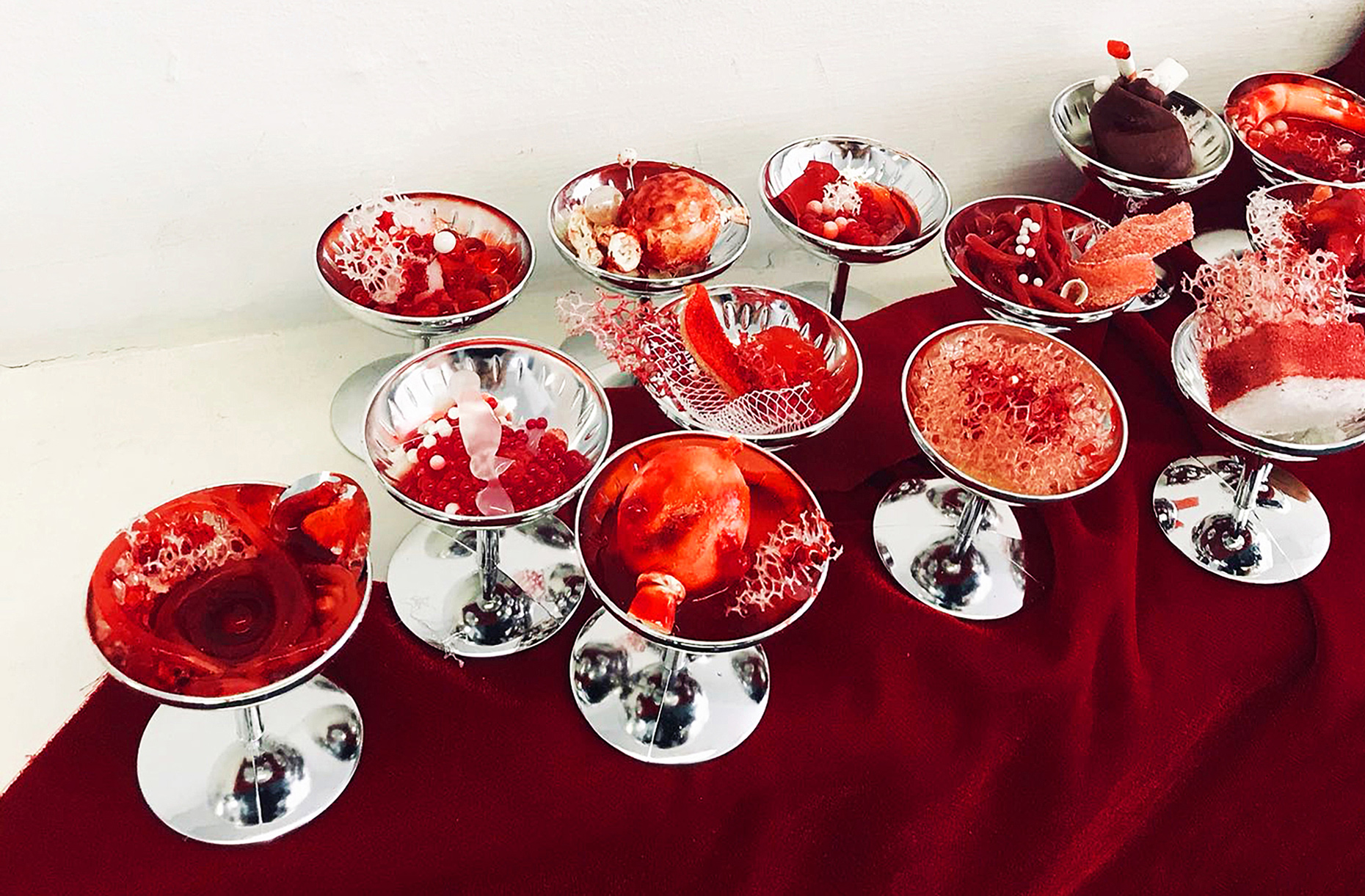
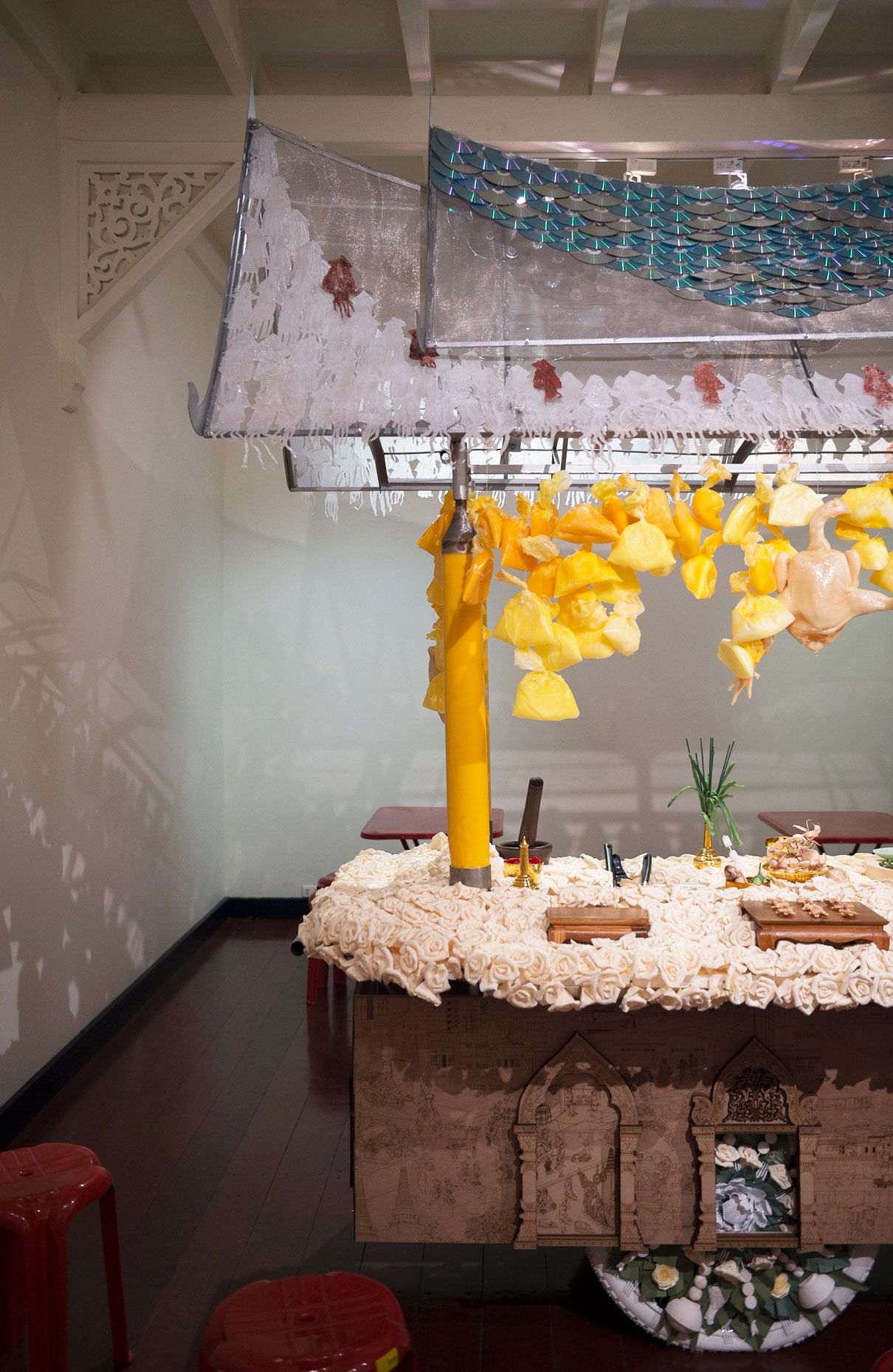
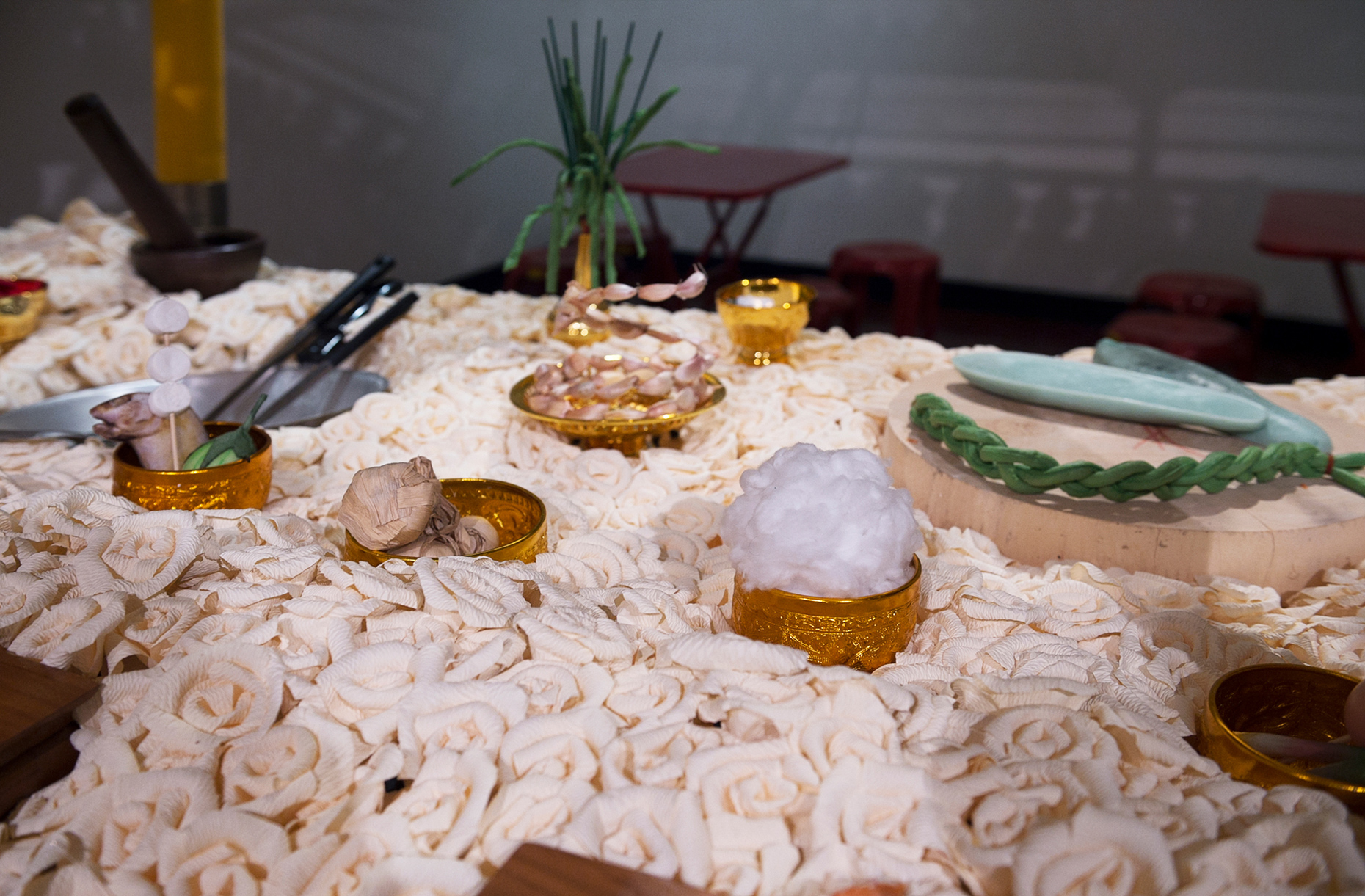
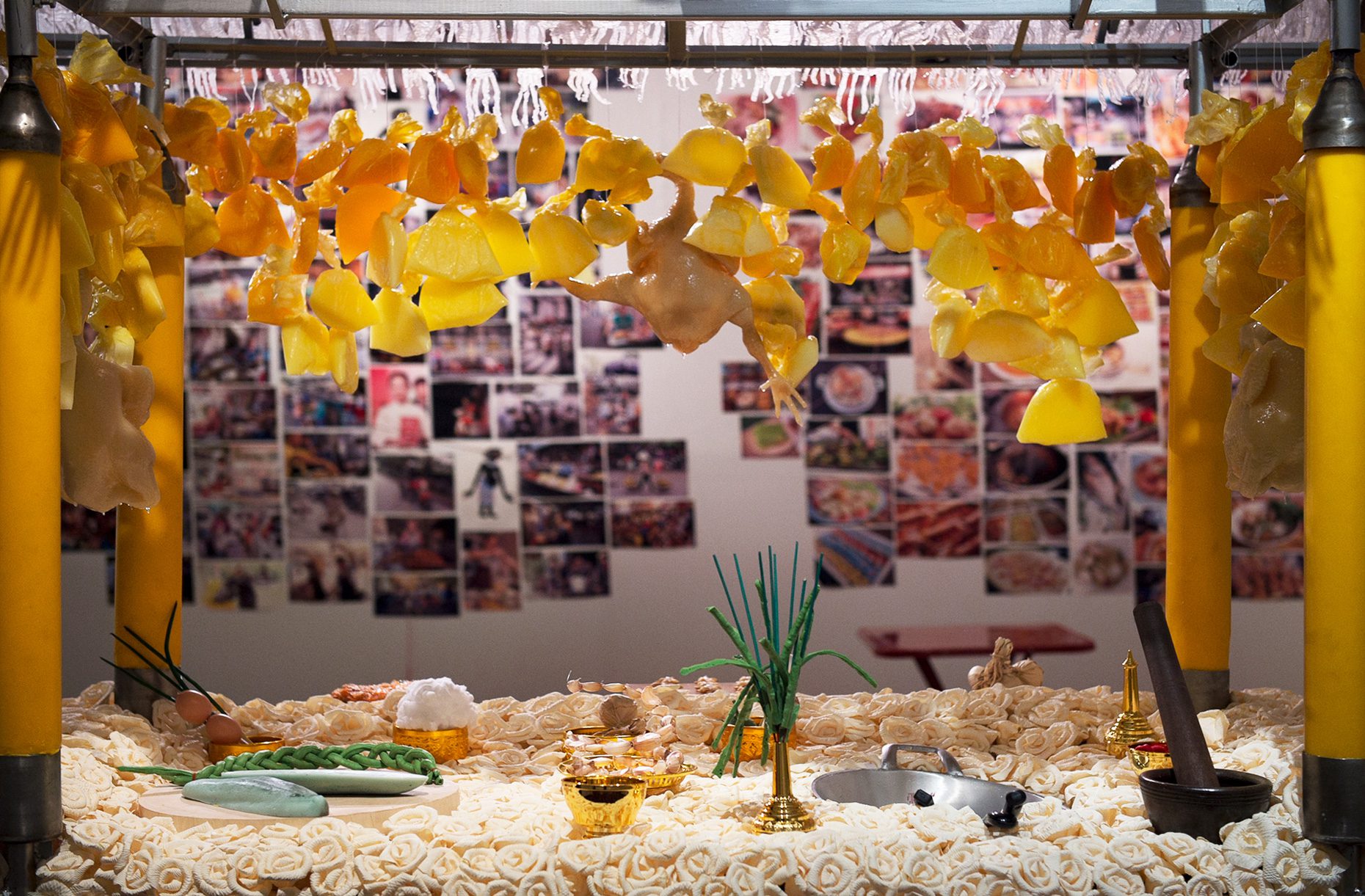
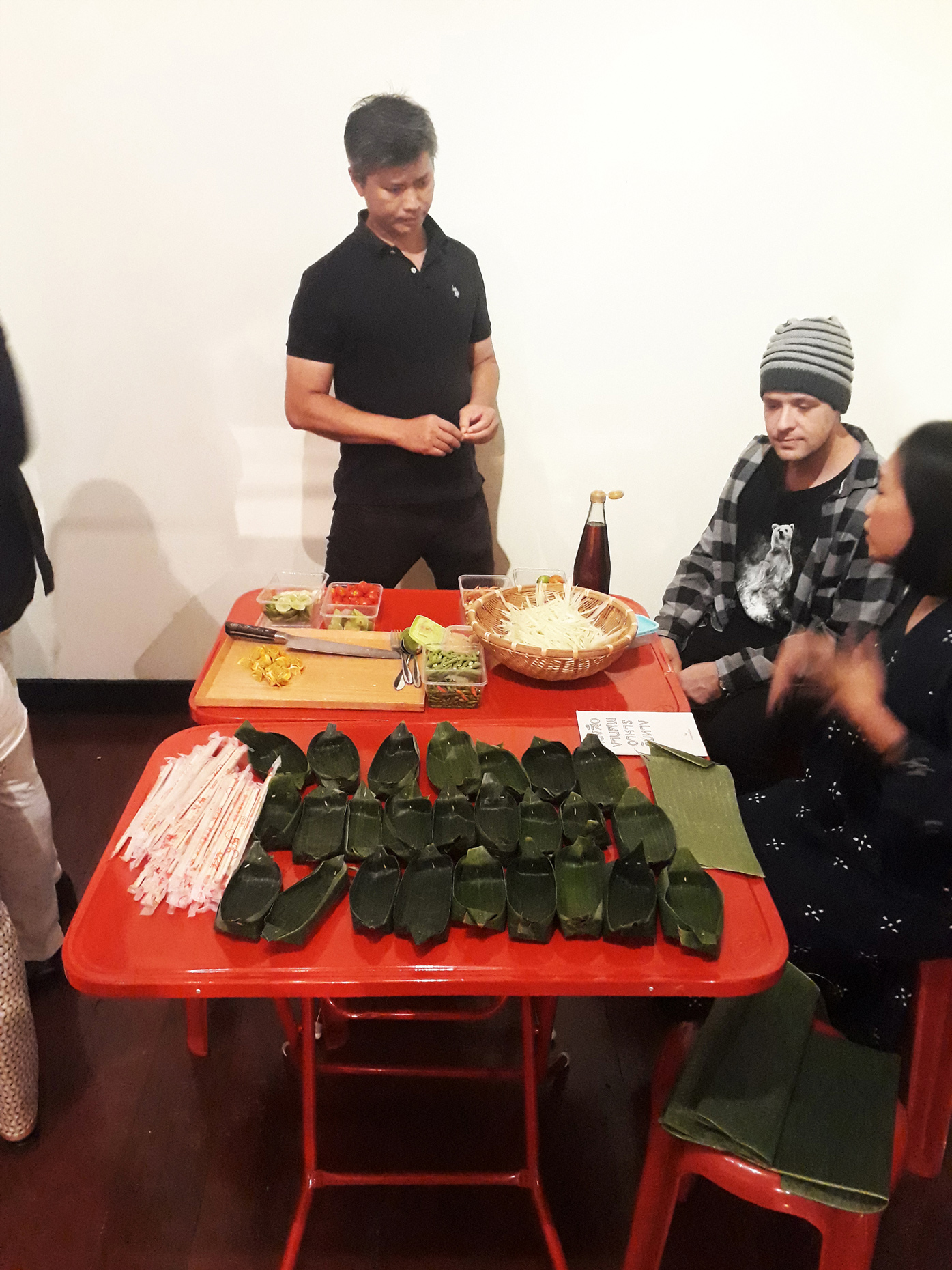
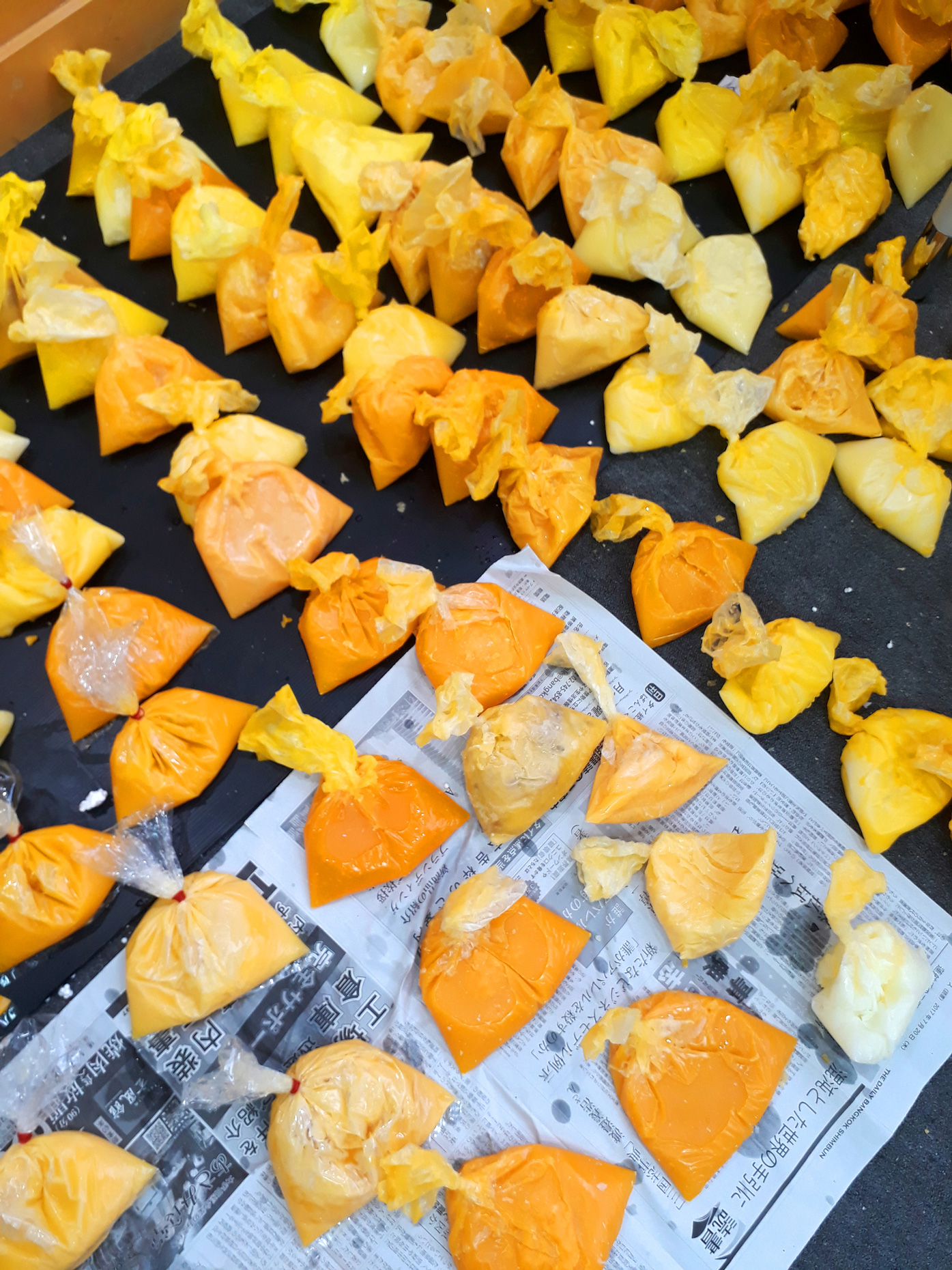
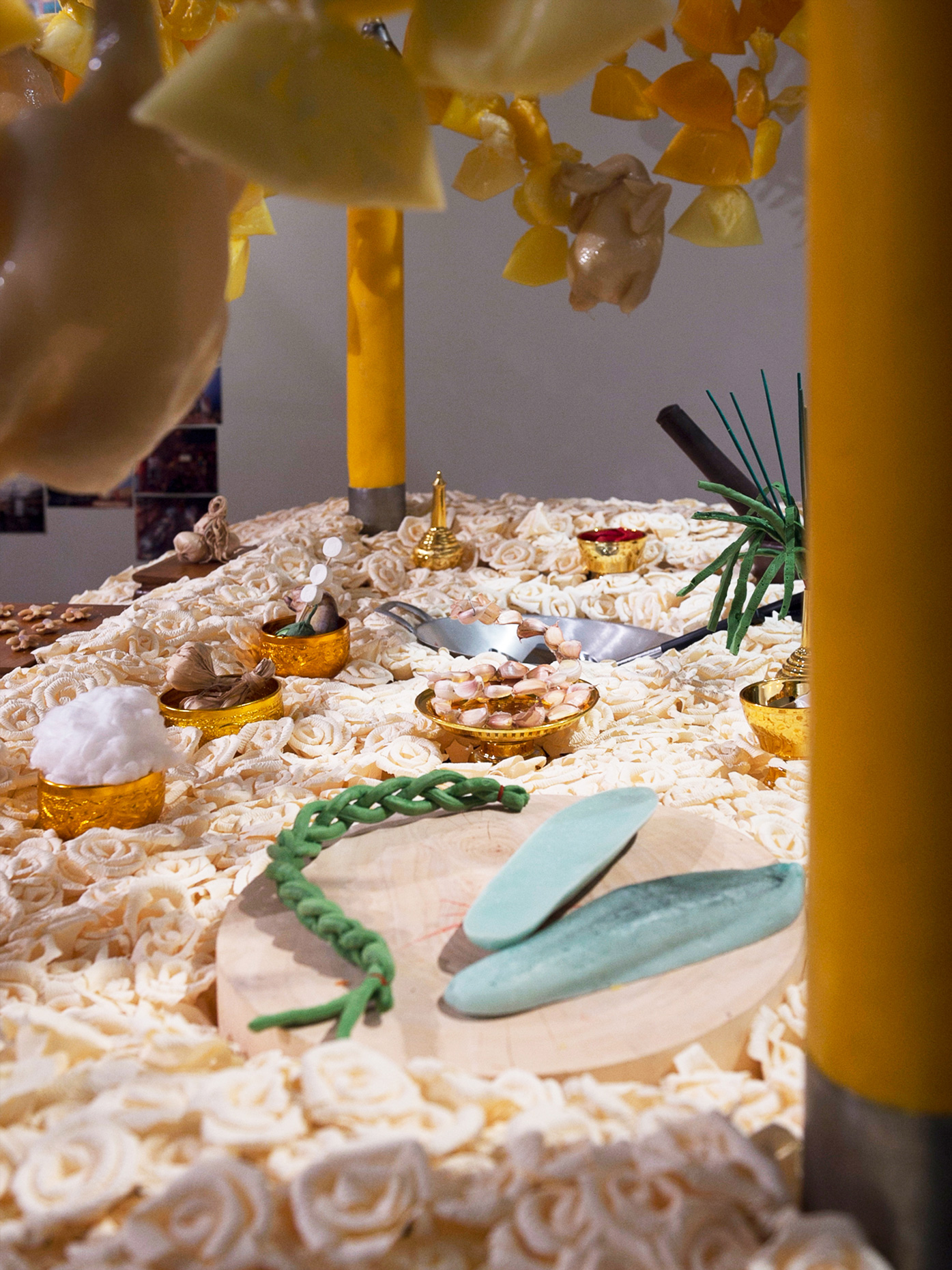
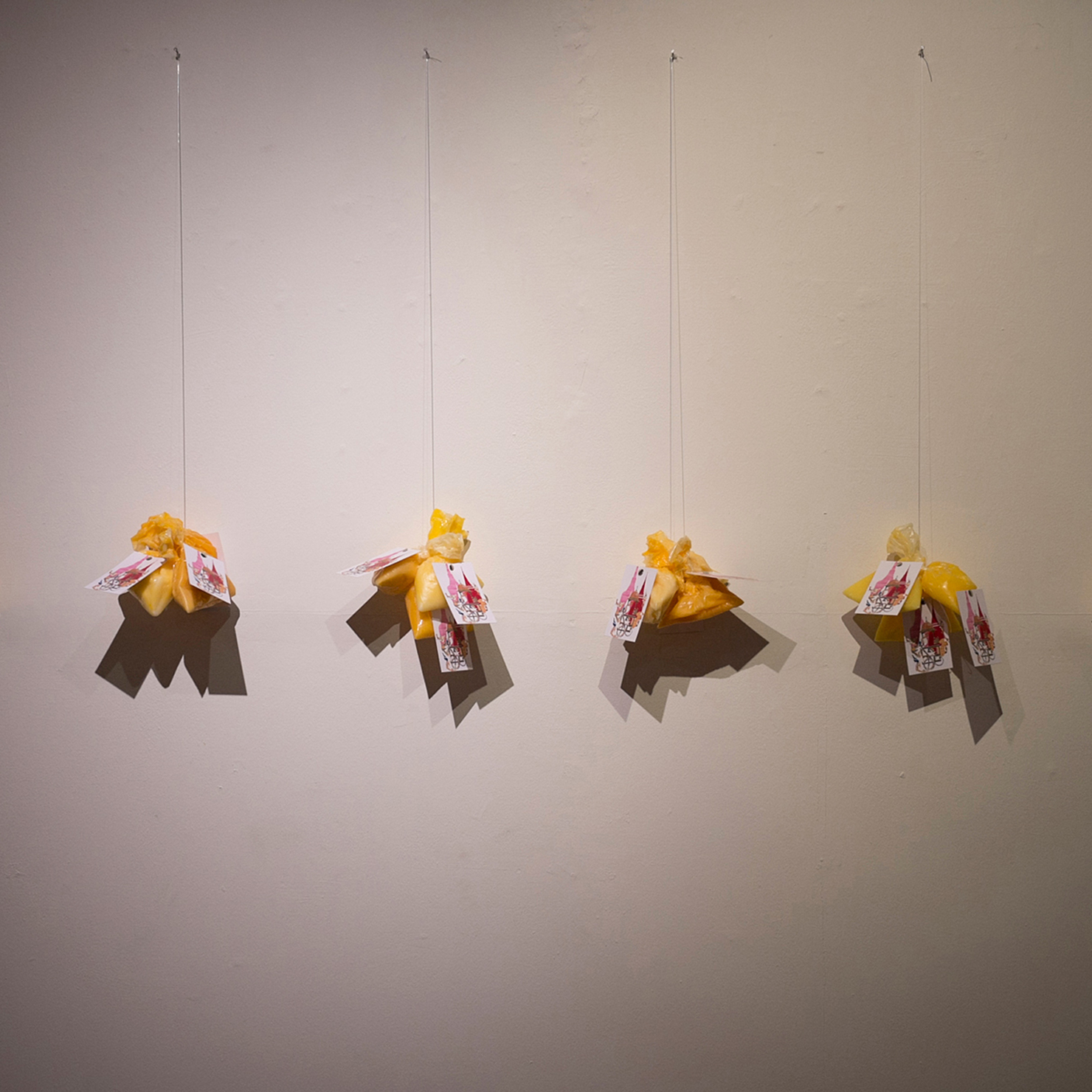
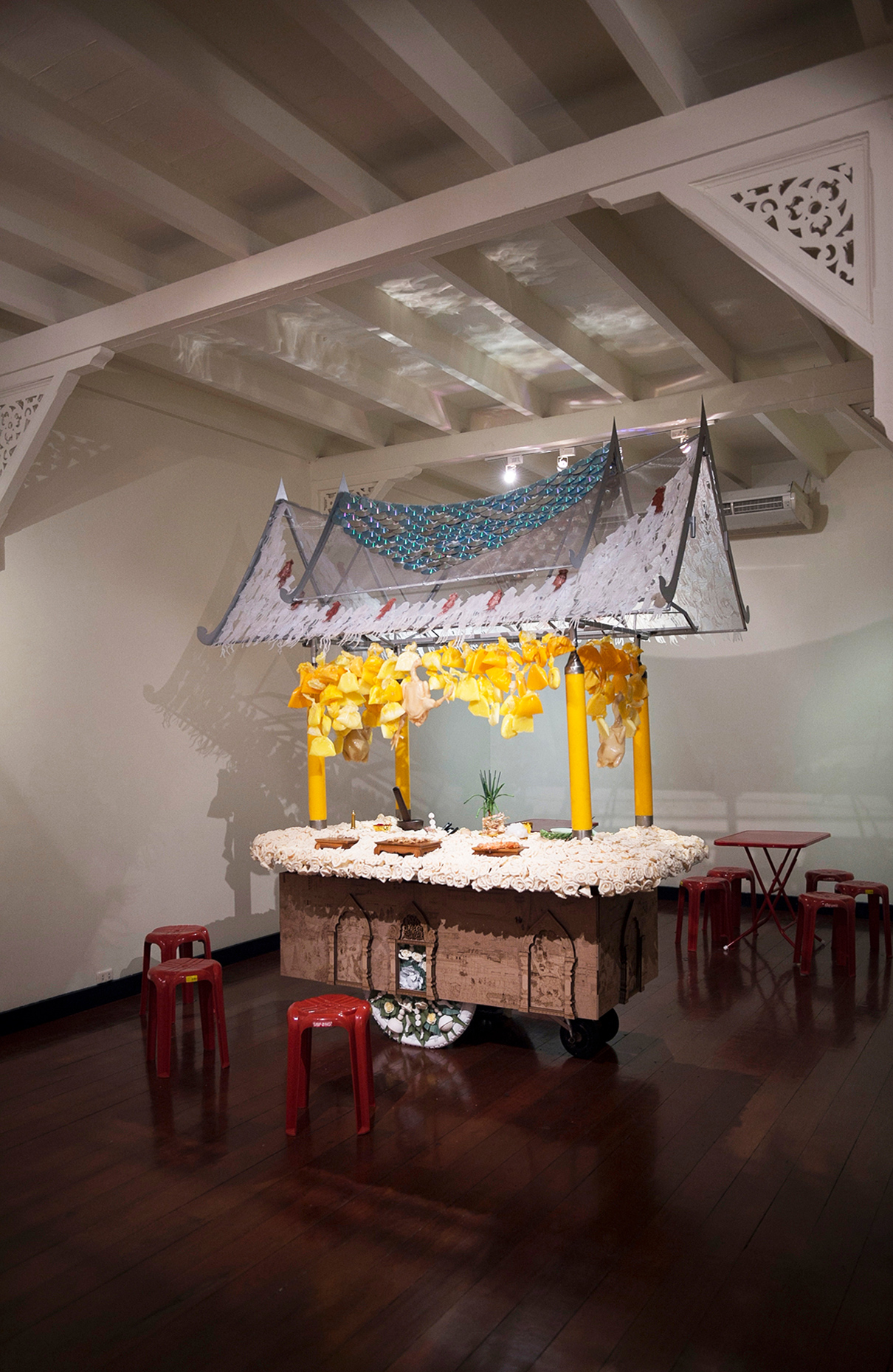
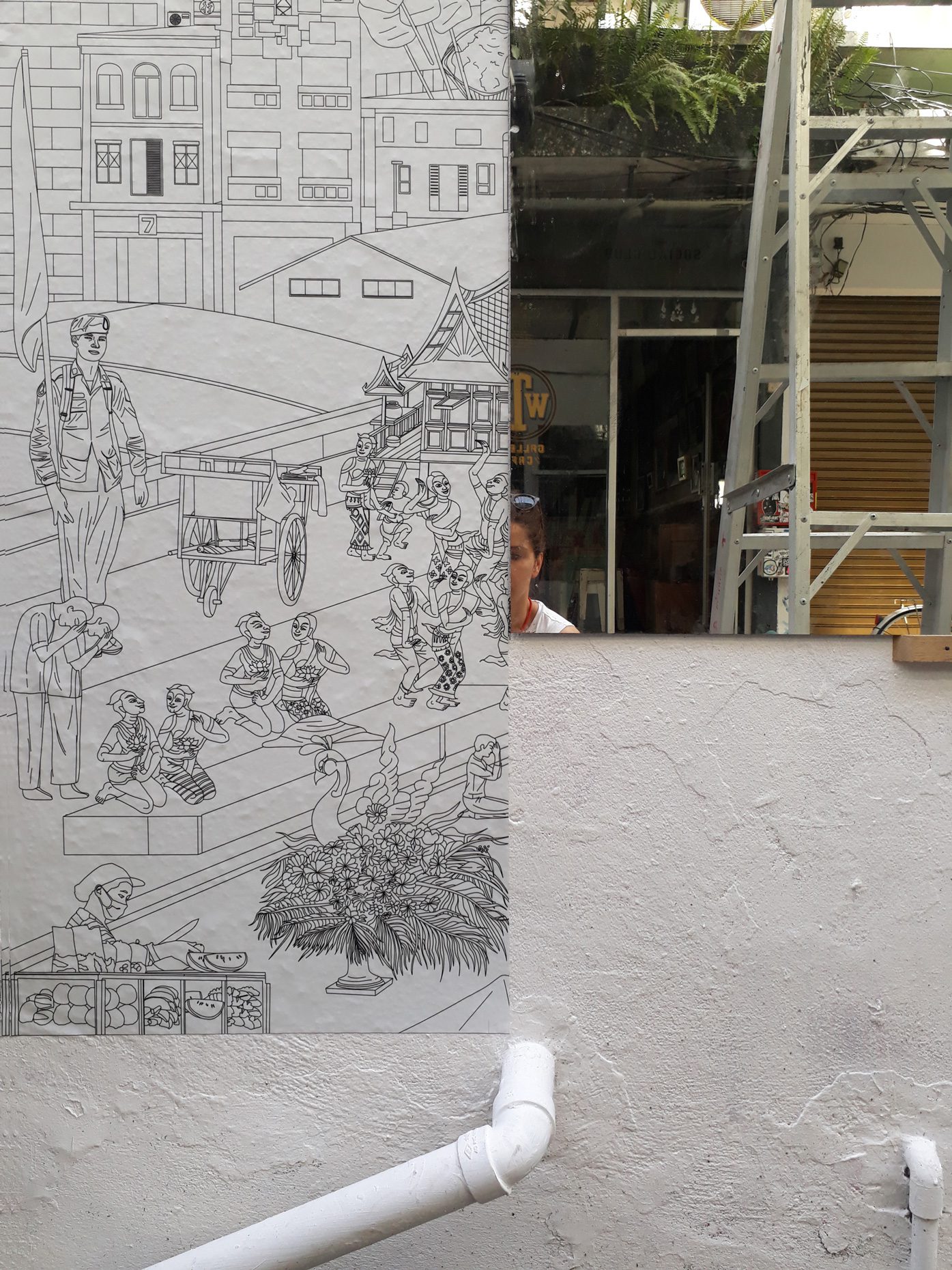
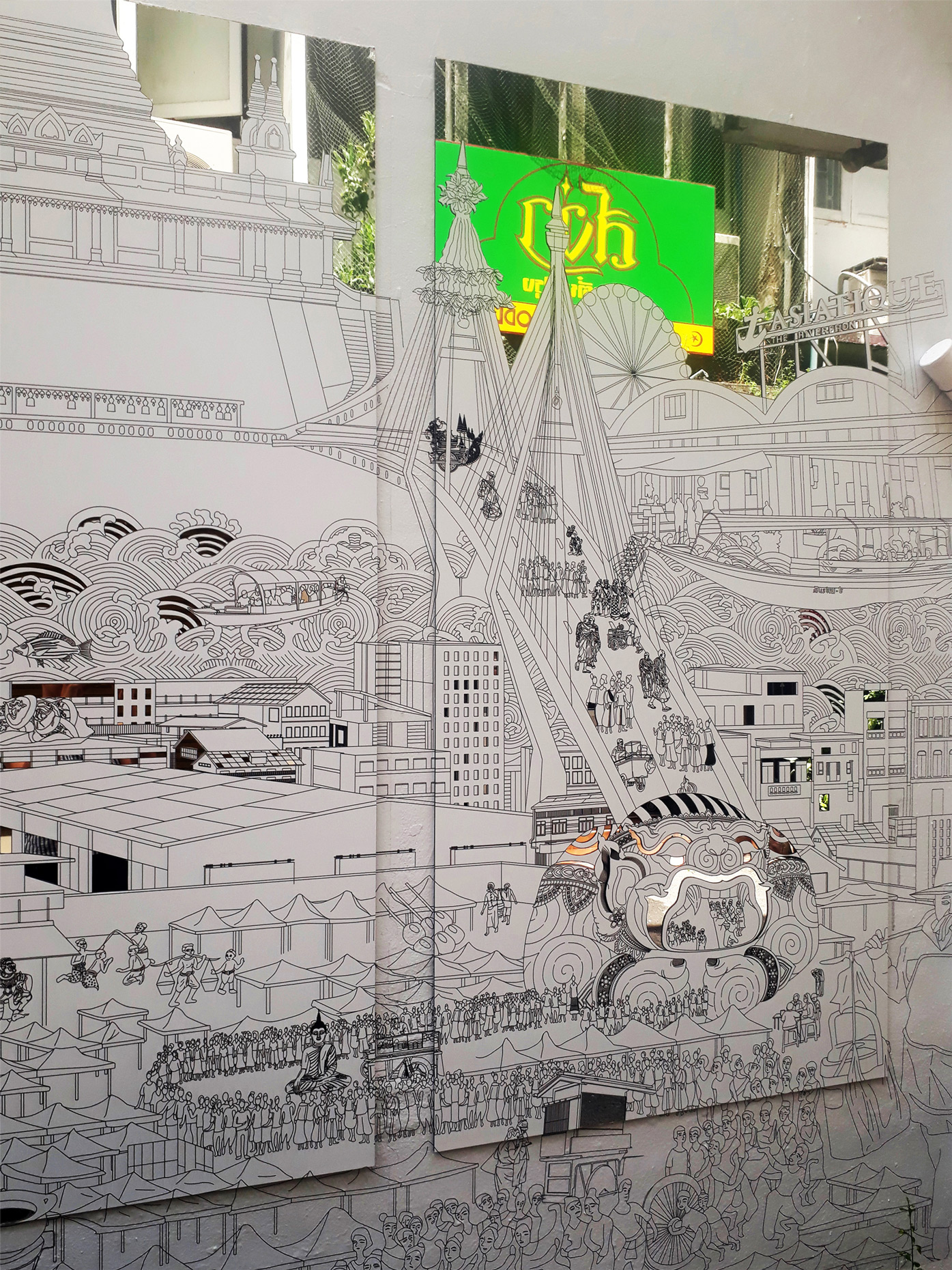
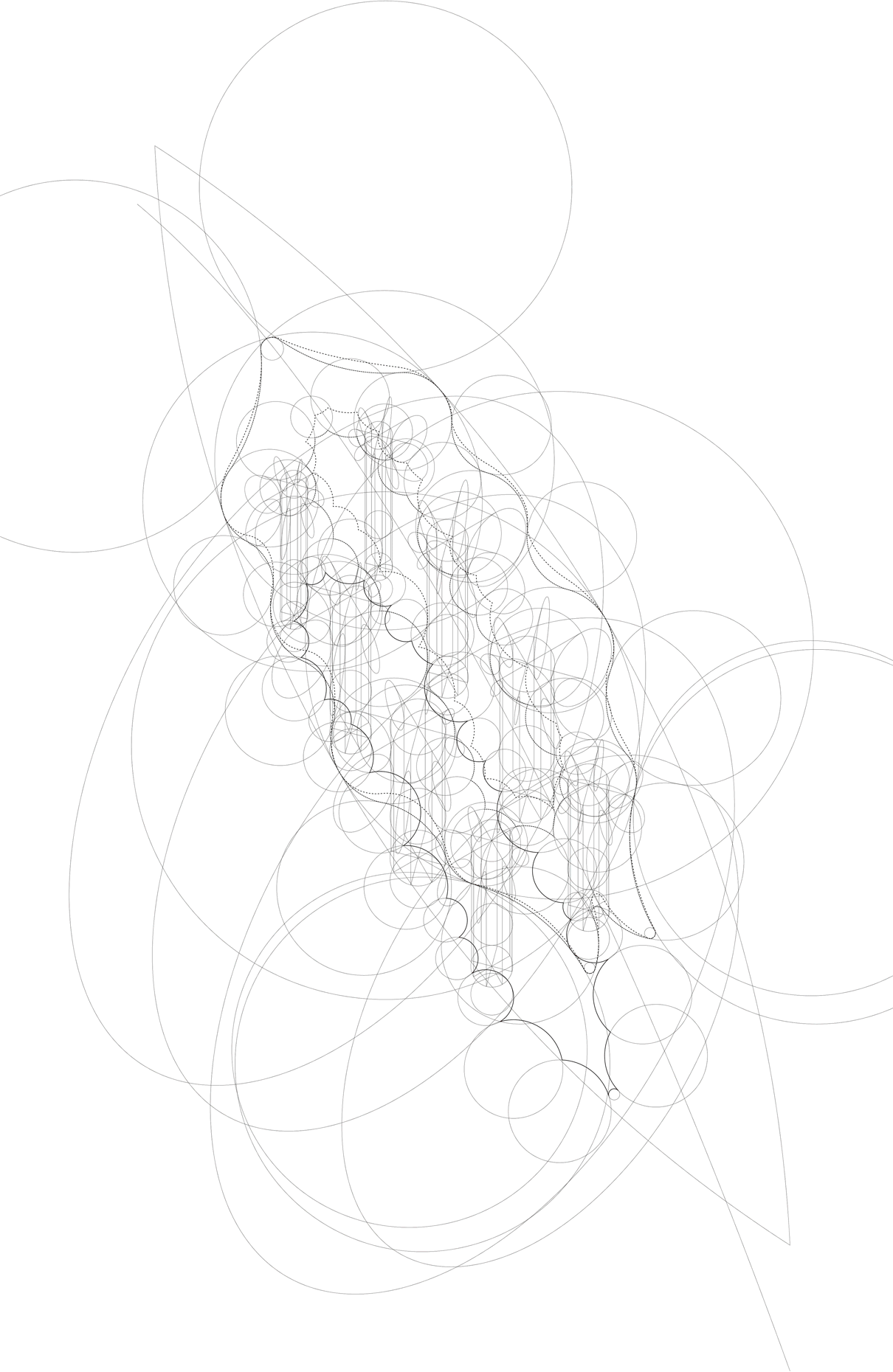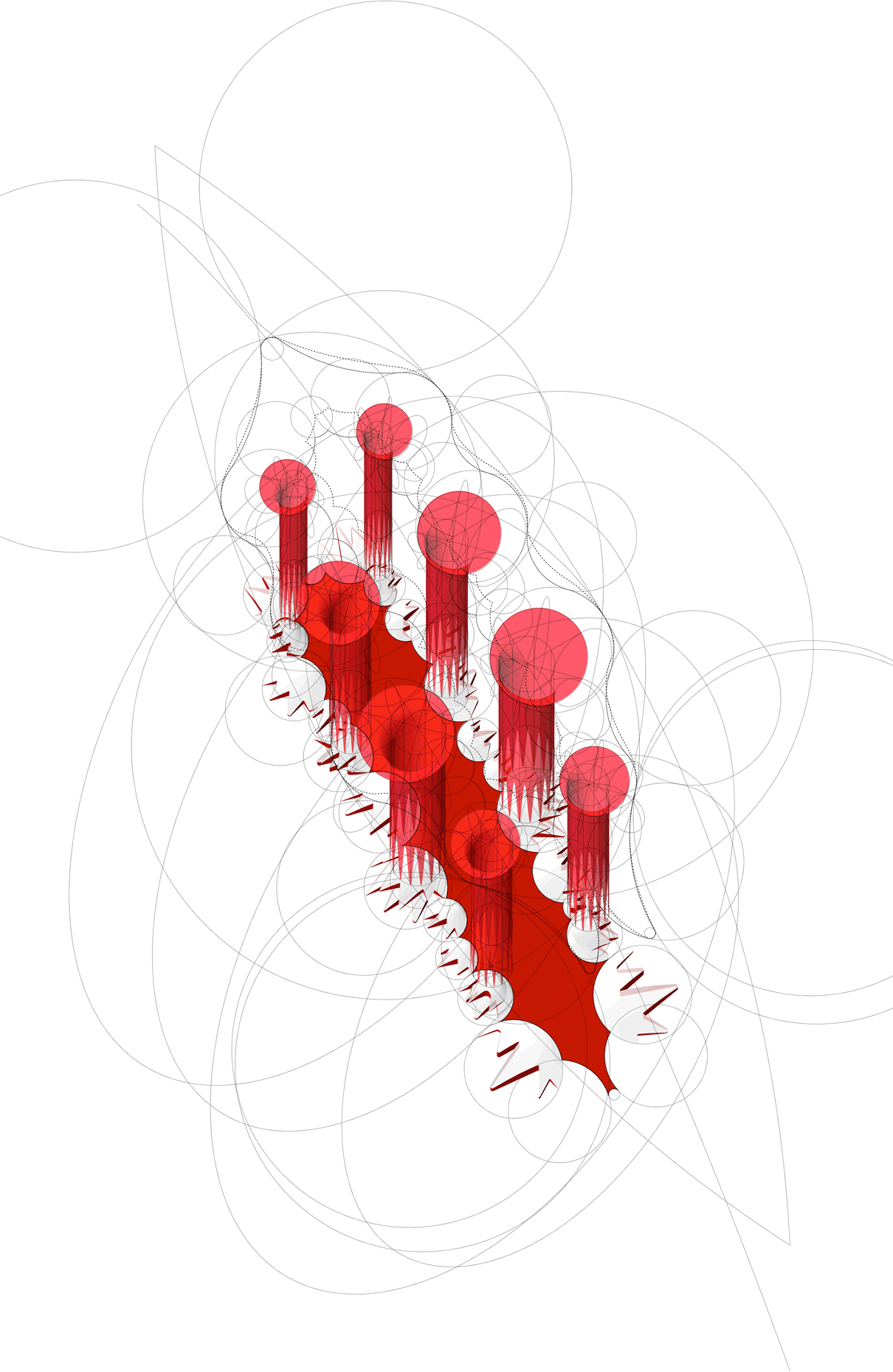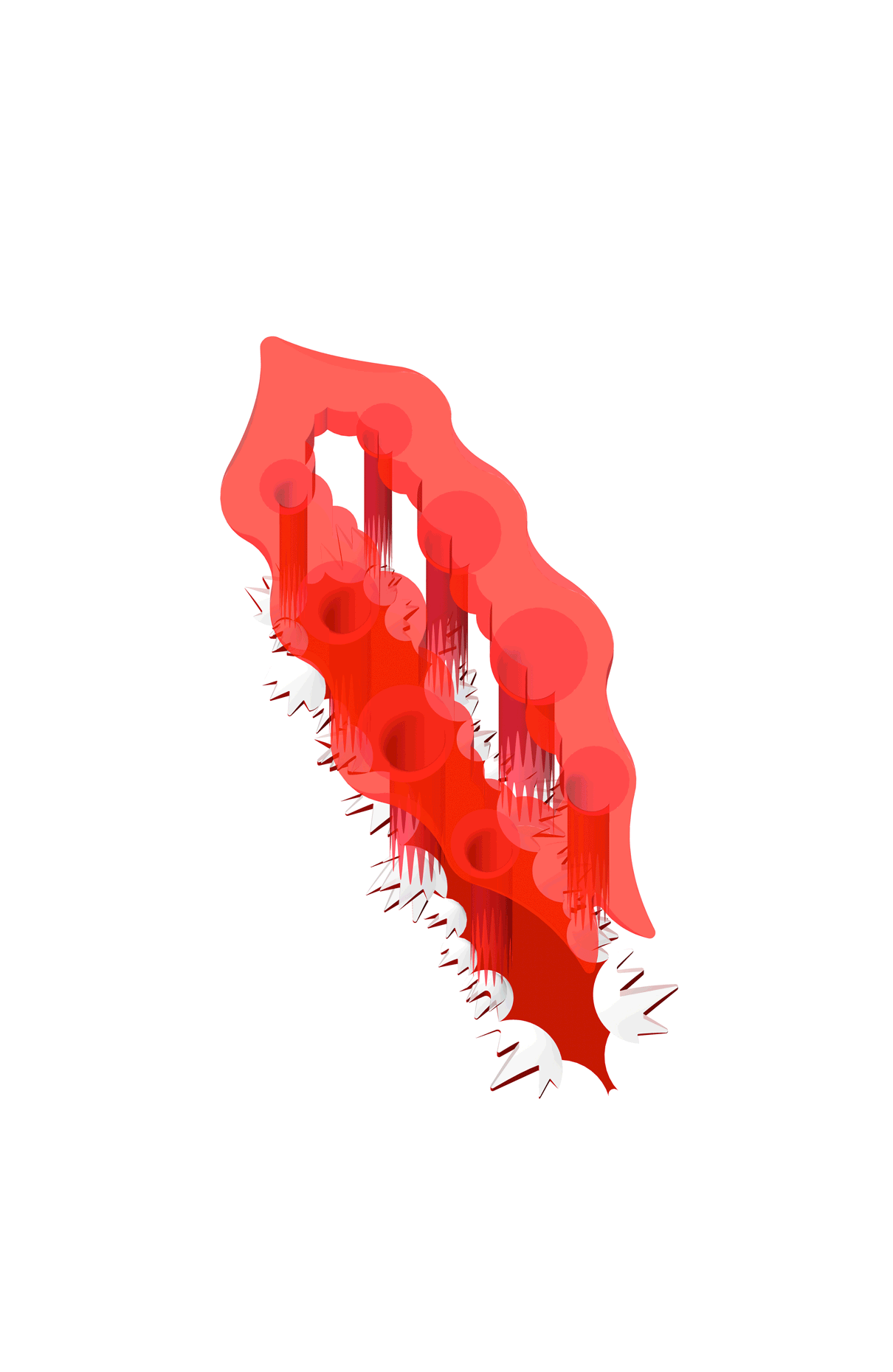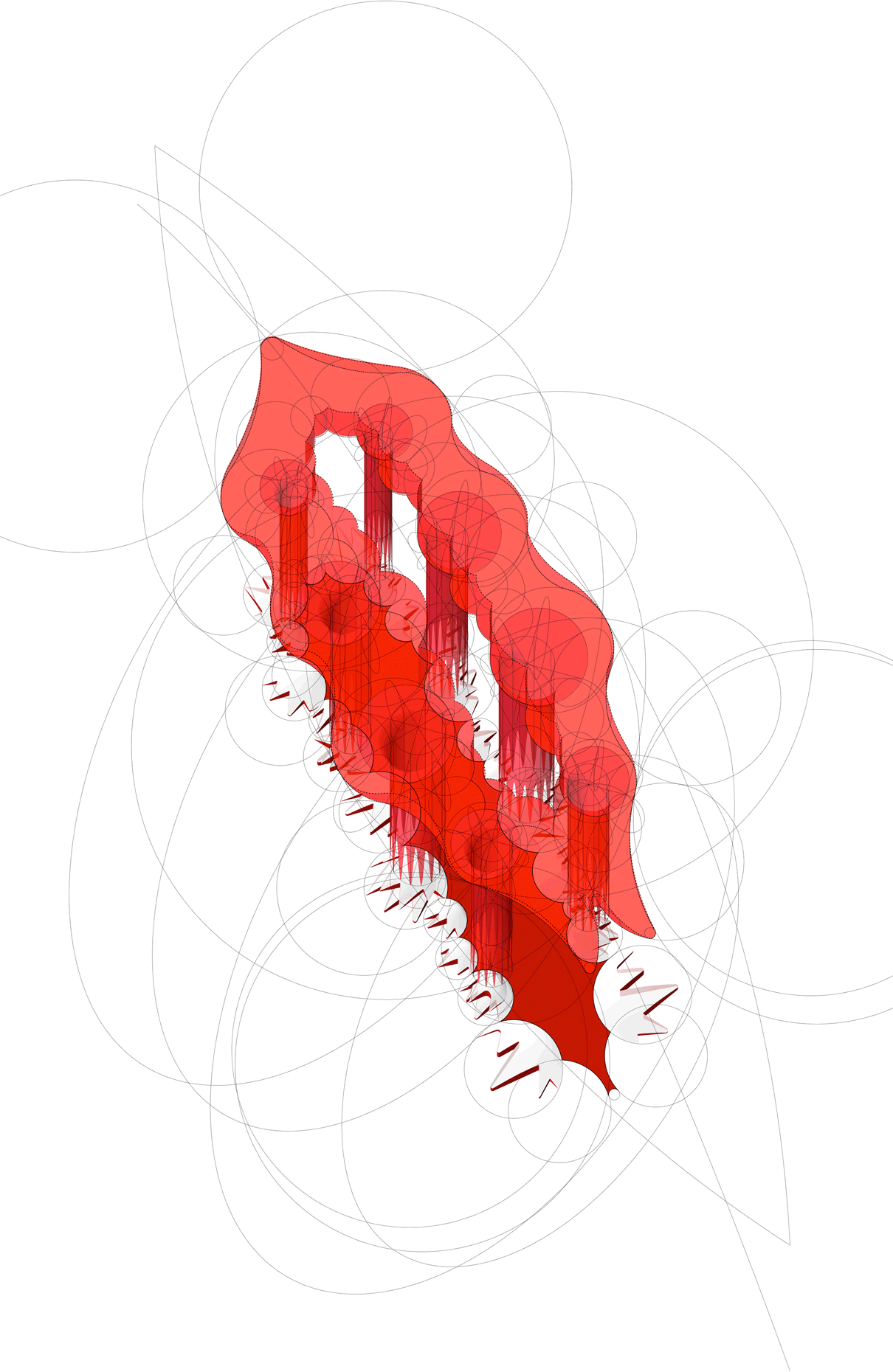
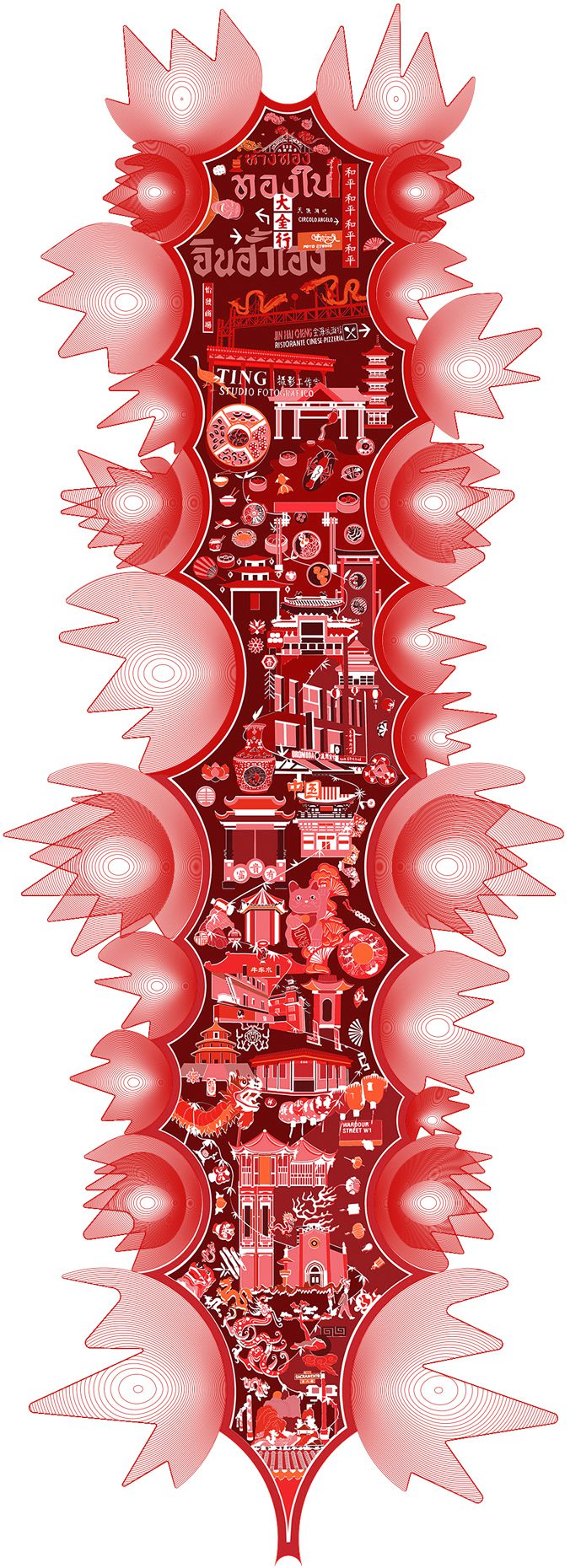
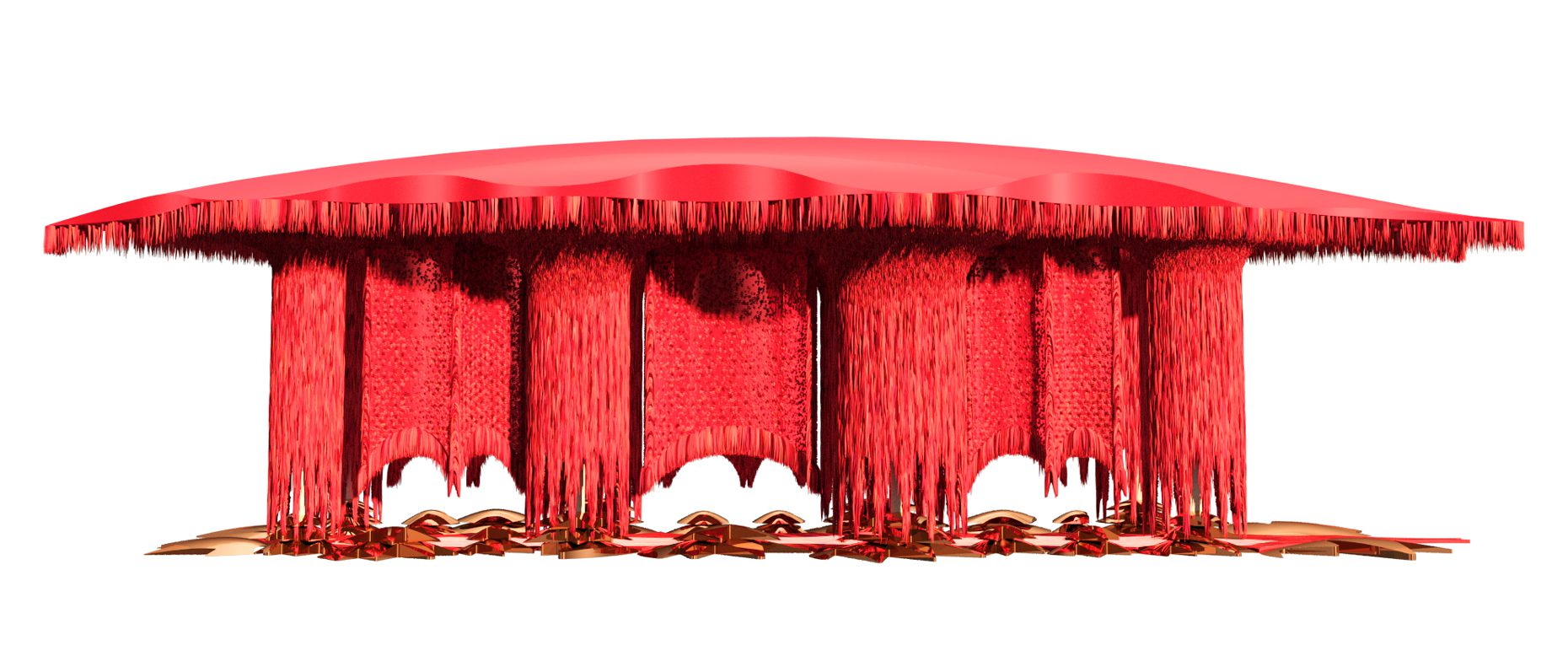
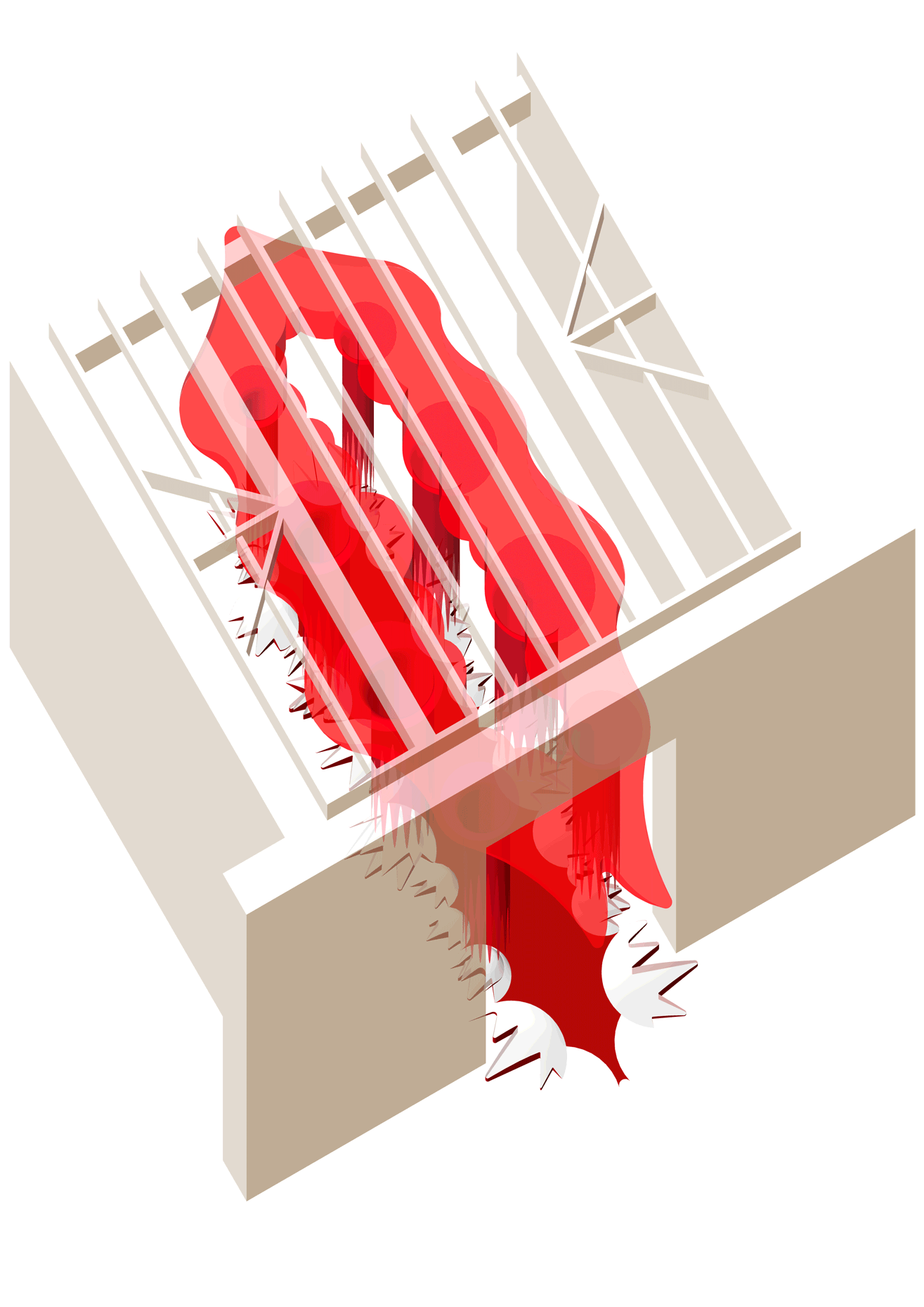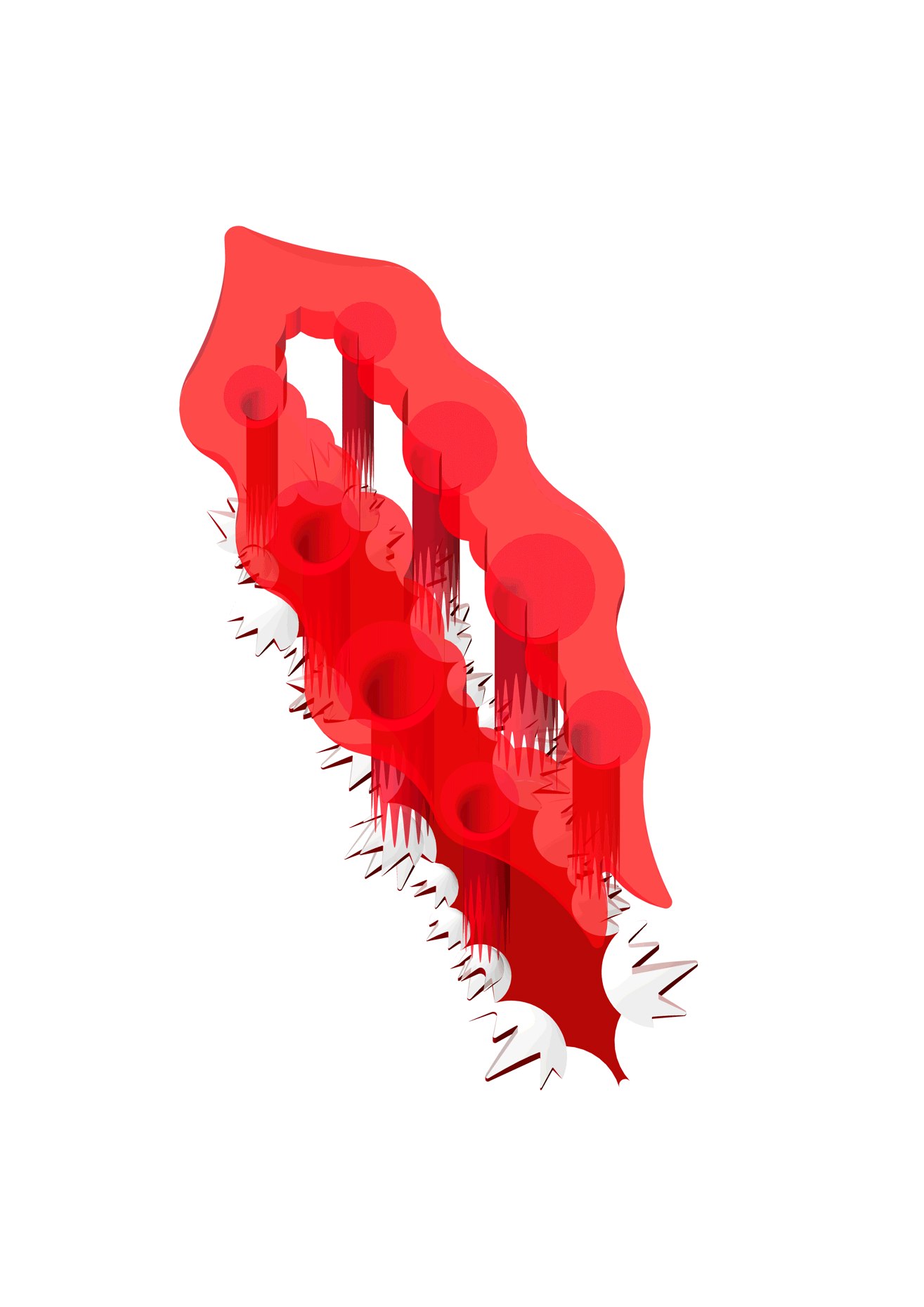
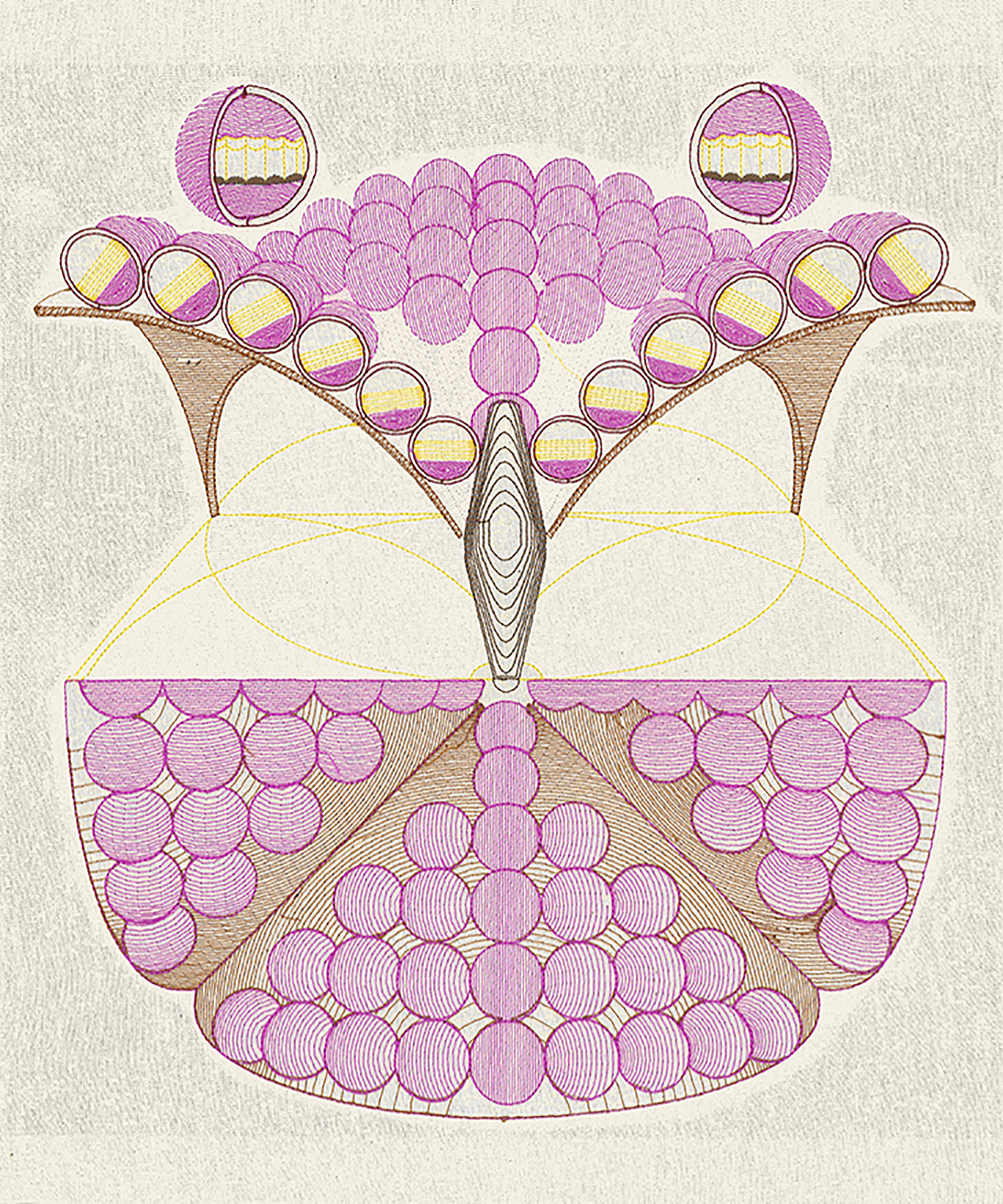
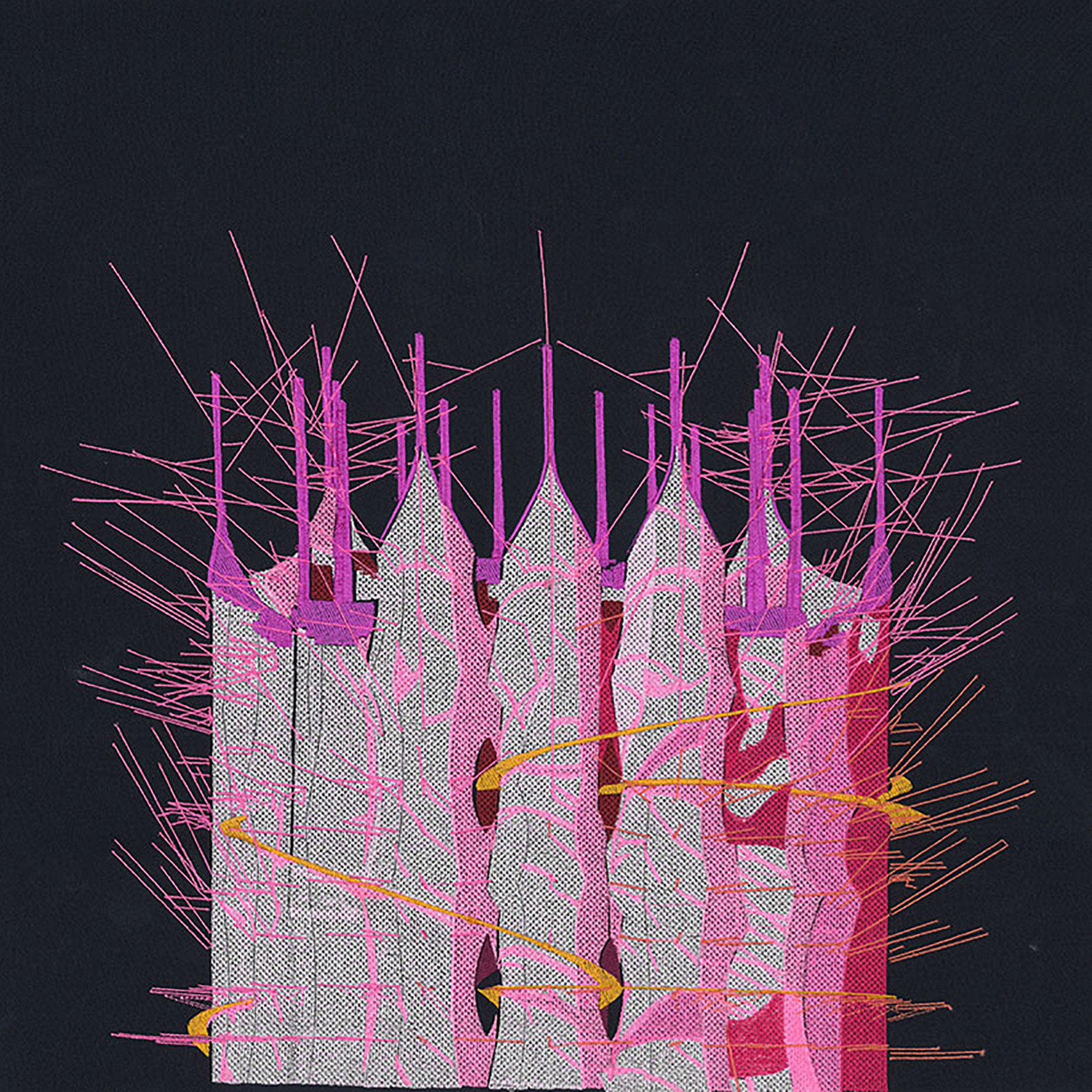
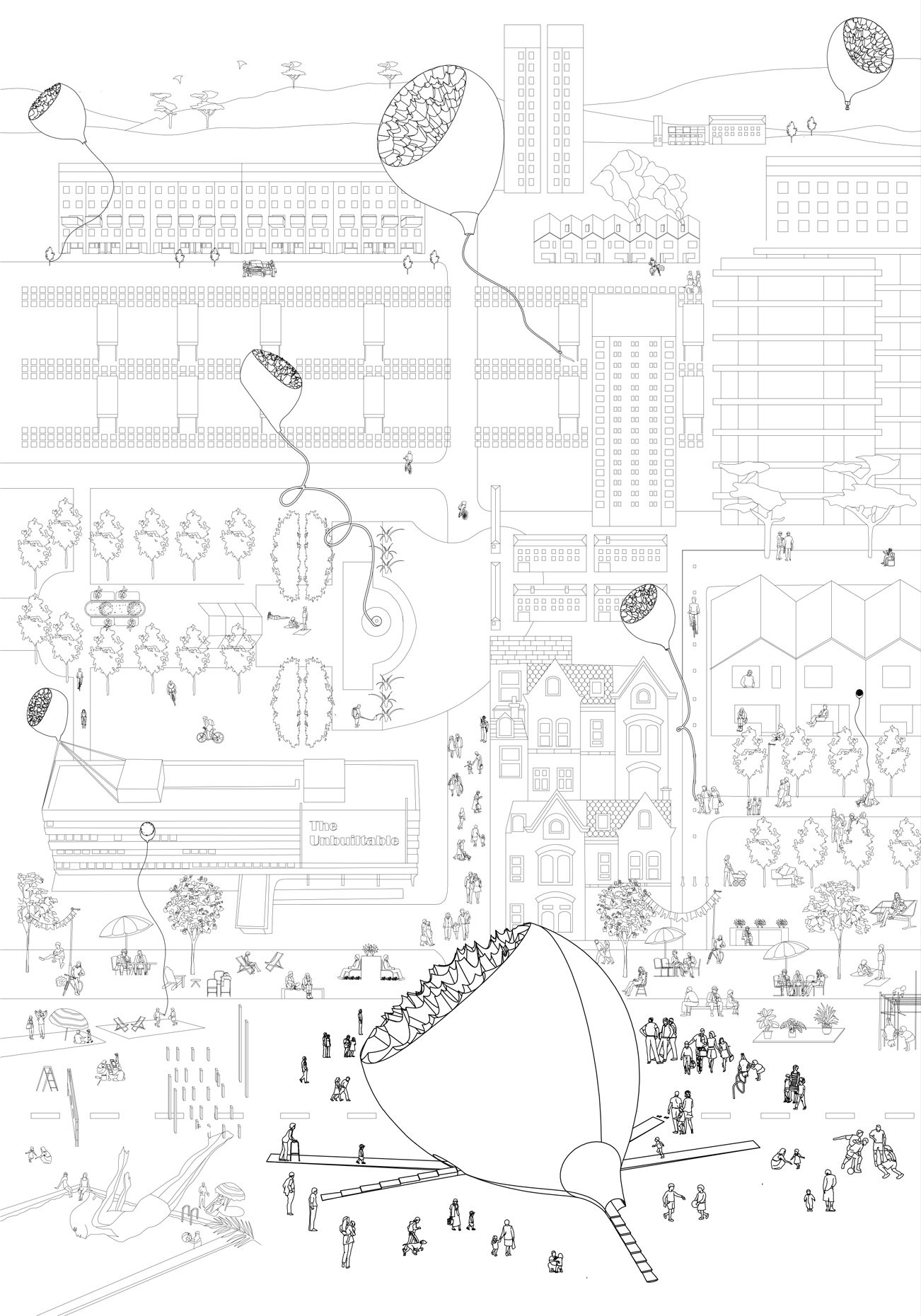
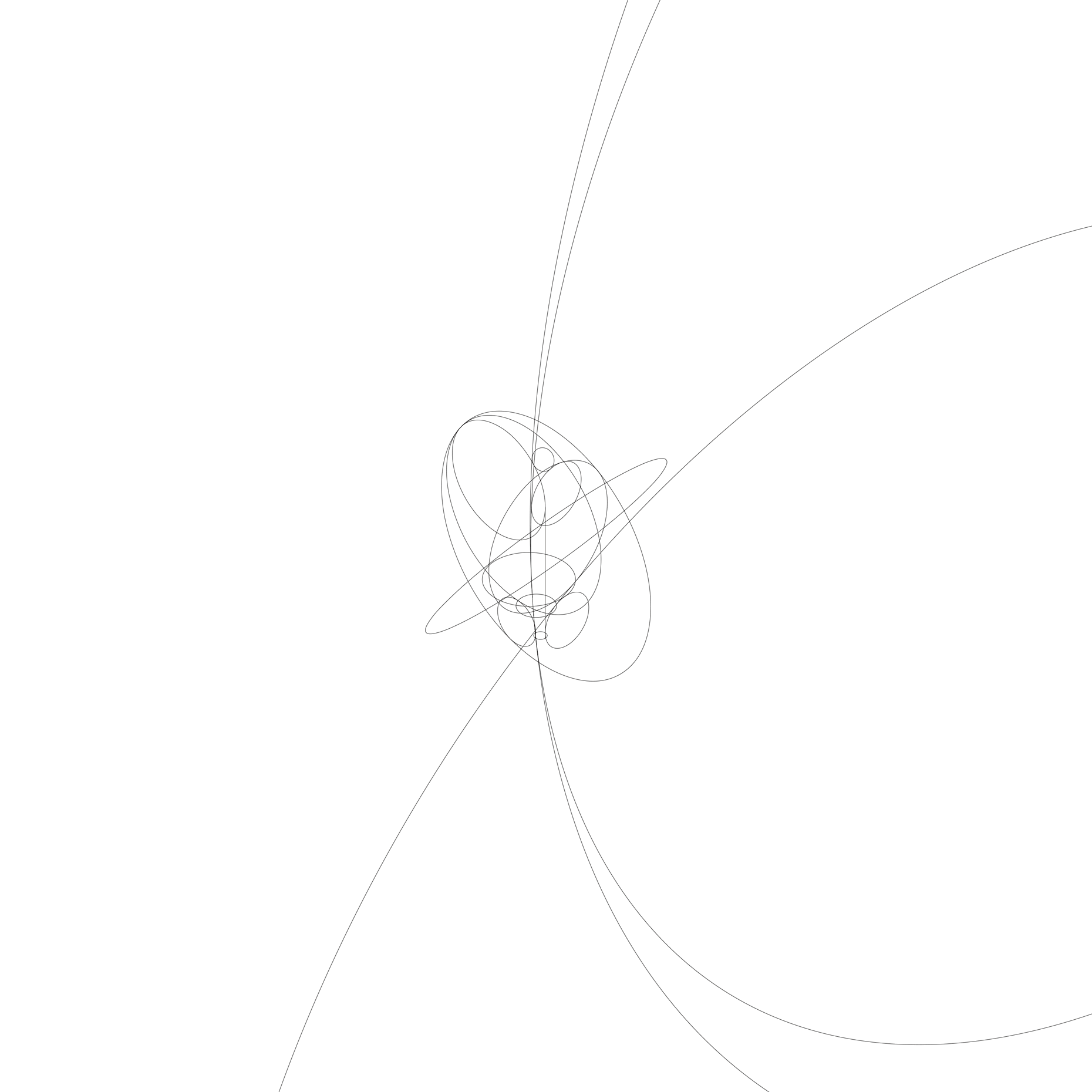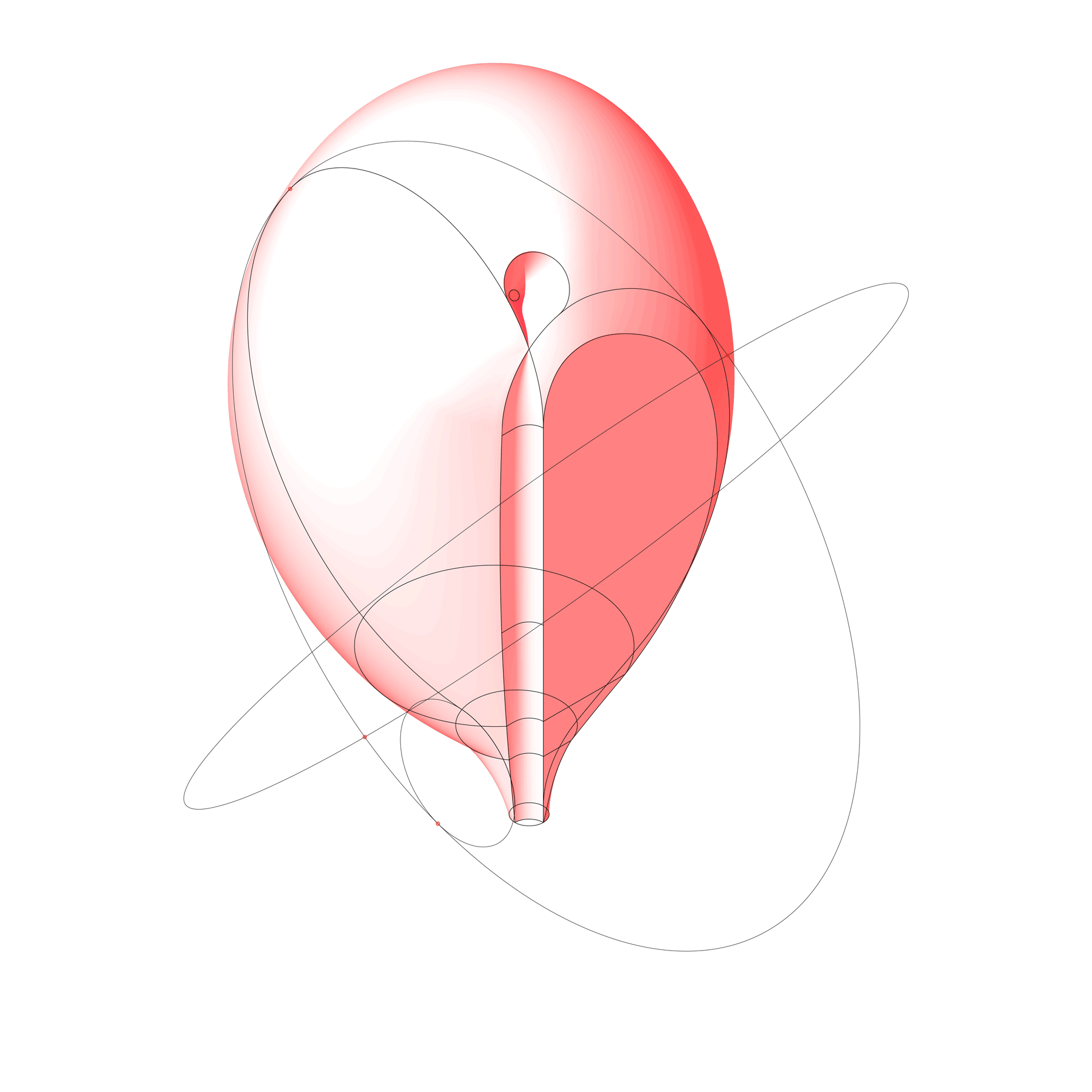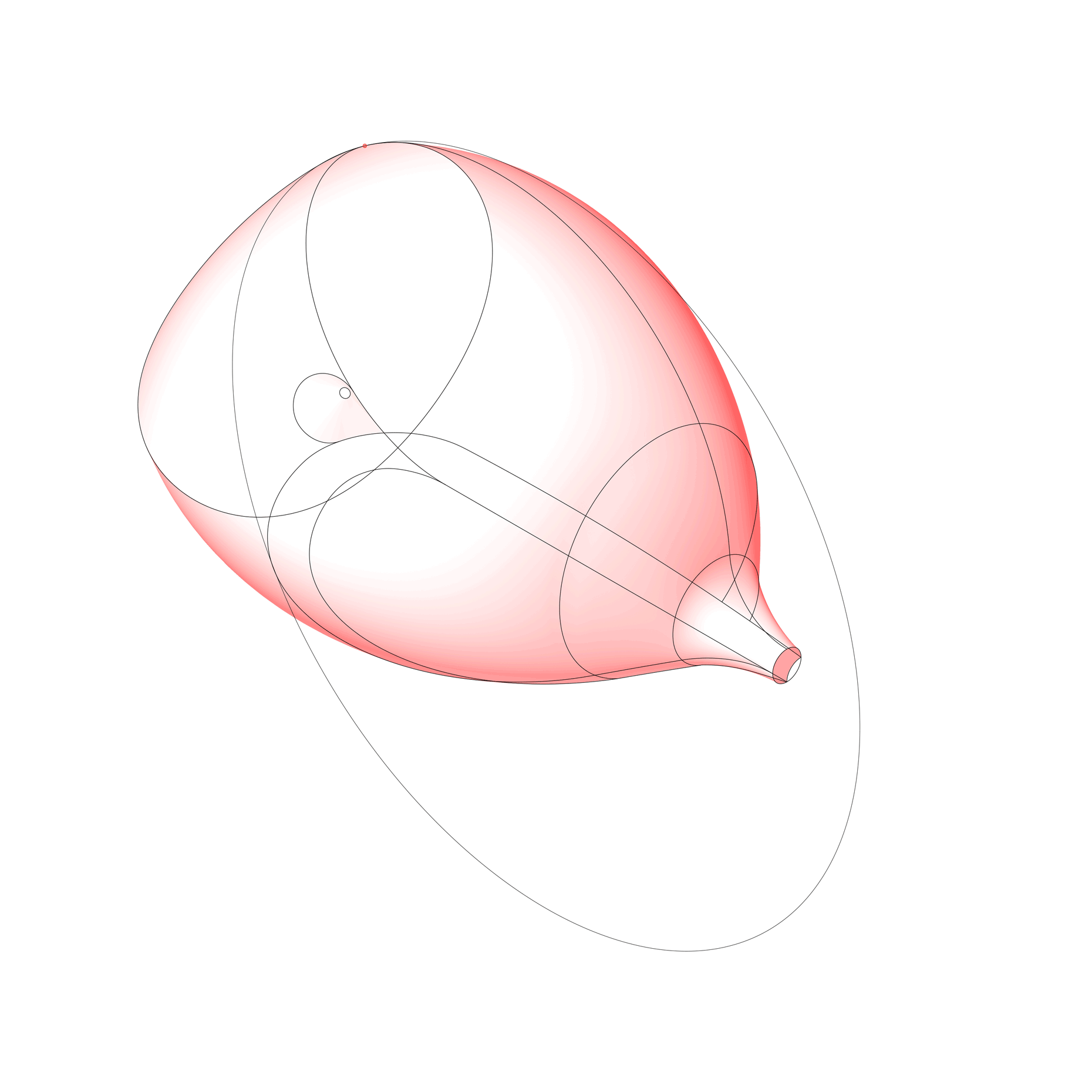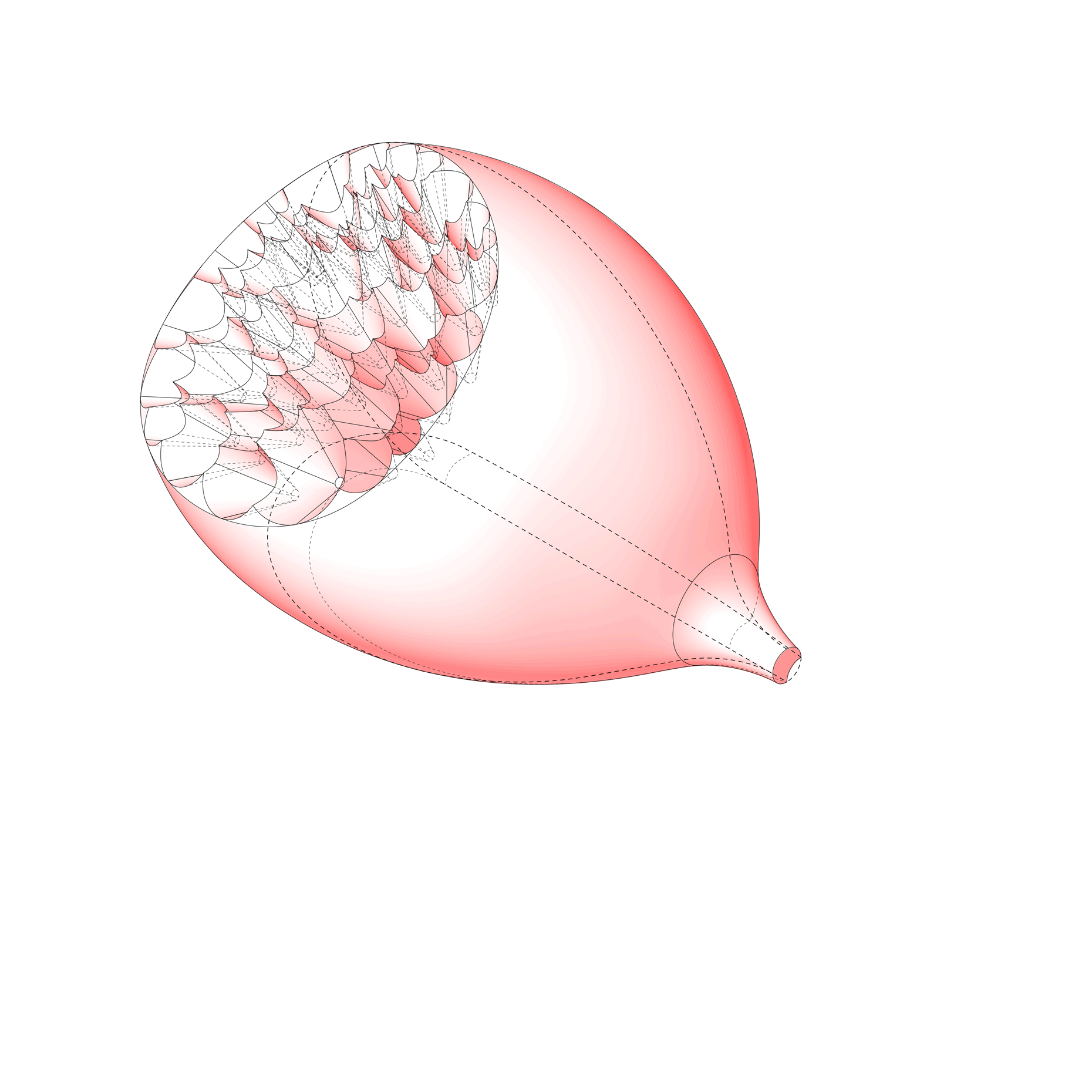
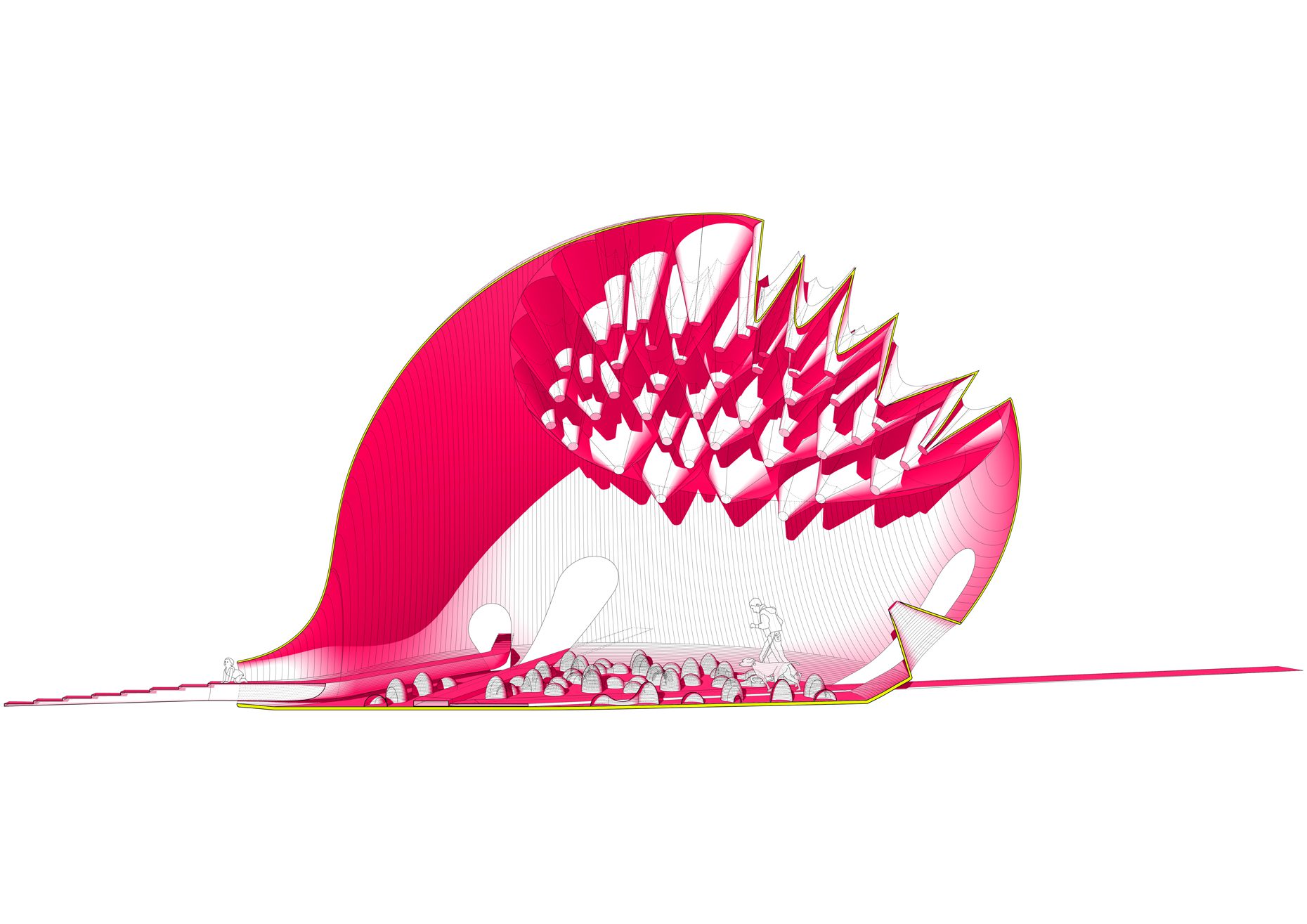
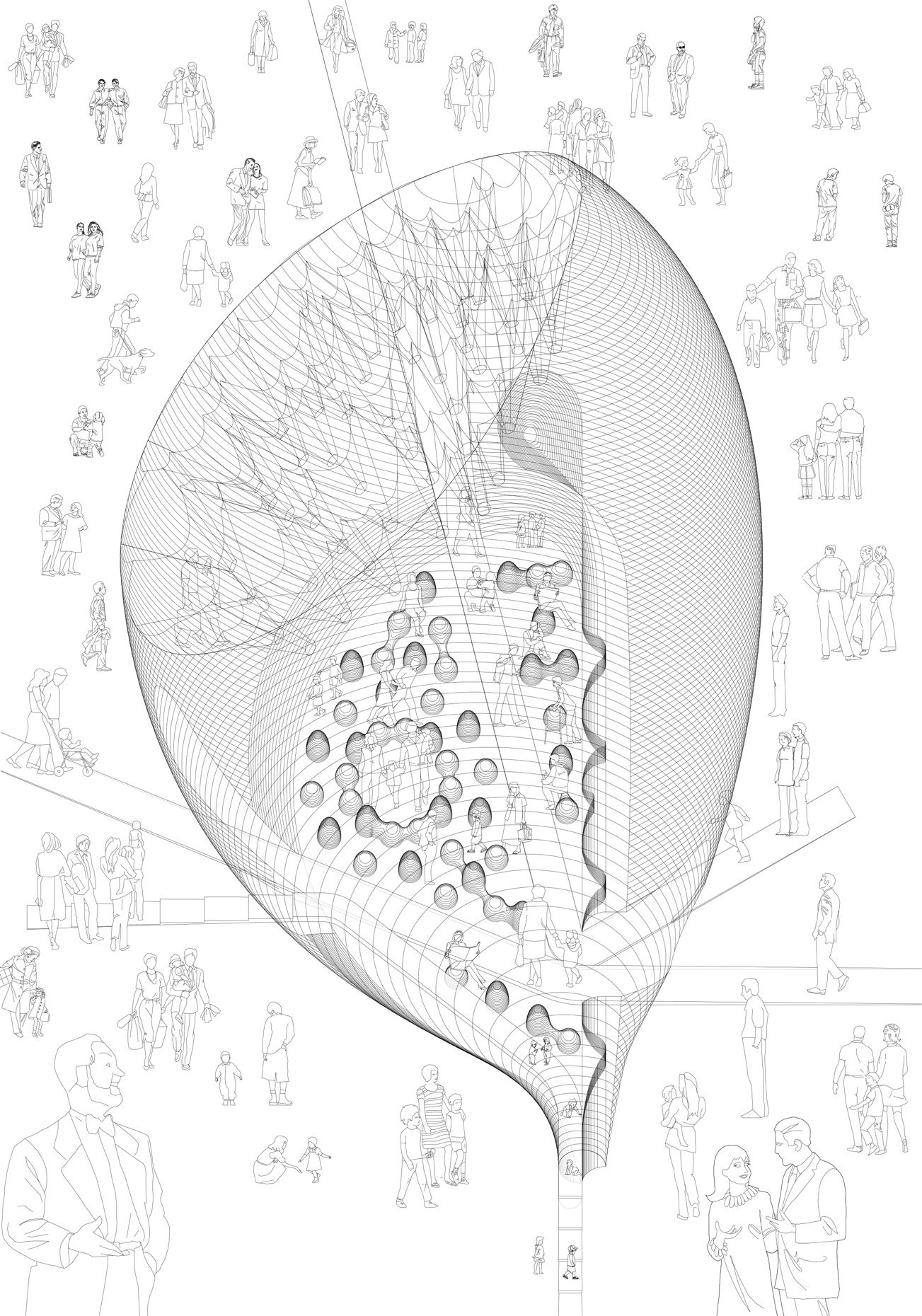
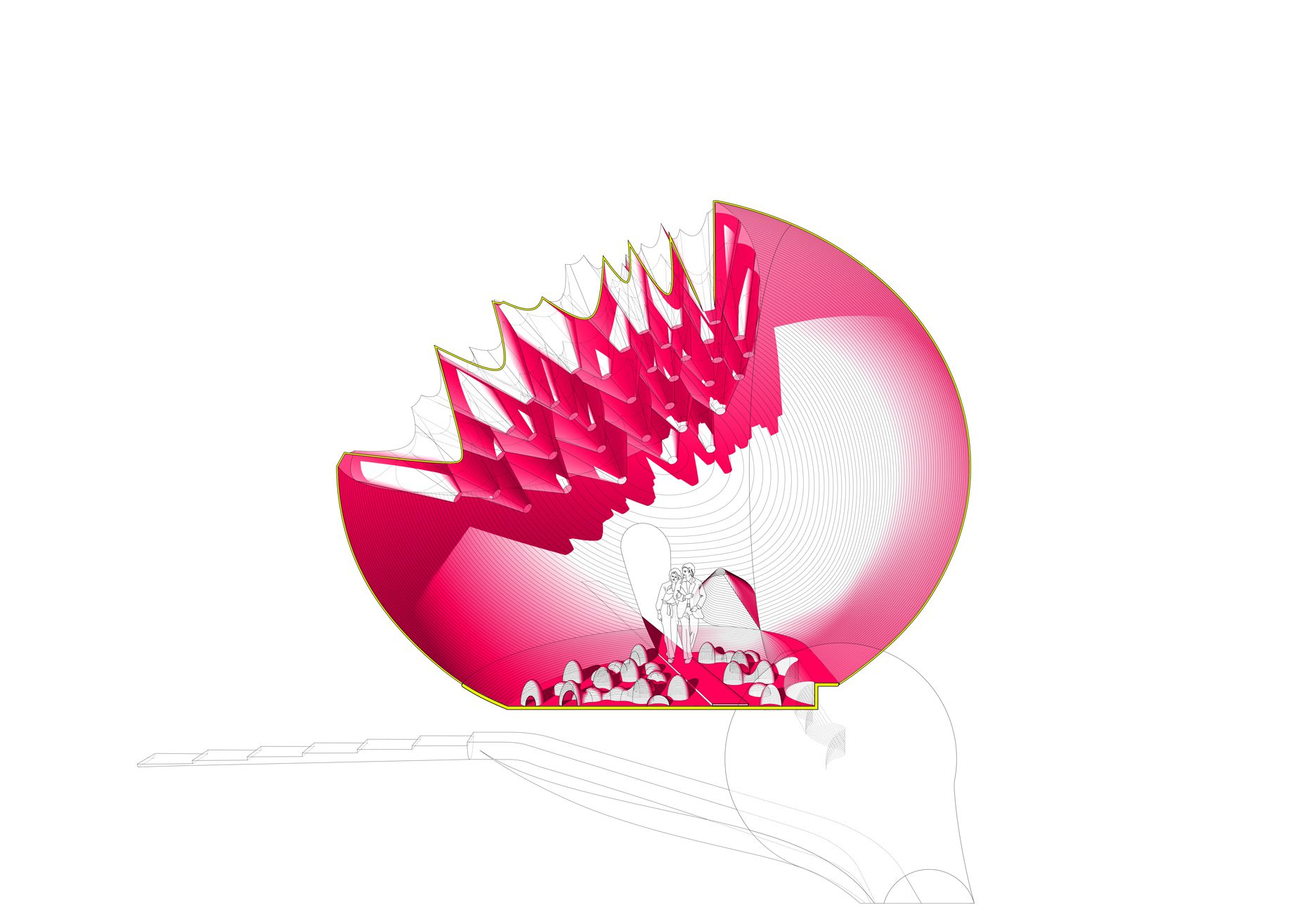
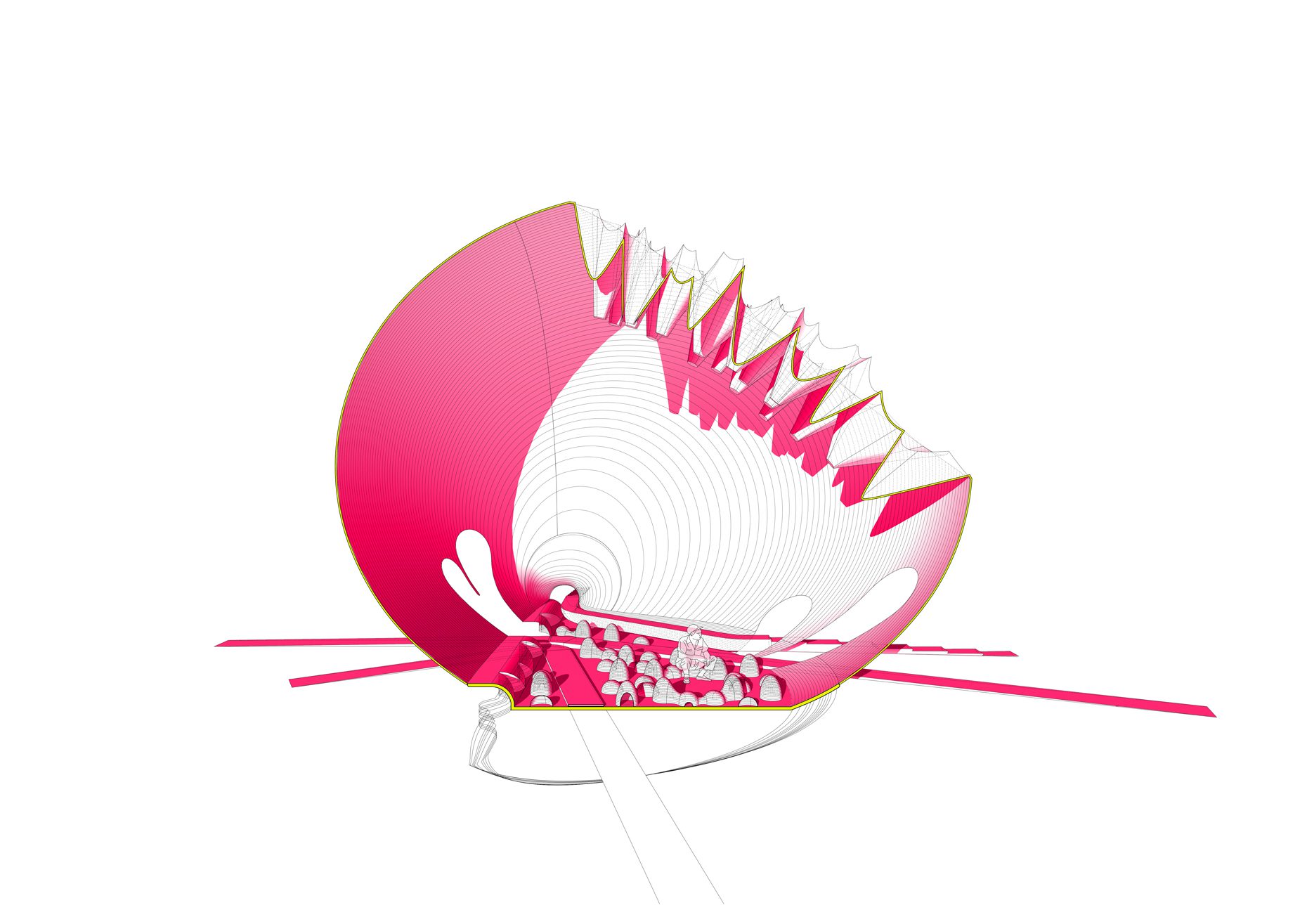
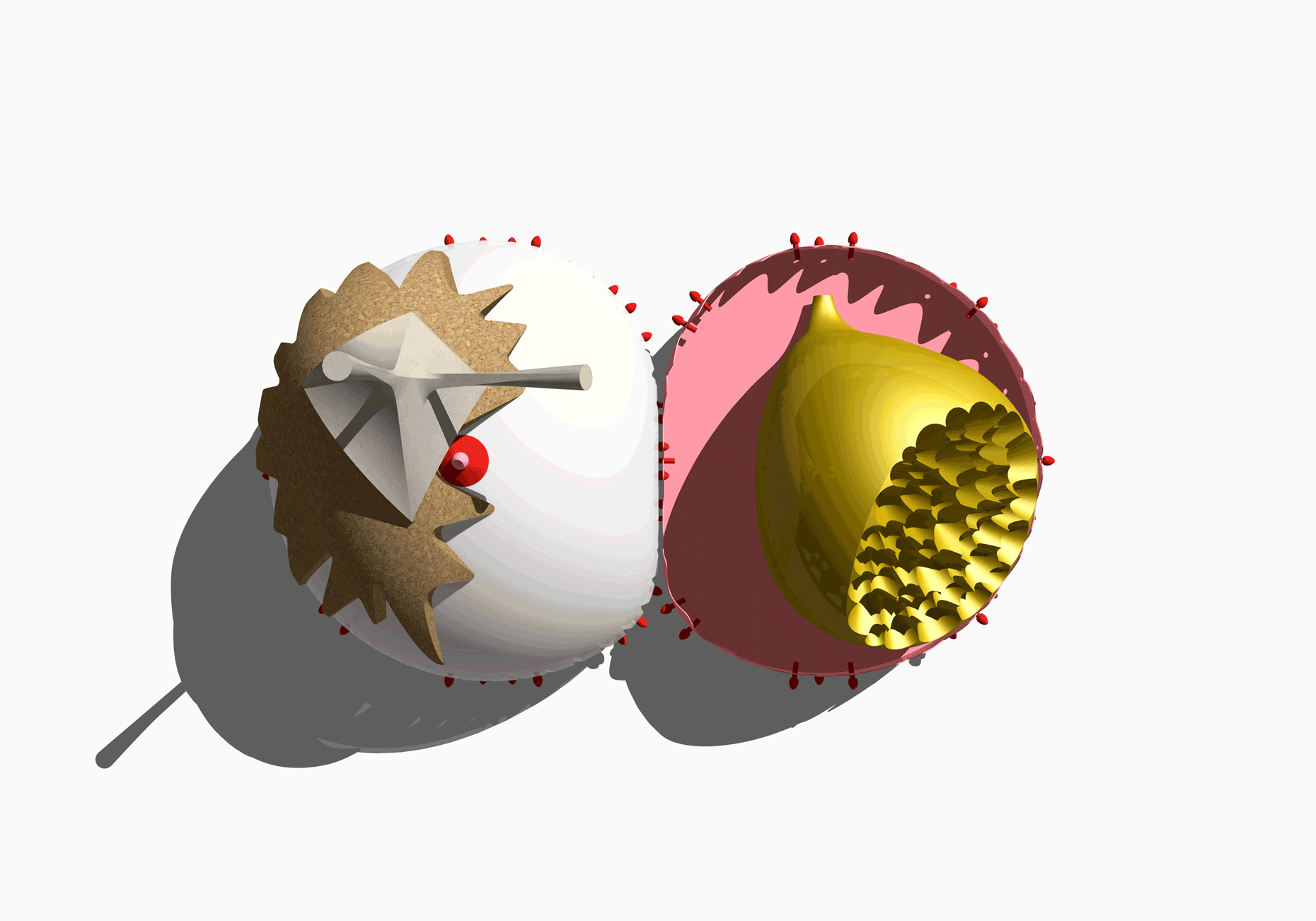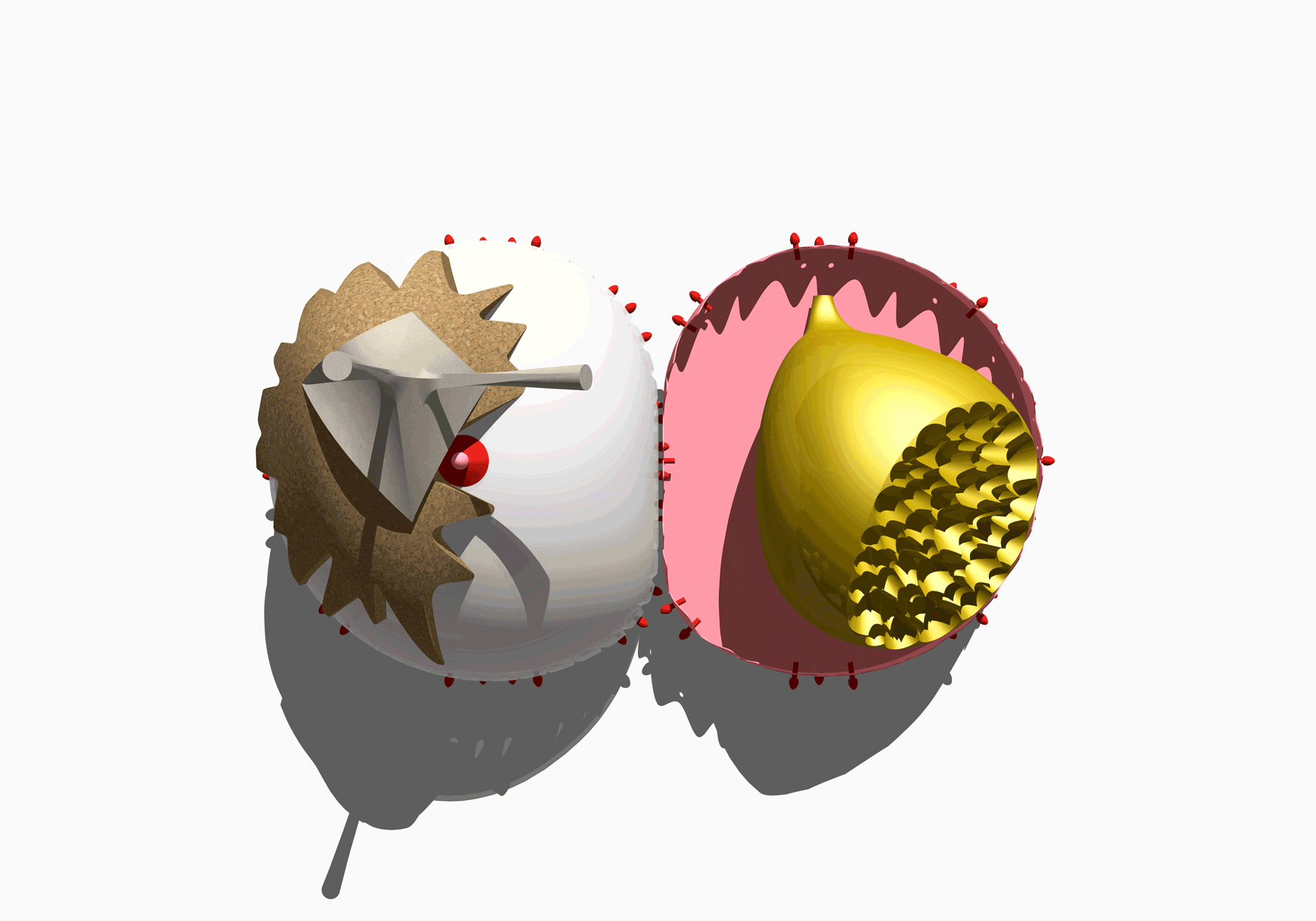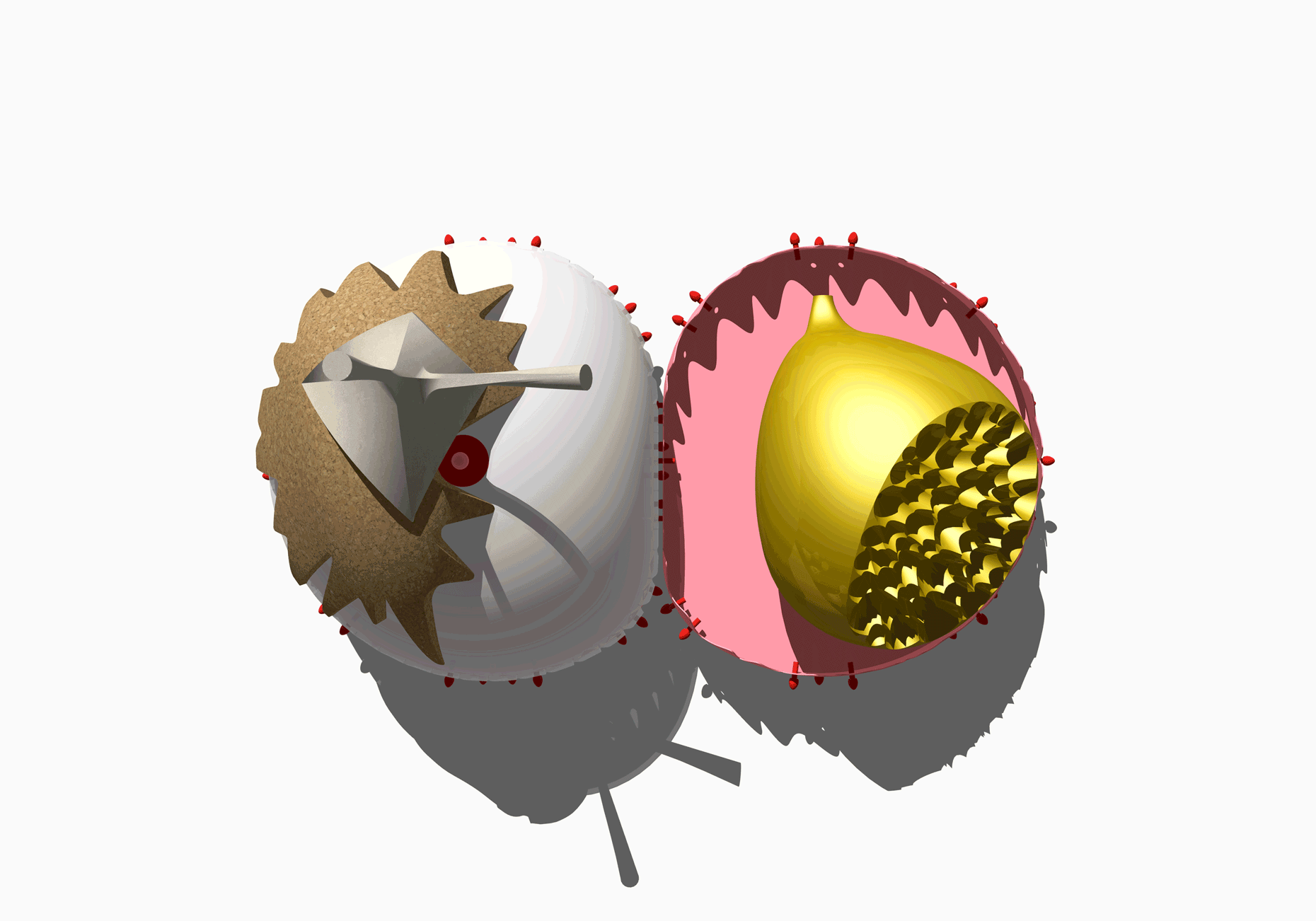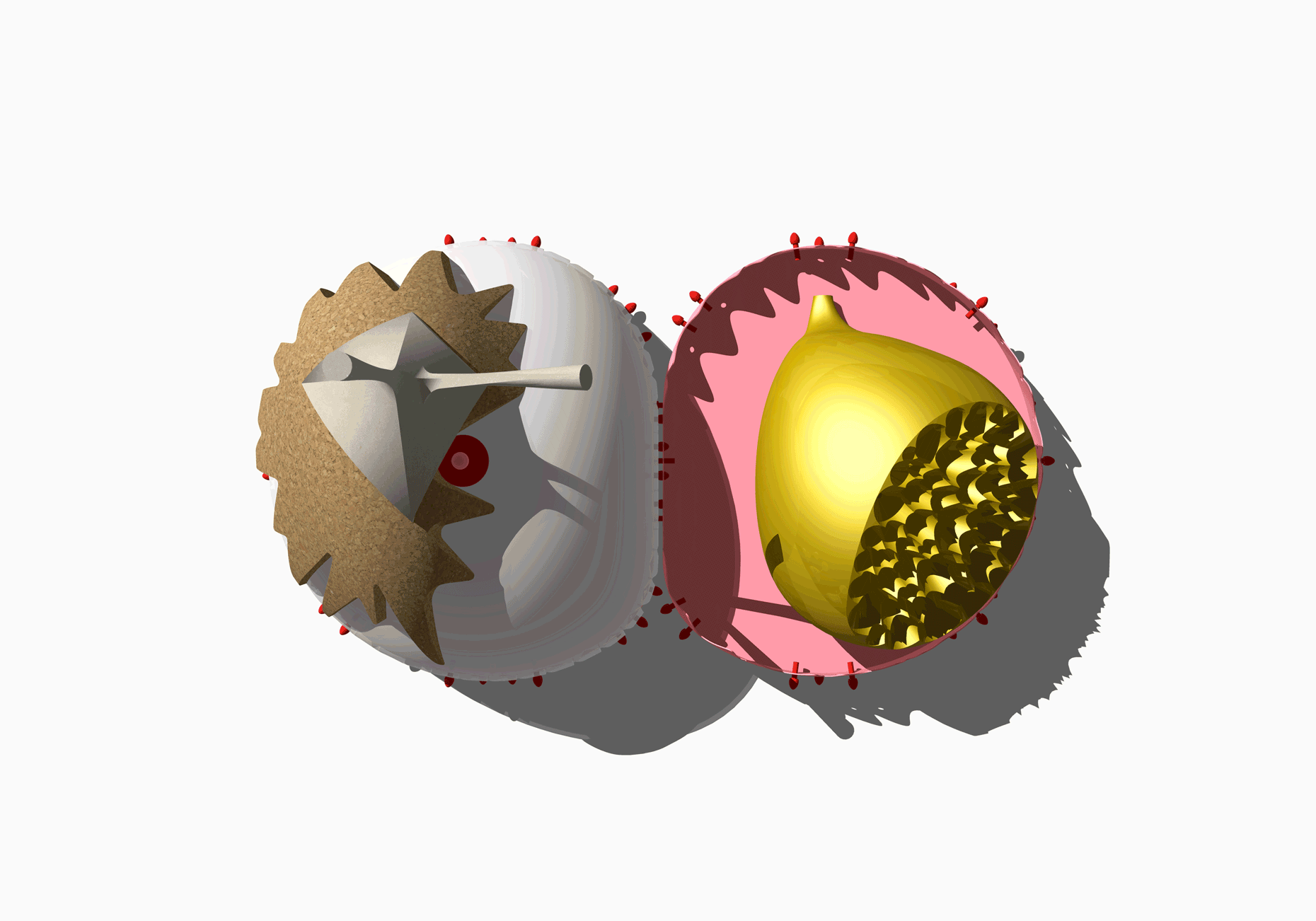
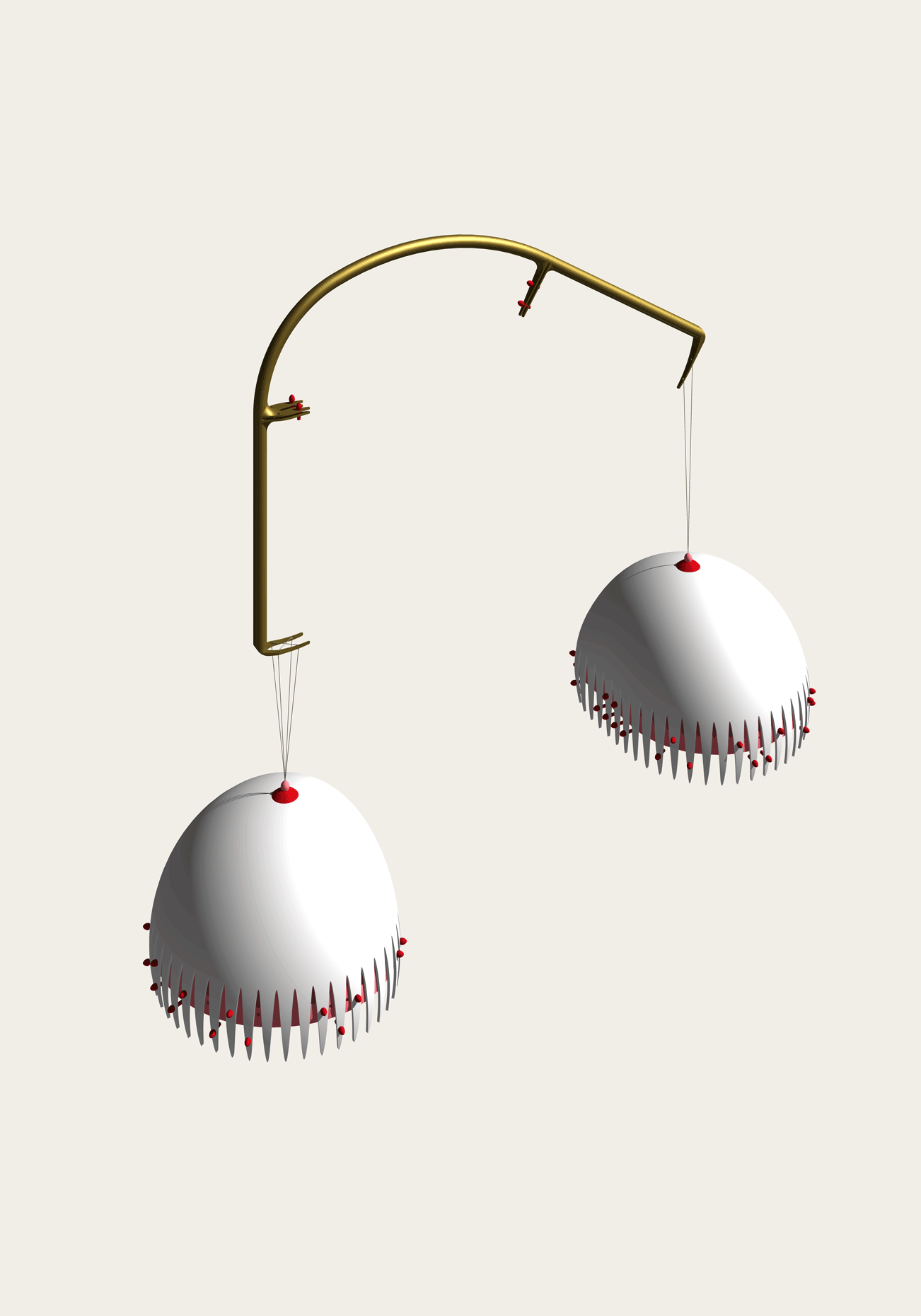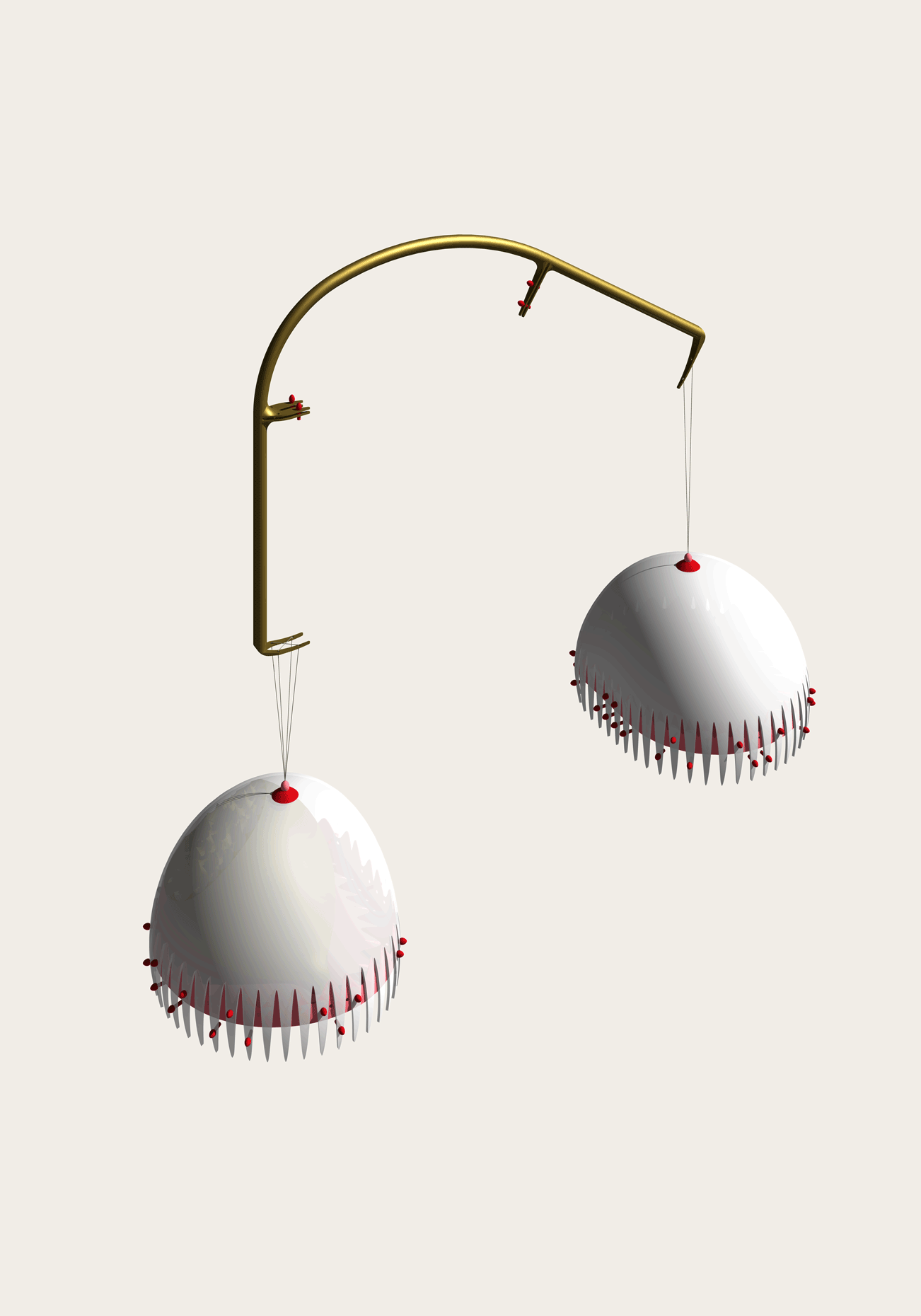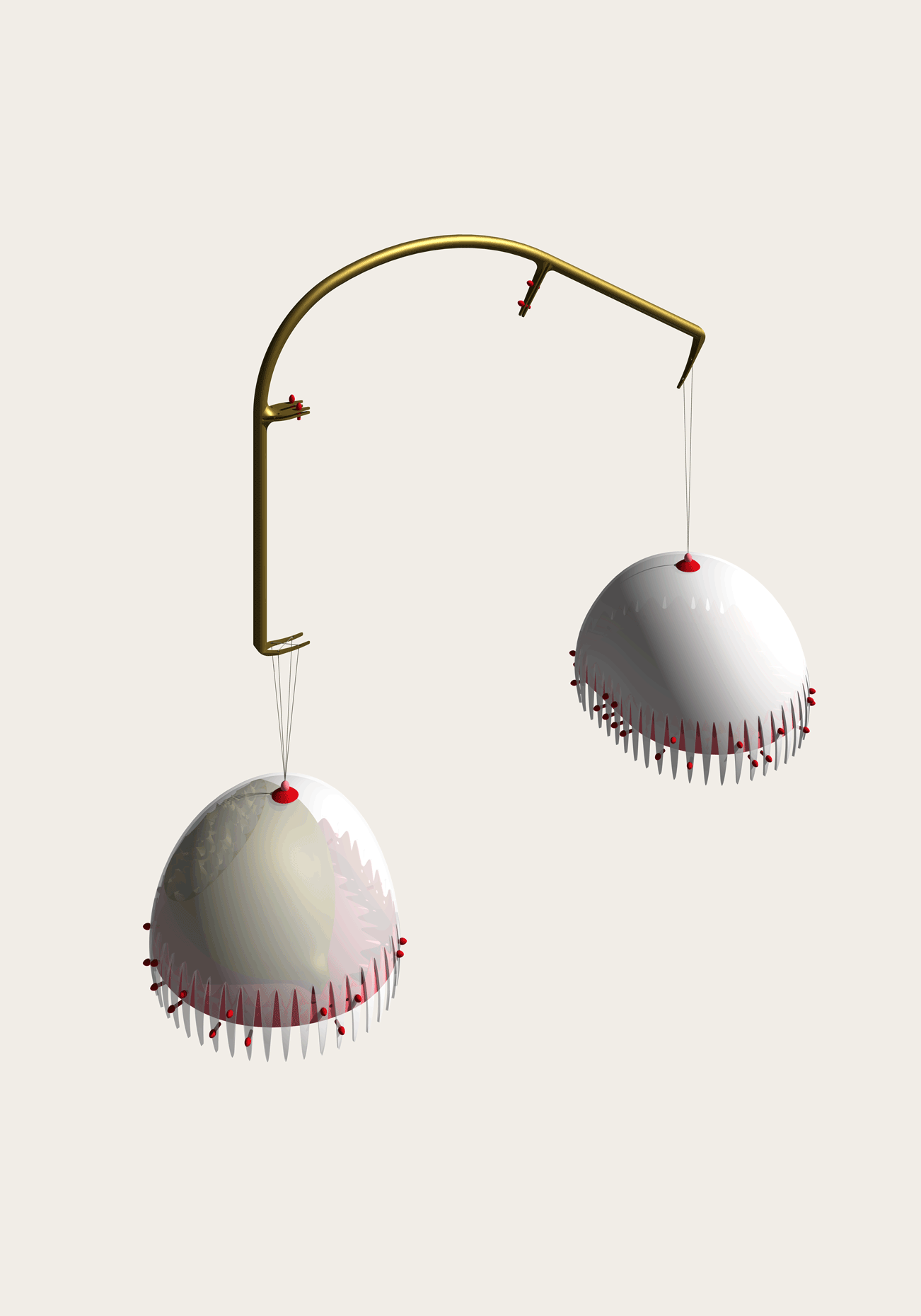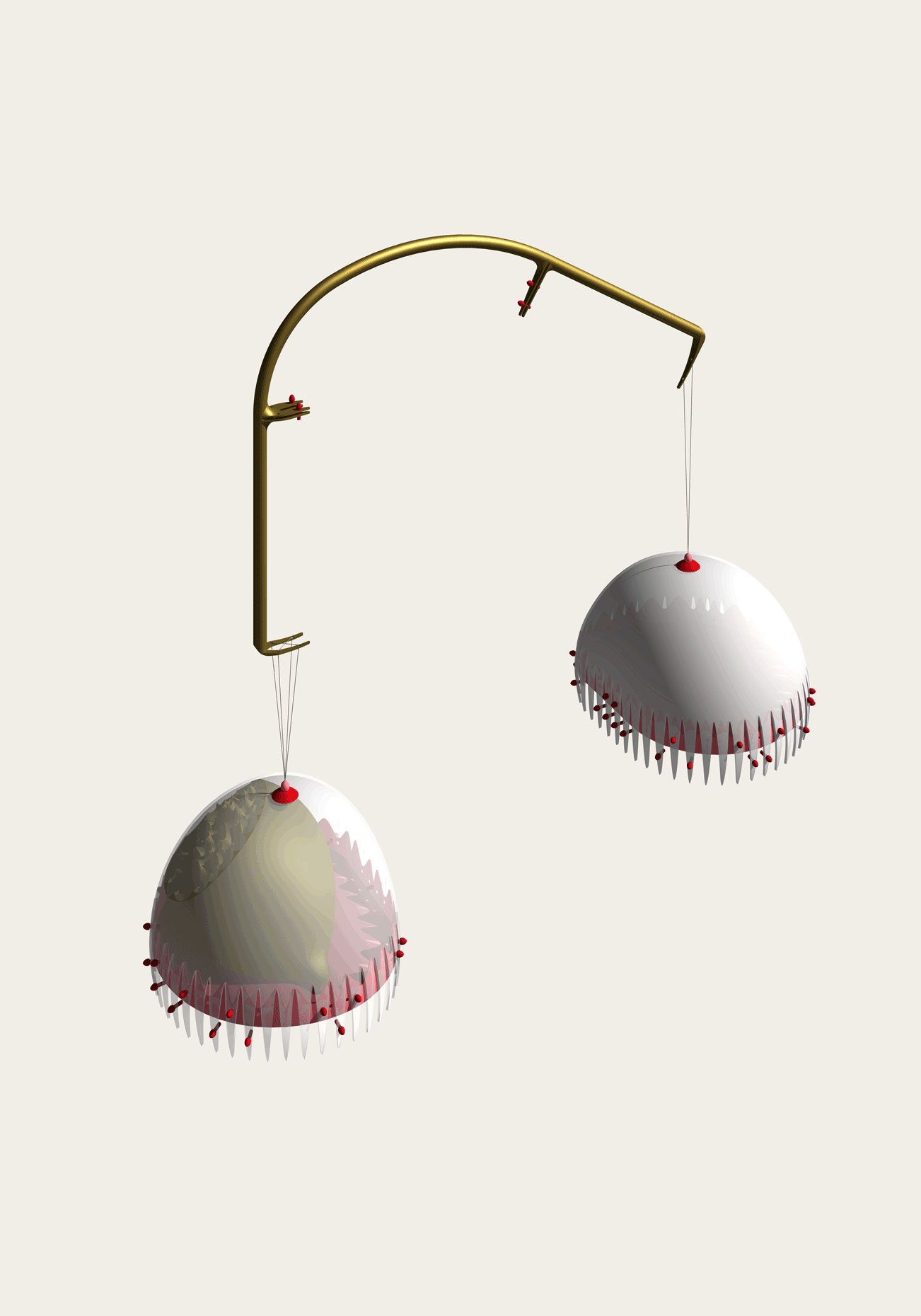
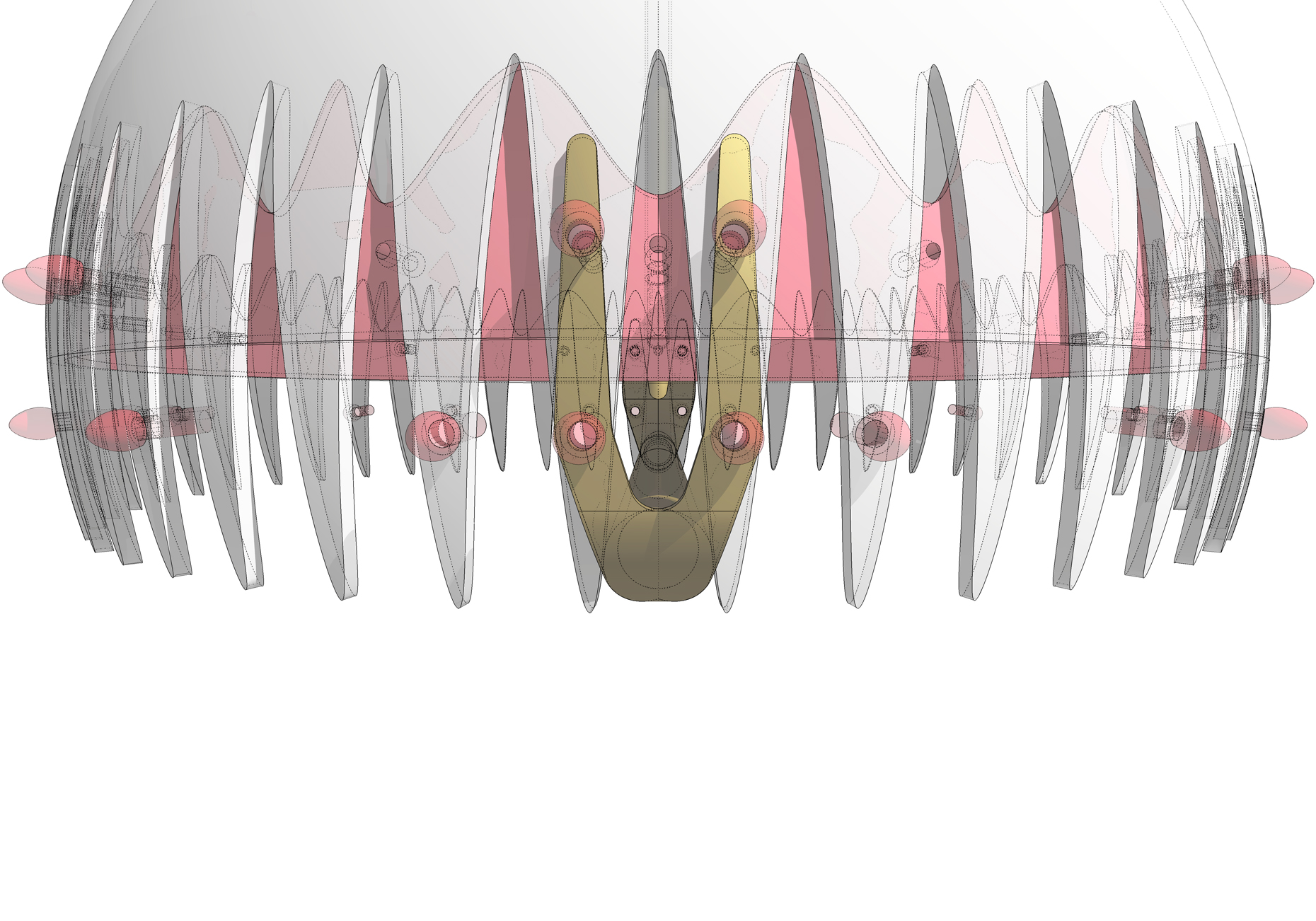
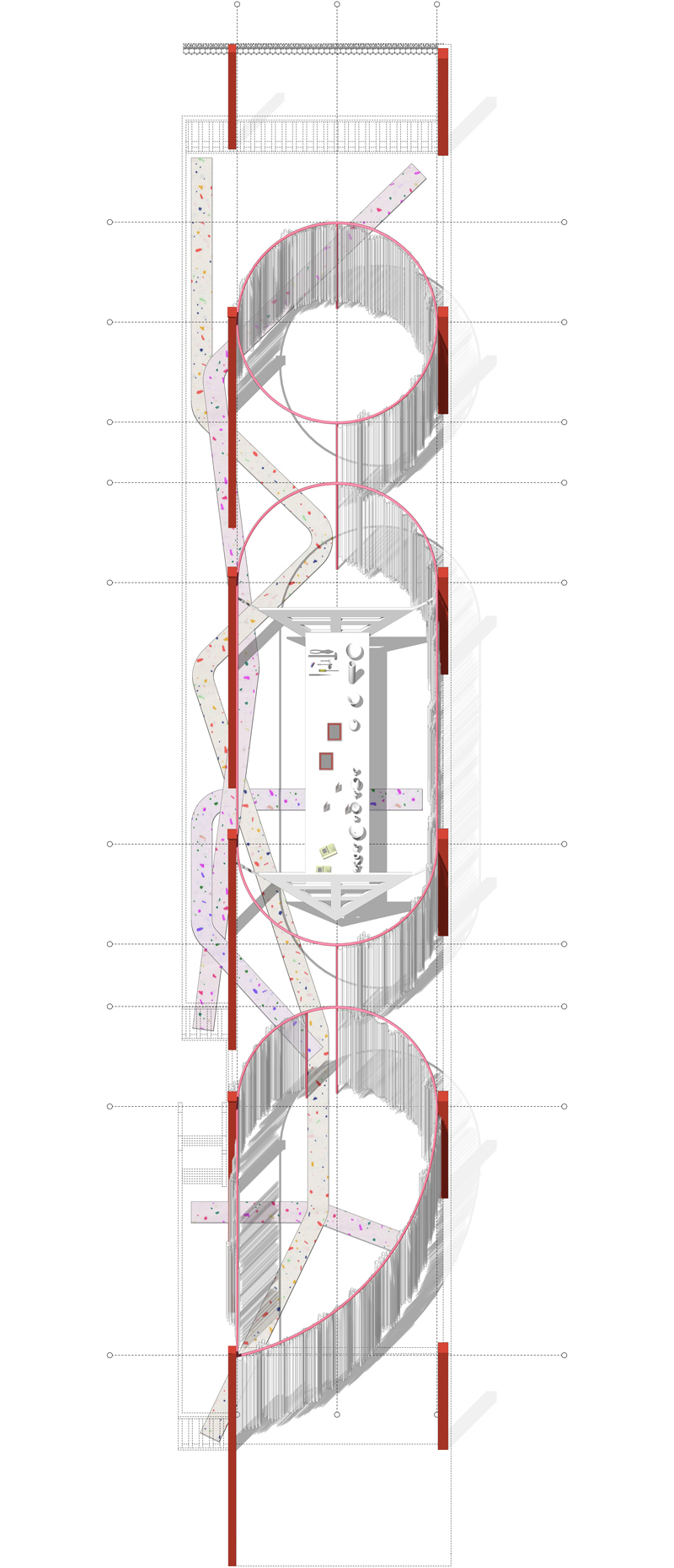
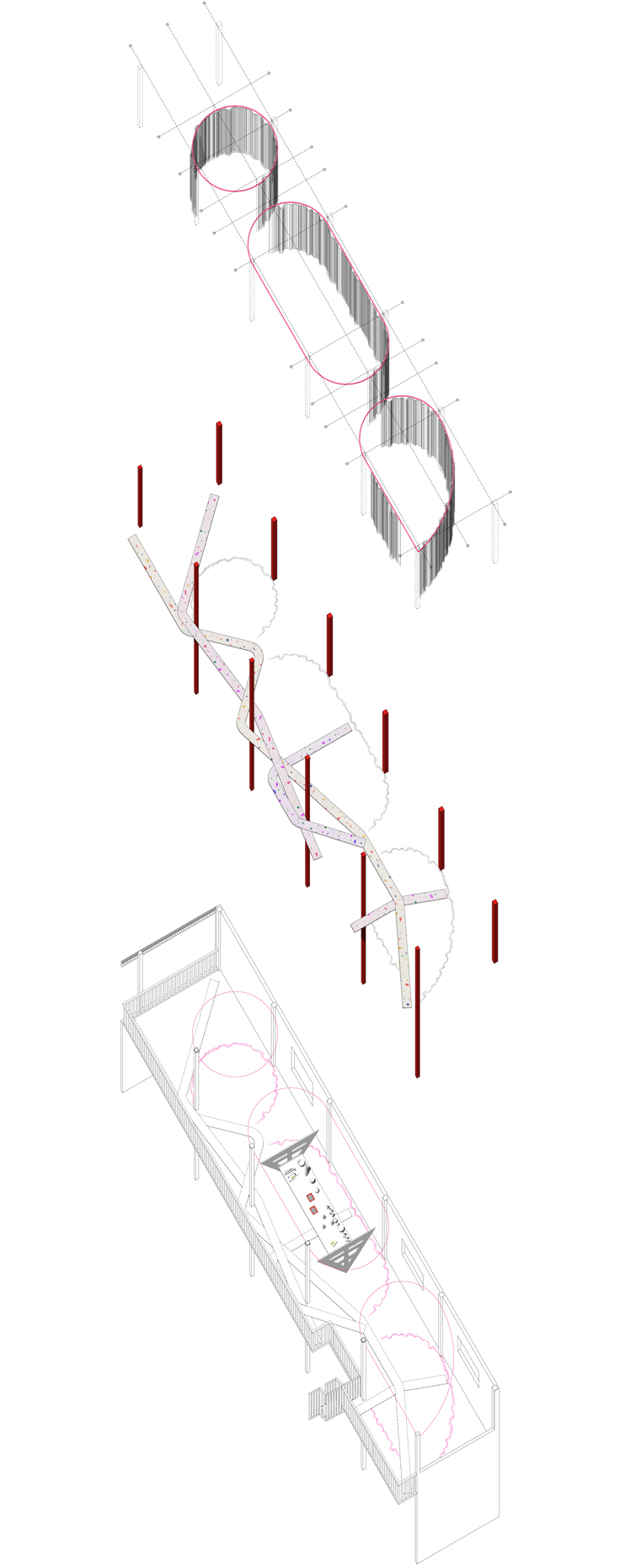
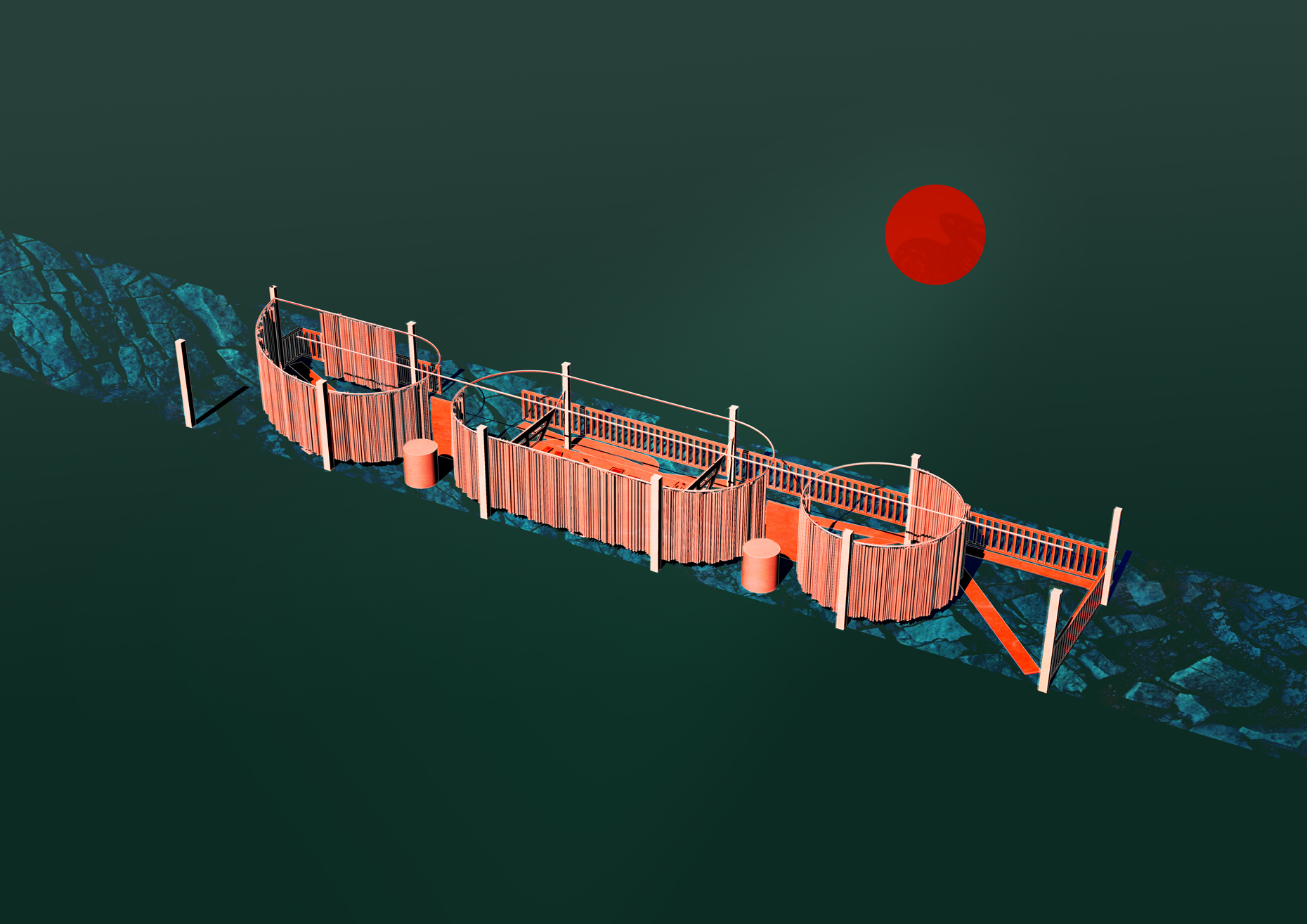
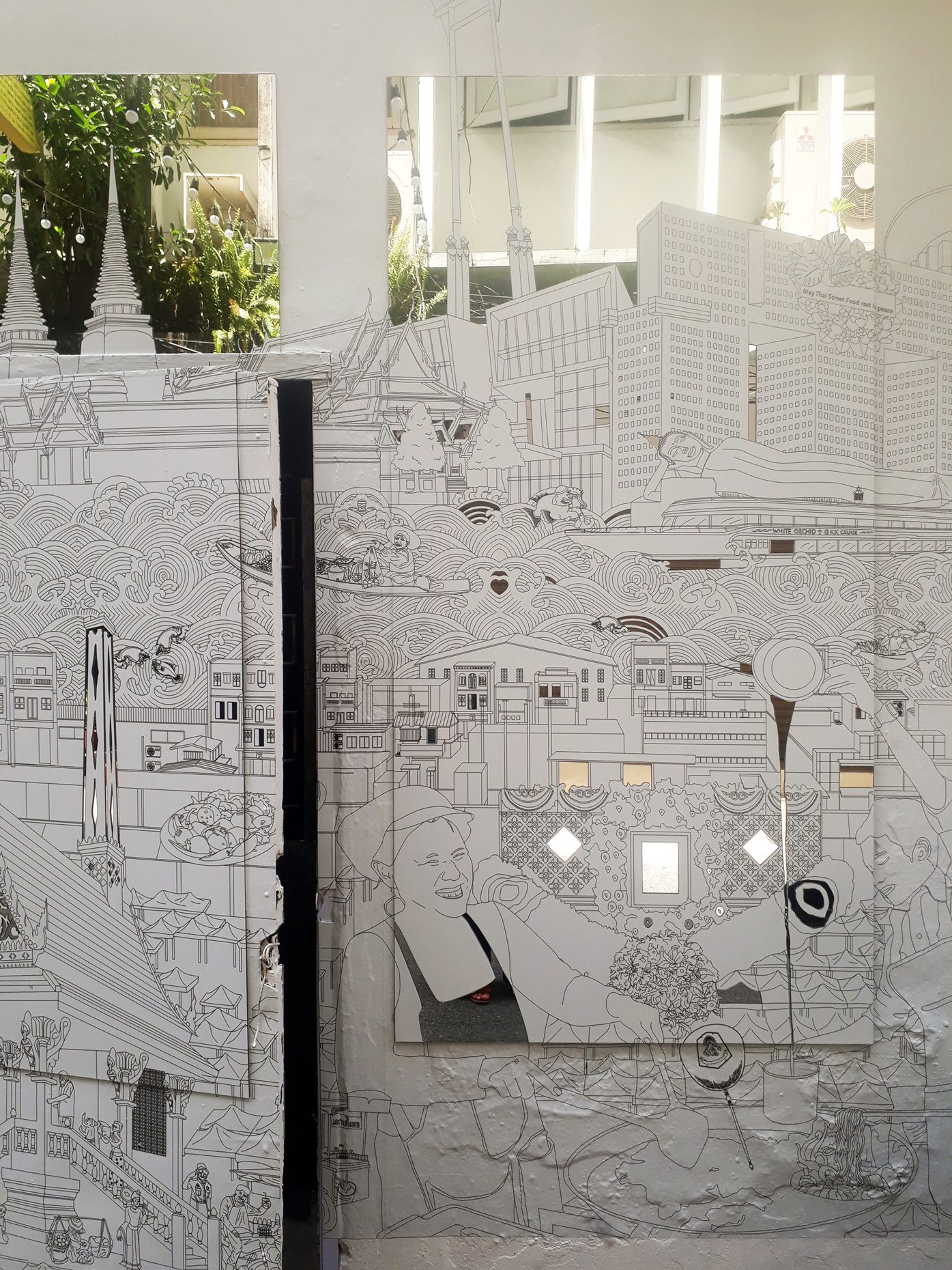
“The Chinatown effect” is a temporary installation at the ATT19 gallery designed and constructed in four weeks by INDA students in Bangkok. The project starts as a site-specific stage set, a series of props and composite videos investigating the notion of commonality and stereotype - in relationship to the world of Chinatown(s) as social typologies. When analysed through the Chinese cultural attitude towards reproducibility, the proliferation of Chinatowns reveals a network of what we define “authentic trans-territorial clichés”. We need to craft challenging techniques for the legitimization and preservation of such a specific yet diffused identity: Chinatowns are constantly reconstructed and experienced in different parts of the world, growing into a familiar system of habits, reminiscences and iconographical values that became a simulacrum of a sophisticated, layered domesticity for everybody.
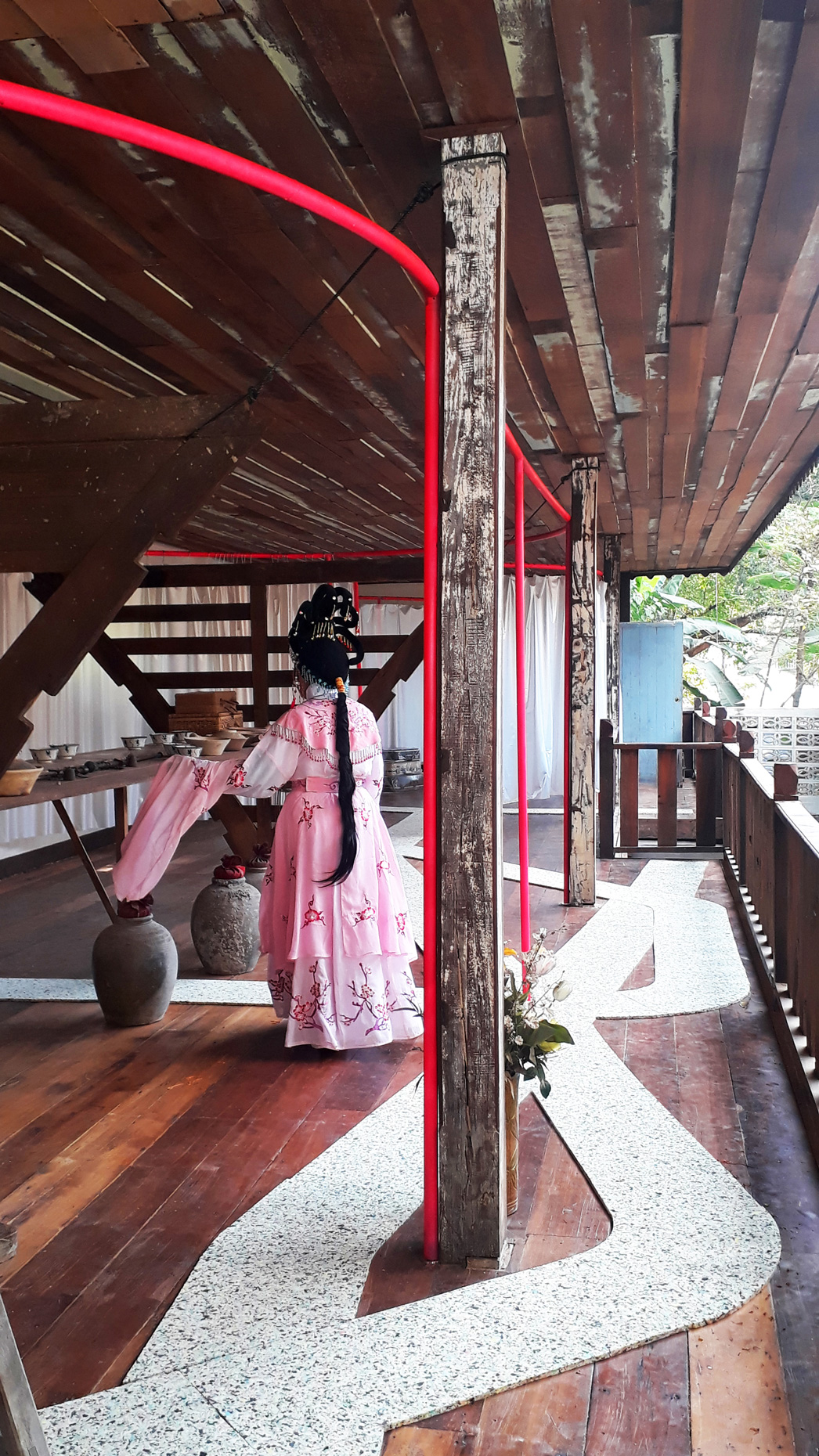
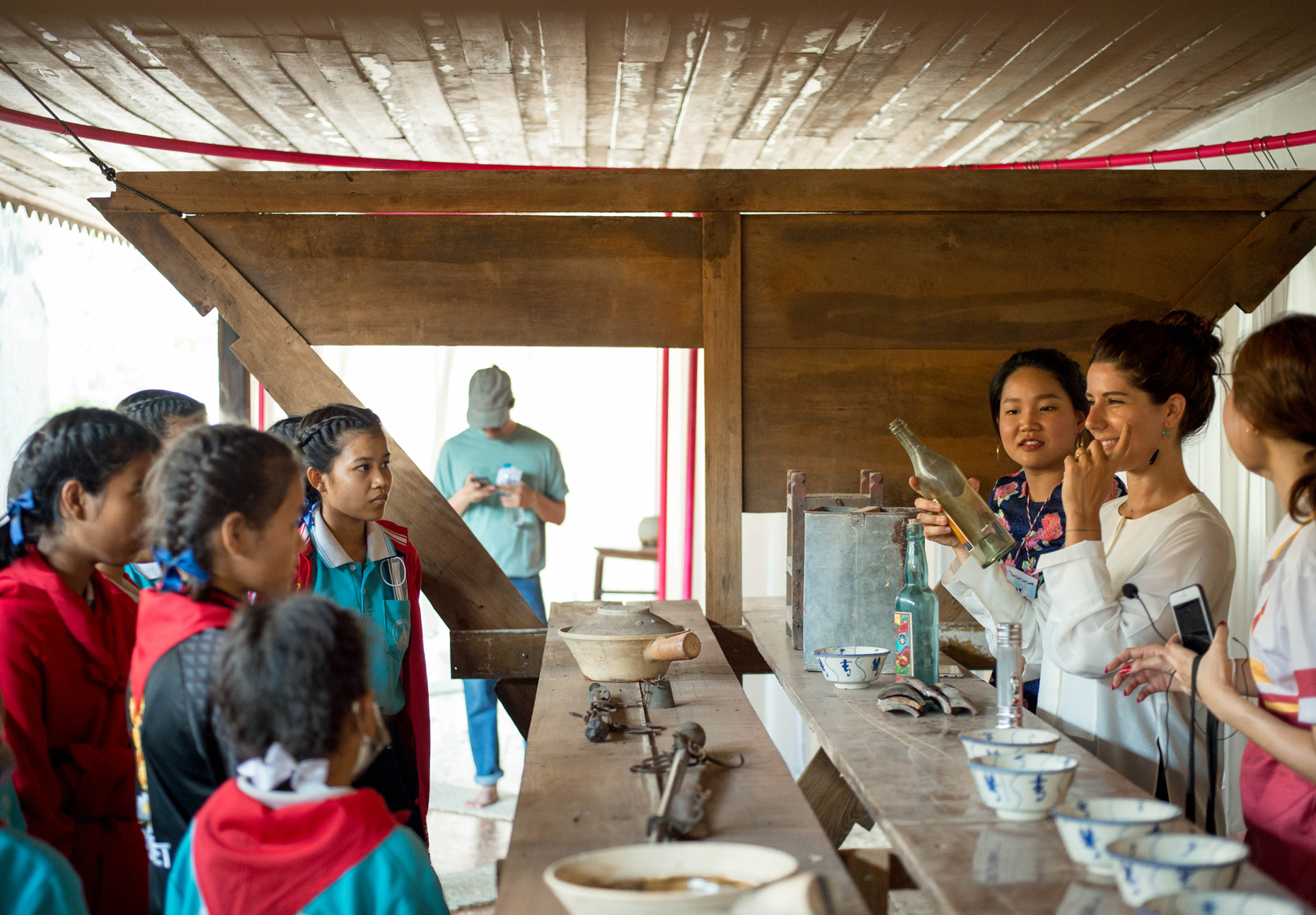
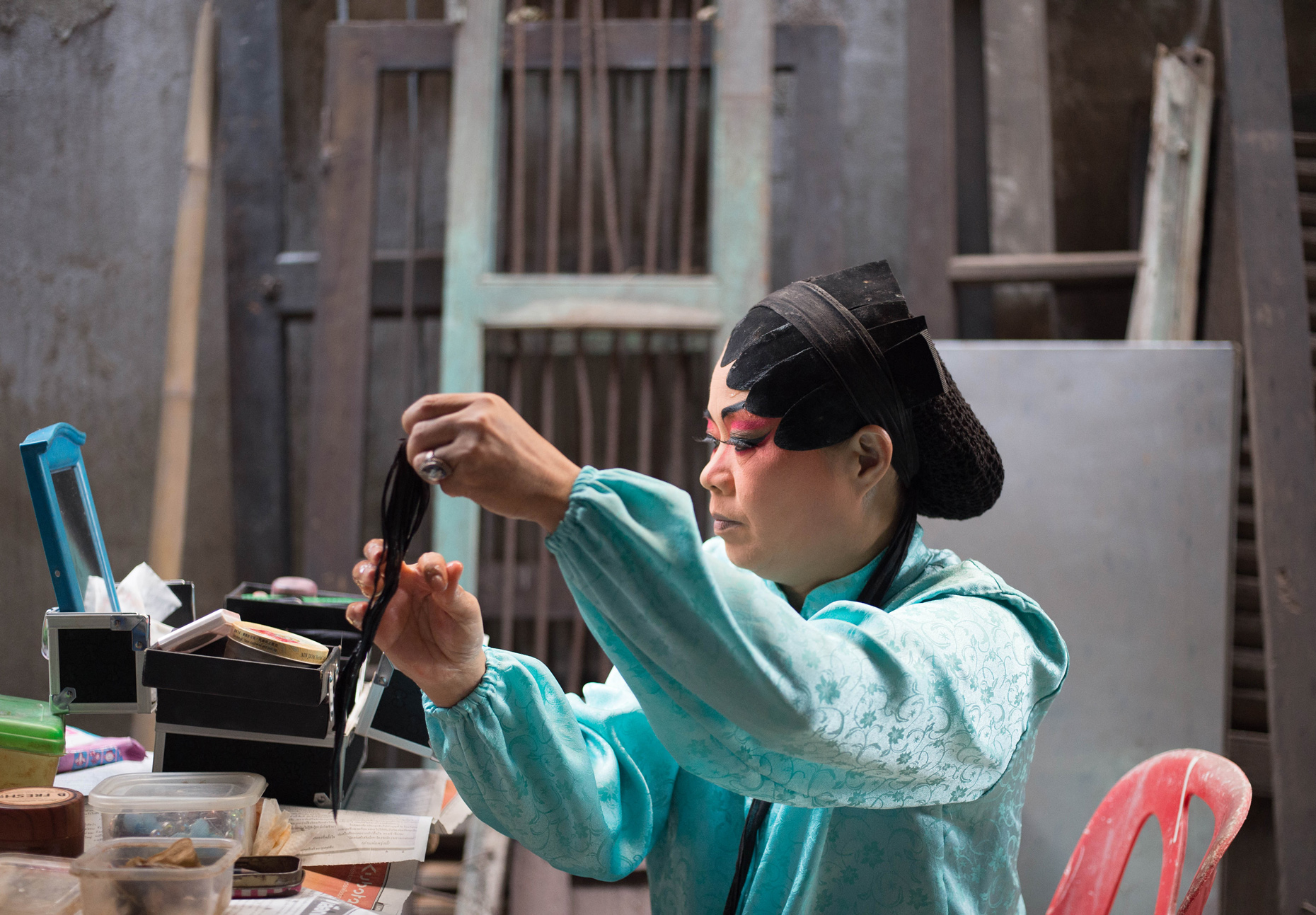
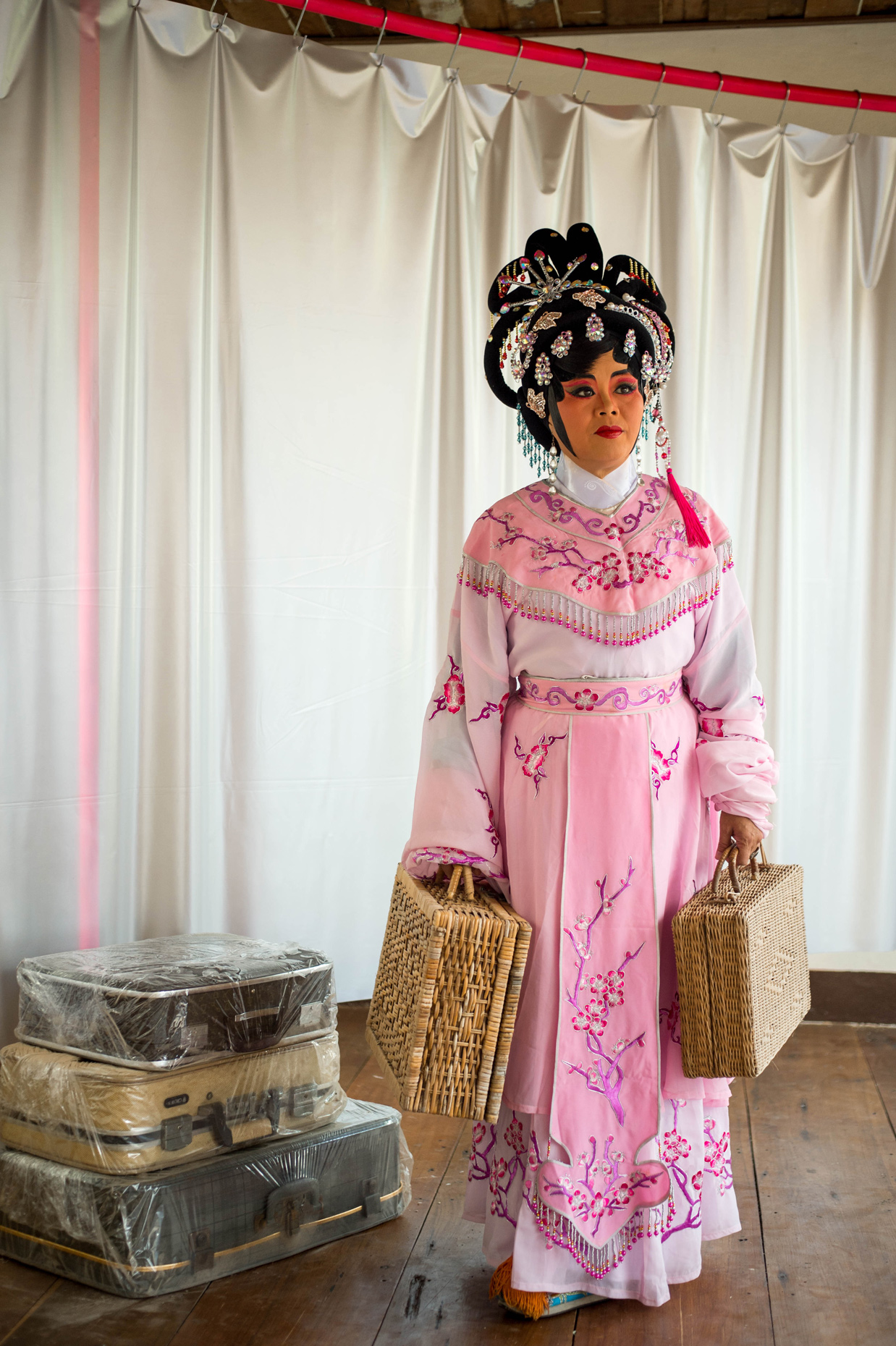
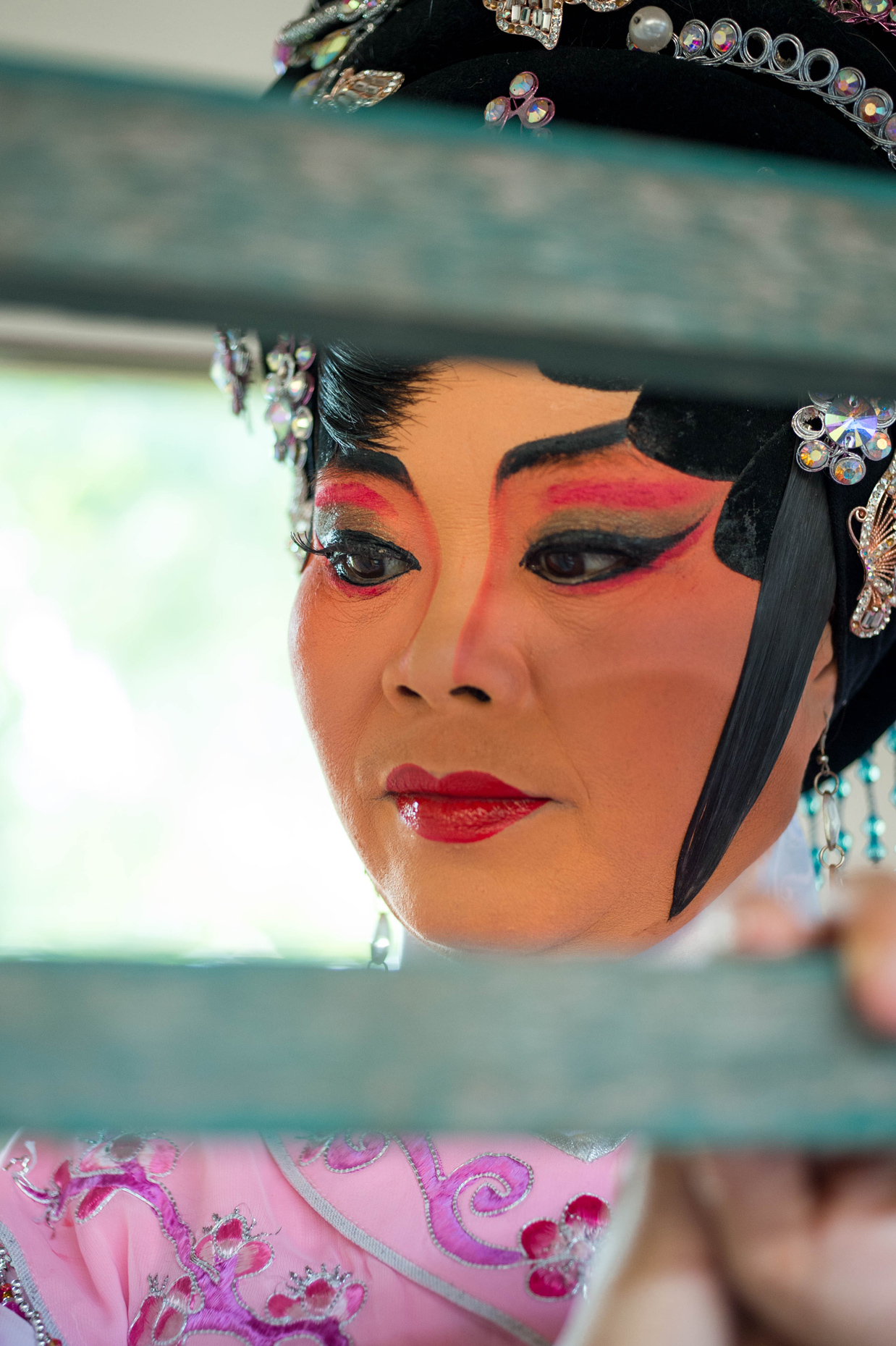
Once inside the pavilion, the spectator, through videos on multiple screens, inhabit a “Chinatownised “ world made of communal rituals. The stage set itself, through its materiality, structure and ornaments, is a spatial manifestation of stereotypical yet identitarian forces: an inhabitable red folie, a dragon, a votive pavilion - a purposely recognizable architectural cliché. The project was first conceived and exhibited in Bangkok, then it will travel around the globe, to be showcased in the Chinatowns of different continents.
The Oxford Dictionary defines “Chinatown” as “a district of any non-Chinese town, especially a city or seaport, in which the population is predominantly of Chinese origin”. However, some Chinatowns may have little to do with China, while they certainly have in common with other Chinatowns in different locations. Indeed, if one hand these communities were able to resist and preserve their cultural origins more than other ethnic enclaves, they were also subject to a natural process of diffusion, exposure and commodification - that witnessed the rise of a worldwide shared "Chinatownised" identity. Travellers find there secure places where to recollect memories and authentic experiences. Clusters of exotic stimulating clichés - goods, signs and behaviours - that trigger an intuitive sense of familiarity and international domesticity.
The Chinese have two different concepts of a copy. Fangzhipin are imitations where the difference from the original is obvious. These are small models or copies that can be purchased in a museum shop, for example. The second concept for a copy is Fuzhipin. They are exact reproductions of the original, which, for the Chinese, are of equal value to the original. It has absolutely no negative connotations. The discrepancy with regard to the understanding of what a copy has often led to misunderstandings and arguments between Chinese and Western culture. Especially for Europeans, it’s difficult to accept that identity and renewal can be not mutually exclusive. Instead, in the Chinese culture - where continual reproduction represents a technique for conservation and preservation - replicas are anything but mere copies.
Taught and curated by
Lemonot
with
INDA students
Mook Attakanwong
Mook Attakanwong